Cathepsin Inhibitor 1Cathepsin inhibitor CAS# 225120-65-0 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- L 006235
Catalog No.:BCC2361
CAS No.:294623-49-7
- E-64
Catalog No.:BCC1222
CAS No.:66701-25-5
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
- SID 26681509
Catalog No.:BCC2362
CAS No.:958772-66-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 225120-65-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 44224135 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24ClN5O2 | M.Wt | 401.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO > 10 mM | ||
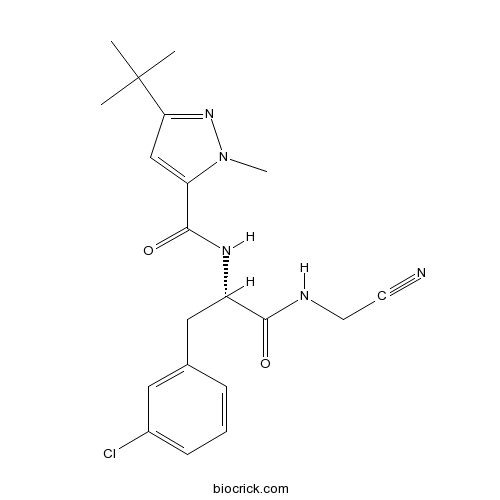
| Chemical Name | 5-tert-butyl-N-[(2S)-3-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-(cyanomethylamino)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]-2-methylpyrazole-3-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=NN(C(=C1)C(=O)NC(CC2=CC(=CC=C2)Cl)C(=O)NCC#N)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | MZRVIHRERYCHBL-HNNXBMFYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24ClN5O2/c1-20(2,3)17-12-16(26(4)25-17)19(28)24-15(18(27)23-9-8-22)11-13-6-5-7-14(21)10-13/h5-7,10,12,15H,9,11H2,1-4H3,(H,23,27)(H,24,28)/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 Dilution Calculator

Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4882 mL | 12.4412 mL | 24.8824 mL | 49.7649 mL | 62.2061 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4976 mL | 2.4882 mL | 4.9765 mL | 9.953 mL | 12.4412 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2488 mL | 1.2441 mL | 2.4882 mL | 4.9765 mL | 6.2206 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0498 mL | 0.2488 mL | 0.4976 mL | 0.9953 mL | 1.2441 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0249 mL | 0.1244 mL | 0.2488 mL | 0.4976 mL | 0.6221 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
pIC50: 7.9, 6.7, 6.0, 5.5 and 5.2 for Cathepsin (L, L2, S, K, B), respectively
Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 is an inhibitor of Cathepsin. Osteoarthritis is currently recognized as a chronic degenerative disease, which is caused by the loss of articular cartilage and damage to underlying bone, resulting in joint instability and pain. The lysosomal cysteine protease2 Cathepsin L (CatL) is found to be a potential target for intervention in treatment of osteoarthritis. After secreted into the extracellular matrix, CatL can degrade proteoglycans such as aggrecan4 and type II collagen, which are the major components of articular cartilage.
In vitro: The CatL pIC50 value of Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 was found to exceed that of its analog by 1.6 units. Moreover, CatS (ΔpIC50 = -0.1) and CatL2 (ΔpIC50 = 0.5) were much less sensitive to the structural change of Cathepsin Inhibitor 1, leading to an improved selectivity profile relative to its analog. Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 was as least as selective with respect to CatB and CatS as previously described CatL inhibitors. The crystal structure of its another analog bound to CatL provided the rationale for the SAR observed for Cathepsin Inhibitor 1. The 1-methyl group of the pyrazole made some contact with Leu69 and appeared to force the pyrazole ring out of co-planarity with the amide, likely functioning as a conformational lock [1].
In vivo: So far, there is no in vivo animal data available for Cathepsin Inhibitor 1 is an inhibitor of Cathepsin.
Clinical trial: N/A
Reference:
[1] Asaad N, Bethel PA, Coulson MD, Dawson JE, Ford SJ, Gerhardt S, Grist M, Hamlin GA, James MJ, Jones EV, Karoutchi GI, Kenny PW, Morley AD, Oldham K,Rankine N, Ryan D, Wells SL, Wood L, Augustin M, Krapp S, Simader H, Steinbacher S. Dipeptidyl nitrile inhibitors of Cathepsin L. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Aug 1;19(15):4280-3.
