CA 074Cathepsin B inhibitor CAS# 134448-10-5 |
- Leupeptin, Microbial
Catalog No.:BCC1217
CAS No.:103476-89-7
- Calpain Inhibitor II, ALLM
Catalog No.:BCC1234
CAS No.:136632-32-1
- CA-074 Me
Catalog No.:BCC3649
CAS No.:147859-80-1
- Cathepsin Inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4896
CAS No.:225120-65-0
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- E-64-c
Catalog No.:BCC3588
CAS No.:76684-89-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 134448-10-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 122165 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H29N3O6 | M.Wt | 383.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 125 mg/mL (326.00 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
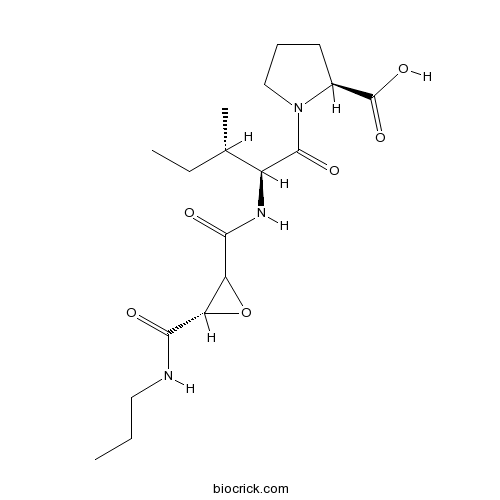
| Chemical Name | (2S)-1-[(2S,3S)-3-methyl-2-[[(3S)-3-(propylcarbamoyl)oxirane-2-carbonyl]amino]pentanoyl]pyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCCNC(=O)C1C(O1)C(=O)NC(C(C)CC)C(=O)N2CCCC2C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZEZGJKSEBRELAS-KSFNBINOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H29N3O6/c1-4-8-19-15(22)13-14(27-13)16(23)20-12(10(3)5-2)17(24)21-9-6-7-11(21)18(25)26/h10-14H,4-9H2,1-3H3,(H,19,22)(H,20,23)(H,25,26)/t10-,11-,12-,13-,14?/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of cathepsin B (Ki = 2-5 nM). Displays selectivity over cathepsins H and L (Ki = 40-200 μM). Shown to reduce bone metastasis in a 4T1.2 breast cancer model. |

CA 074 Dilution Calculator

CA 074 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.608 mL | 13.0398 mL | 26.0797 mL | 52.1594 mL | 65.1992 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5216 mL | 2.608 mL | 5.2159 mL | 10.4319 mL | 13.0398 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2608 mL | 1.304 mL | 2.608 mL | 5.2159 mL | 6.5199 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0522 mL | 0.2608 mL | 0.5216 mL | 1.0432 mL | 1.304 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0261 mL | 0.1304 mL | 0.2608 mL | 0.5216 mL | 0.652 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||
Abstract
CA-074 is better-suited for cathepsin B specific inactivation in living cells, since it selectively inhibited cathepsin B leaving cathepsin L unaffected.
Abstract
Intravenous administration of CA-074 exhibited excellent inhibition against cathepsin B and saved CA1 neurons from delayed neuronal death in monkeys undergoing a complete 20 min whole brain ischaemia.
Abstract
CA-074 was used to inhibit cathepsin B activity in order to measure cathepsin L activity in samples.

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
CA-074, a specific cathepsin B inhibitor, also abolished the neurotoxic effects caused by Abeta42-activated BV2 cell [1]. Co-treatment of cultures with the cathepsin B inhibitors CA-074 or Z-FA-FMK suppressed the cytostatic effects of TPA and activation of pro-uPA [2]. Administration of CA-074 suppresses the response to exogenous antigens, such as hepatitis B virus antigen, ovalbumin and Leishmania major antigen, and induces switching of the helper T cell responses from Th-2 to Th-1 of CD4+ T cell, thereby down regulating the production of IgE and IgG1 [3]. Pharmacological inhibition of cat B in catB(+/+) mice with L-3-trans-(propylcarbamoyl)oxirane-2-carbonyl-Lisoleucyl-L-proline (CA-074 Me) also reduced TNF-alpha-induced liver damage. [4] Administration of cathepsin B inhibitors, E-64, CA-074 and vitamin B6, caused the strong suppression of the Th-2 type immune responses .
Inhibitor of cathepsin B (Ki = 2-5 nM). Displays selectivity over cathepsins H and L (Ki = 40-200 μM). Shown to reduce bone metastasis in a 4T1.2 breast cancer model.
