Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLNCalpain I/II/ B/L inhibitor CAS# 110044-82-1 |
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- CA-074 Me
Catalog No.:BCC3649
CAS No.:147859-80-1
- PD 150606
Catalog No.:BCC2353
CAS No.:179528-45-1
- SID 26681509
Catalog No.:BCC2362
CAS No.:958772-66-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 110044-82-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 443118 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H37N3O4 | M.Wt | 383.54 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Calpain inhibitor-1 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 16.67 mg/mL (43.46 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
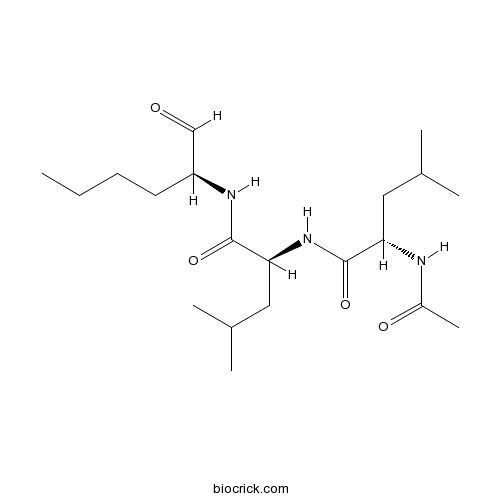
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-acetamido-4-methyl-N-[(2S)-4-methyl-1-oxo-1-[[(2S)-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]pentan-2-yl]pentanamide | ||
| SMILES | CCCCC(C=O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FMYKJLXRRQTBOR-BZSNNMDCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H37N3O4/c1-7-8-9-16(12-24)22-19(26)18(11-14(4)5)23-20(27)17(10-13(2)3)21-15(6)25/h12-14,16-18H,7-11H2,1-6H3,(H,21,25)(H,22,26)(H,23,27)/t16-,17-,18-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Calpain inhibitor (IC50 = 0.09 μM) that activates p53-dependent apoptosis in tumor cell lines. Increases activated p53, p21 and caspase levels and promotes cell cycle arrest through inhibition of cyclin D degradation in vitro. Also attenuates ischemia/reperfusion injury in cardiomyocytes, hepatocytes and renal tubular cells through downregulation of iNOS and COX-2 expression. |

Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN Dilution Calculator

Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6073 mL | 13.0364 mL | 26.0729 mL | 52.1458 mL | 65.1822 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5215 mL | 2.6073 mL | 5.2146 mL | 10.4292 mL | 13.0364 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2607 mL | 1.3036 mL | 2.6073 mL | 5.2146 mL | 6.5182 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0521 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 1.0429 mL | 1.3036 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2607 mL | 0.5215 mL | 0.6518 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Calpain Inhibitor I is an inhibitor of calpain I, calpain II, cathepsin B and cathepsin L with Ki values of 190 nM, 220 nM, 150 nM and 500 pM, respectively.
Calpain inhibitor I?combined with Ad/gTRAIL induced cell death dramatically in DLD1-TRAIL/R cells, while calpain alone had only minimal killing effects. ?The combination of calpain inhibitor I and TRAIL protein resulted in cleavage of both caspase-8 and caspase-3 to active subunits [1].
Calpain inhibitor I treated male Sprangue-Dawley rats have seen reductions of P-selectin/ICAM-1 expression, neutrophil infiltration, lipid peroxidation, nitrotyrosine, PAR formation as well as IκB-α degradation [2].
References:
[1] Zhu H1,?Zhang L,?Huang X,?Davis JJ,?Jacob DA,?Teraishi F,?Chiao P,?Fang B.Overcoming acquired resistance to TRAIL by chemotherapeutic agents and calpain inhibitor I through distinct mechanisms. Mol Ther.?2004 May;9(5):666-73.
[2] Marzocco S1,?Di Paola R,?Autore G,?Mazzon E,?Pinto A,?Caputi AP,?Thiemermann C,?Cuzzocrea S. Calpain inhibitor I reduces intestinal ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat. Shock.?2004 Jan;21(1):38-44.
?
- Tussilagonone
Catalog No.:BCC8365
CAS No.:110042-38-1
- Taurohyodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCC8363
CAS No.:110026-03-4
- 8-O-Ethylyunaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN6260
CAS No.:110011-77-3
- Sorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2218
CAS No.:110-44-1
- Fumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5989
CAS No.:110-17-8
- Maleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8426
CAS No.:110-16-7
- Succinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5890
CAS No.:110-15-6
- ITD 1
Catalog No.:BCC6409
CAS No.:1099644-42-4
- Kifunensine
Catalog No.:BCC7601
CAS No.:109944-15-2
- Sodium prasterone sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC9149
CAS No.:1099-87-2
- Granisetron
Catalog No.:BCC1601
CAS No.:109889-09-0
- CGS 9343B
Catalog No.:BCC7303
CAS No.:109826-27-9
- Strophantin K (mixture)
Catalog No.:BCC8256
CAS No.:11005-63-3
- 7-Hydroxy-3-(4-hydroxybenzylidene)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN1624
CAS No.:110064-50-1
- 12-Epinapelline
Catalog No.:BCN2800
CAS No.:110064-71-6
- Plerixafor (AMD3100)
Catalog No.:BCC1158
CAS No.:110078-46-1
- des-His1-[Glu9]-Glucagon (1-29) amide
Catalog No.:BCC5885
CAS No.:110084-95-2
- Ascomycin
Catalog No.:BCN8286
CAS No.:11011-38-4
- Indoximod (NLG-8189)
Catalog No.:BCC5584
CAS No.:110117-83-4
- Methyl hesperidin
Catalog No.:BCN6341
CAS No.:11013-97-1
- 4-Galloylquinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3733
CAS No.:110170-37-1
- Ouabain Octahydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5211
CAS No.:11018-89-6
- JZL184
Catalog No.:BCC4790
CAS No.:1101854-58-3
- 1,5,8-Trihydroxy-3-methoxy-2-prenylxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN1623
CAS No.:110187-11-6
[Analgesic effect of calpain inhibitor ALLN on the zymosan-induced paw inflammatory pain and its effect on the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in the spinal dorsal horn].[Pubmed:22737715]
Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 2012 Feb;34(1):25-31.
OBJECTIVE: To examine the analgesic effect of calpain inhibitor ALLN on the zymosan-induced paw inflammatory pain and its effect on the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in the spinal dorsal horn. METHODS: Forty-eight Sprague-Dawley rats were equally divided into three groups: control group, sham-operated group, and zymosan group. According to Meller's method, zymosan (1.25 mg) was injected intraplantarly to induce paw inflammation in zymosan group; an equal volume of PBS was administered in the sham-operated group. Mechanical withdrawal threshold (MWT) and maximum thickness of paw were tested or measured before and 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 hours after injection. All rats were killed at different occasions following surgery to examine calpain activity in the spinal dorsal horn with Western blot analysis. Another sixty-four Sprague-Dawley rats were divided into three groups: sham-operated group, zymosan-induced paw inflammation with intraperitoneal dimethyl sulphoxide (DMSO) treatment group, and zymosan-induced paw inflammation with intraperitoneal calpain inhibitor ALLN treatment group. MWT and maximum thickness of paw were tested or measured before and 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 hours after injection. All rats were killed at different occasions following surgery to examine the COX-2 expression in the spinal dorsal horn with Western blot analysis. RESULTS: MWT significantly decreased in the rats with zymosan-induced paw inflammation, while the maximum thickness of paw significantly increased, compared with control and sham-operated rats (P < 0.05). Calpain in the ipsilateral spinal dorsal horn was dramatically activated after zymosan injection (P < 0.01). Intraperitoneal ALLN injection significantly increased zymosan-induced MWT and decreased paw edema at the same time points after zymosan injection compared with DMSO treatment group (P < 0.05). Meanwhile, calpain inhibitor ALLN treatment significantly decreased the COX-2 expression in the spinal dorsal horn compared with DMSO treatment (P < 0.01). CONCLUSION: Administration of calpain inhibitor ALLN is effective to attenuate zymosan-induced paw inflammatory pain. Calpain activation may be one aspect of the signaling cascade that increases the COX-2 expression in the spinal cord and contributes to mechanical hyperalgesia after peripheral inflammatory injury.
Calpain inhibitor-1 reduces renal ischemia/reperfusion injury in the rat.[Pubmed:11380809]
Kidney Int. 2001 Jun;59(6):2073-83.
BACKGROUND: Activation of the cysteine protease calpain has been implicated in renal ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of calpain inhibitor-1 (Cal I-1) in an in vivo model of renal I/R injury. METHODS: Male Wistar rats were administered Cal I-1 (10 mg/kg, IP) 30 minutes before undergoing bilateral renal ischemia (45 minutes) followed by reperfusion (6 hours). Plasma concentrations of urea, creatinine, Na(+), gamma-glutamyl transferase (gamma GT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and urinary Na(+), glutathione S-transferase (GST), and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) were measured for the assessment of renal dysfunction and I/R injury. Creatinine clearance (C(Cr)) and fractional excretion of Na(+) (FE(Na)) were used as indicators of glomerular and tubular function, respectively. Kidney myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels were measured for assessment of neutrophil infiltration and lipid peroxidation, respectively. Renal sections were used for histologic grading of renal injury and for immunohistochemical localization of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2). RESULTS: Cal I-1 significantly reduced I/R-mediated increases in urea, creatinine, gamma GT, AST, NAG, and FE(Na) and significantly improved C(Cr). Cal I-1 also significantly reduced kidney MPO activity and MDA levels. Cal I-1 also reduced histologic evidence of I/R-mediated renal damage and caused a substantial reduction in the expression of iNOS and COX-2, both of which involve activation of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B). CONCLUSIONS: : These results suggest that Cal I-1 reduces the renal dysfunction and injury associated with I/R of the kidney. We suggest that the mechanism could involve the inhibition of I/R-mediated activation of NF-kappa B.
Calpain inhibitor 1 activates p53-dependent apoptosis in tumor cell lines.[Pubmed:10845425]
Cell Growth Differ. 2000 May;11(5):247-53.
Reports suggest a role of calpains in degradation of wild-type p53, which may regulate p53 induction of apoptosis. A calpain inhibitor, n-acetyl-leu-leu-norleucinal (calpain inhibitor 1), was assessed for ability to enhance p53-dependent apoptosis in human tumor cell lines with endogenous wild-type p53 and in altered p53 cell lines with the replacement of wild-type p53 by a recombinant adenovirus (rAd-p53). Calpain inhibitor 1 treatment resulted in increased levels of activated p53, increased p21 protein, and activation of caspases. Cell lines with wild-type, but not mutated or null, p53 status arrested in G0/G1 and were sensitive to calpain inhibitor-induced apoptosis. Regardless of endogenous p53 status, calpain inhibitor treatment combined with rAd-p53, but not empty vector virus, enhanced apoptosis in tumor cell lines. These results demonstrate p53-dependent apoptosis induced by a calpain inhibitor and further suggest a role for calpains in the regulation of p53 activity and induction of apoptotic pathways.