References:
1. Identification of cathepsin B as a mediator of neuronal death induced by Abeta-activated microglial cells using a functional genomics approach. Gan, L., Ye, S., Chu, A., Anton, K., Yi, S., Vincent, V.A., von Schack, D., Chin, D., Murray, J., Lohr, S., Patthy, L., Gonzalez-Zulueta, M., Nikolich, K., Urfer, R. J. Biol. Chem. (2004)
2. Phorbol ester activation of a proteolytic cascade capable of activating latent transforming growth factor-betaL a process initiated by the exocytosis of cathepsin B. Guo, M., Mathieu, P.A., Linebaugh, B., Sloane, B.F., Reiners, J.J. J. Biol. Chem. (2002)
3. Insights into the roles of cathepsins in antigen processing and presentation revealed by specific inhibitors. Katunuma, N., Matsunaga, Y., Himeno, K., Hayashi, Y. Biol. Chem. (2003)
4. Cathepsin B knockout mice are resistant to tumor necrosis factor-alpha-mediated hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury: implications for therapeutic applications. Guicciardi, M.E., Miyoshi, H., Bronk, S.F., Gores, G.J. Am. J. Pathol. (2001)
- Dehydroandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN1260
CAS No.:134418-28-3
- Seocalcitol
Catalog No.:BCC1944
CAS No.:134404-52-7
- Epoxomicin
Catalog No.:BCC1235
CAS No.:134381-21-8
- Ro 0437626
Catalog No.:BCC7276
CAS No.:134362-79-1
- Epoxymicheliolide
Catalog No.:BCN8275
CAS No.:1343403-10-0
- 2-ThioUTP tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7625
CAS No.:1343364-70-4
- alpha,beta-Methyleneadenosine 5'-triphosphate trisodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC7603
CAS No.:1343364-54-4
- Tolcapone
Catalog No.:BCC2334
CAS No.:134308-13-7
- BIMU 8
Catalog No.:BCC7928
CAS No.:134296-40-5
- 3,5-Dibromo-4-[3-(dimethylamino)propoxy]cinnamic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1582
CAS No.:134276-56-5
- Daphnelantoxin B
Catalog No.:BCN3228
CAS No.:134273-12-4
- RKI-1447
Catalog No.:BCC1903
CAS No.:1342278-01-6
- Discodermide
Catalog No.:BCN1834
CAS No.:134458-00-7
- BW-B 70C
Catalog No.:BCC7013
CAS No.:134470-38-5
- Richenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6185
CAS No.:134476-74-7
- Trimethylvinylammonium(1+)
Catalog No.:BCN1820
CAS No.:13448-18-5
- 1-Cinnamoyl-3-hydroxypyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCN6497
CAS No.:1344876-77-2
- Gardenoin J
Catalog No.:BCN7666
CAS No.:1345109-46-7
- U 90042
Catalog No.:BCC7465
CAS No.:134516-99-7
- Atorvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC2319
CAS No.:134523-03-8
- AM095
Catalog No.:BCC1351
CAS No.:1345614-59-6
- ETP-46464
Catalog No.:BCC3913
CAS No.:1345675-02-6
- Arginase inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4034
CAS No.:1345808-25-4
- Altiratinib
Catalog No.:BCC6385
CAS No.:1345847-93-9
CA-074, but not its methyl ester CA-074Me, is a selective inhibitor of cathepsin B within living cells.[Pubmed:12437121]
Biol Chem. 2002 Jul-Aug;383(7-8):1305-8.
Studies using inhibitors that reportedly discriminate between cathepsin B and related lysosomal cysteine proteinases have implicated the enzyme in a wide range of physiological and pathological processes. The most popular substance to selectively inhibit cathepsin B in vivo is CA-074Me, the methyl ester of the E-64 derivative CA-074. However, we now have found that CA-074Me inactivates both cathepsin B and cathepsin L within murine fibroblasts. In contrast, exposure of these cells to the parental compound CA-074 leads to the selective inhibition of endogenous cathepsin B, while intracellular cathepsin L remains unaffected. These results indicate that CA-074 rather than CA-074Me should be used to specifically inactivate cathepsin B within living cells.
Inhibition of ischaemic hippocampal neuronal death in primates with cathepsin B inhibitor CA-074: a novel strategy for neuroprotection based on 'calpain-cathepsin hypothesis'.[Pubmed:9751144]
Eur J Neurosci. 1998 May;10(5):1723-33.
Although Cornu Ammonis (CA) 1 neurons of the hippocampus are known to be vulnerable to transient ischaemia, the mechanism of ischaemic neuronal death is still unknown, and there are very few strategies to prevent neuronal death at present. In a previous report we demonstrated micro-calpain activation at the disrupted lysosomal membrane of postischaemic CA1 neurons in the monkey undergoing a complete 20 min whole brain ischaemia. Using the same experimental paradigm, we observed that the enzyme activity of the lysosomal protease cathepsin B increased throughout the hippocampus on days 3-5 after the transient ischaemia. Furthermore, by immunocytochemistry cathepsin B showed presence of extralysosomal immunoreactivity with specific localization to the cytoplasm of CA1 neurons and the neuropil of the vulnerable CA1 sector. When a specific inhibitor of cathepsin B, the epoxysuccinyl peptide CA-074 (C18H29N3O6) was intravenously administered immediately after the ischaemic insult, approximately 67% of CA1 neurons were saved from delayed neuronal death on day 5 in eight monkeys undergoing 20 min brain ischaemia: the extent of inhibition was excellent in three of eight and good in five of eight monkeys. The surviving neurons rescued by blockade of lysosomal activity, showed mild central chromatolysis and were associated with the decreased immunoreactivity for cathepsin B. These observations indicate that calpain-induced cathepsin B release is crucial for the development of the ischaemic neuronal death, and that a specific inhibitor of cathepsin B is of potential therapeutic utility in ischaemic injuries to the human CNS.
Cathepsin B inhibition limits bone metastasis in breast cancer.[Pubmed:22266111]
Cancer Res. 2012 Mar 1;72(5):1199-209.
Metastasis to bone is a major cause of morbidity in breast cancer patients, emphasizing the importance of identifying molecular drivers of bone metastasis for new therapeutic targets. The endogenous cysteine cathepsin inhibitor stefin A is a suppressor of breast cancer metastasis to bone that is coexpressed with cathepsin B in bone metastases. In this study, we used the immunocompetent 4T1.2 model of breast cancer which exhibits spontaneous bone metastasis to evaluate the function and therapeutic targeting potential of cathepsin B in this setting of advanced disease. Cathepsin B abundancy in the model mimicked human disease, both at the level of primary tumors and matched spinal metastases. RNA interference-mediated knockdown of cathepsin B in tumor cells reduced collagen I degradation in vitro and bone metastasis in vivo. Similarly, intraperitoneal administration of the highly selective cathepsin B inhibitor CA-074 reduced metastasis in tumor-bearing animals, a reduction that was not reproduced by the broad spectrum cysteine cathepsin inhibitor JPM-OEt. Notably, metastasis suppression by CA-074 was maintained in a late treatment setting, pointing to a role in metastatic outgrowth. Together, our findings established a prometastatic role for cathepsin B in distant metastasis and illustrated the therapeutic benefits of its selective inhibition in vivo.
Voltage-gated Sodium Channel Activity Promotes Cysteine Cathepsin-dependent Invasiveness and Colony Growth of Human Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:19176528]
J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8680-91.
Voltage-gated sodium channels (Na(V)) are functionally expressed in highly metastatic cancer cells derived from nonexcitable epithelial tissues (breast, prostate, lung, and cervix). MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells express functional sodium channel complexes, consisting of Na(V)1.5 and associated auxiliary beta-subunits, that are responsible for a sustained inward sodium current at the membrane potential. Although these channels do not regulate cellular multiplication or migration, their inhibition by the specific blocker tetrodotoxin impairs both the extracellular gelatinolytic activity (monitored with DQ-gelatin) and cell invasiveness leading to the attenuation of colony growth and cell spreading in three-dimensional Matrigel-composed matrices. MDA-MB-231 cells express functional cysteine cathepsins, which we found play a predominant role ( approximately 65%) in cancer invasiveness. Matrigel invasion is significantly decreased in the presence of specific inhibitors of cathepsins B and S (CA-074 and Z-FL-COCHO, respectively), and co-application of tetrodotoxin does not further reduce cell invasion. This suggests that cathepsins B and S are involved in invasiveness and that their proteolytic activity partly depends on Na(V) function. Inhibiting Na(V) has no consequence for cathepsins at the transcription, translation, and secretion levels. However, Na(V) activity leads to an intracellular alkalinization and a perimembrane acidification favorable for the extracellular activity of these acidic proteases. We propose that Na(v) enhance the invasiveness of cancer cells by favoring the pH-dependent activity of cysteine cathepsins. This general mechanism could lead to the identification of new targets allowing the therapeutic prevention of metastases.
Novel epoxysuccinyl peptides. A selective inhibitor of cathepsin B, in vivo.[Pubmed:2013329]
FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):311-5.
New derivatives of E-64 (compound CA-030 and CA-074) were tested in vitro and in vivo for selective inhibition of cathepsin B. They exhibited 10,000-30,000 times greater inhibitory effects on purified rat cathepsin B than on cathepsin H and L: their initial Ki values for cathepsin B were about 2-5 nM, like that of E-64-c, whereas their initial Ki values for cathepsins H and L were about 40 200 microM. In in vivo conditions, such as intraperitoneal injection of compound CA-030 or CA-074 into rats, compound CA-074 is an especially potent selective inhibitor of cathepsin B, whereas compound CA-030 does not show selectivity for cathepsin B, although both compounds CA-030 and CA-074 show complete selectivity for cathepsin B in vitro.