- Falcarindiol
Catalog No.:BCN5065
CAS No.:225110-25-8
- IDRA 21
Catalog No.:BCC6974
CAS No.:22503-72-6
- N-(1-hydroxy-2-(hydroxymethyl)-4-(4-octylphenyl)butan-2-yl)acetamide
Catalog No.:BCN1483
CAS No.:2249289-10-9
- Erigeside I
Catalog No.:BCN7172
CAS No.:224824-74-2
- Vardenafil HCl Trihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC2277
CAS No.:224785-90-4
- 18-Norabieta-8,11,13-trien-4-ol
Catalog No.:BCN5064
CAS No.:22478-65-5
- Gymnemagenin
Catalog No.:BCN7841
CAS No.:22467-07-8
- MLCK inhibitor peptide 18
Catalog No.:BCC5828
CAS No.:224579-74-2
- Benfotiamine
Catalog No.:BCC1415
CAS No.:22457-89-2
- Retapamulin
Catalog No.:BCC4837
CAS No.:224452-66-8
- Ginsenoside Rg1
Catalog No.:BCN1066
CAS No.:22427-39-0
- Bayogenin methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN3722
CAS No.:22425-81-6
- 8-Hydroxy-9,10-diisobutyryloxythymol
Catalog No.:BCN7786
CAS No.:22518-08-7
- CTU Guanamine
Catalog No.:BCC8921
CAS No.:22535-90-6
- Ocotillone
Catalog No.:BCN5066
CAS No.:22549-21-9
- Robustine
Catalog No.:BCN6653
CAS No.:2255-50-7
- Isocryptotanshinone
Catalog No.:BCN2499
CAS No.:22550-15-8
- Bisabolol Oxide A
Catalog No.:BCC8133
CAS No.:22567-36-8
- Zeorin
Catalog No.:BCN5067
CAS No.:22570-53-2
- Symphytine
Catalog No.:BCN1975
CAS No.:22571-95-5
- PAR 4 (1-6)
Catalog No.:BCC3956
CAS No.:225779-44-2
- Epifriedelanol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5068
CAS No.:2259-07-6
- Cyclothiazide
Catalog No.:BCC6759
CAS No.:2259-96-3
- (+)-Catechin hydrate
Catalog No.:BCN2309
CAS No.:225937-10-0
Design of Potent and Selective Cathepsin G Inhibitors Based on the Sunflower Trypsin Inhibitor-1 Scaffold.[Pubmed:28045523]
J Med Chem. 2017 Jan 26;60(2):658-667.
Neutrophils are directly responsible for destroying invading pathogens via reactive oxygen species, antimicrobial peptides, and neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs). Imbalance between NSP activity and endogenous protease inhibitors is associated with chronic inflammatory disorders, and engineered inhibitors of NSPs are a potential therapeutic pathway. In this study we characterized the extended substrate specificity (P4-P1) of the NSP cathepsin G using a peptide substrate library. Substituting preferred cathepsin G substrate sequences into sunflower trypsin inhibitor-1 (SFTI-1) produced a potent cathepsin G inhibitor (Ki = 0.89 nM). Cathepsin G's P2' preference was determined by screening against a P2' diverse SFTI-based library, and the most preferred residue at P2' was combined in SFTI-1 with a preferred substrate sequence (P4-P2) and a nonproteinogenic P1 residue (4-guanidyl-l-phenylalanine) to produce a potent (Ki = 1.6 nM) and the most selective (>/=360-fold) engineered cathepsin G inhibitor reported to date. This compound is a promising lead for further development of cathepsin G inhibitors targeting chronic inflammatory disorders.
Morning vs evening dosing of the cathepsin K inhibitor ONO-5334: effects on bone resorption in postmenopausal women in a randomized, phase 1 trial.[Pubmed:26446770]
Osteoporos Int. 2016 Jan;27(1):309-18.
UNLABELLED: The cathepsin K inhibitor, ONO-5334, improves bone mineral density in postmenopausal women with osteoporosis. The effects of morning versus evening administration of ONO-5334 were investigated by measuring bone turnover marker levels in healthy postmenopausal women. Morning administration of ONO-5334 showed a more consistent suppressive effect on bone resorption than evening administration. INTRODUCTION: Bone turnover is thought to be subject to circadian variation, and the efficacy of osteoporosis treatments may be optimized by regulating the time of dosing. This study assessed whether evening administration of the cathepsin K inhibitor, ONO-5334, had a differential effect on the bone turnover marker, C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX-I), compared with morning administration. METHODS: This was a single-center, single blind crossover study. Fourteen healthy postmenopausal women were assigned to receive ONO-5334 150 mg once daily for 5 days in each period; they were randomized to receive either evening doses in the first period and morning doses in the second or vice versa. Serum and urinary levels of CTX-I were measured throughout the study. RESULTS: Both regimens showed similar patterns of reduction in serum and urinary CTX-I; however, CTX-I suppression was more consistently >60% over 24 h following morning administration. Morning administration led to 6% greater suppression of 24-h serum CTX-I area under the effect curve (AUE; 69 vs 63%; P < .05) and 7% greater suppression of urinary CTX-I/creatinine AUE (93 vs 86%; P < .01) than evening administration. Higher plasma ONO-5334 concentrations were observed between 12 and 24 h postdose following morning administration, with mean trough concentrations for the morning and evening regimens at 9.4 and 4.0 ng/mL, respectively. There were no safety findings of concern. CONCLUSION: Morning dosing of ONO-5334 is more efficacious at reducing markers of bone turnover in healthy postmenopausal women than evening dosing. TRIAL REGISTRATION: ClinicalTrials.gov: NCT01384188 , registered on June 27, 2011 EudraCT: 2008-006284-37.
Activation of the P2X(7) receptor induces migration of glial cells by inducing cathepsin B degradation of tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase 1.[Pubmed:23017058]
J Neurochem. 2012 Dec;123(5):761-70.
The P2X(7) receptor is an ion-gated channel, which is activated by high extracellular concentrations of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Activation of P2X(7) receptors has been shown to induce neuroinflammatory changes associated with several neurological conditions. The matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are a family of endopeptidases that have several functions including degradation of the extracellular matrix, cell migration and modulation of bioactive molecules. The actions of MMPs are prevented by a family of protease inhibitors called tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). In this study, we show that ATP-treated glial cultures from neonatal C57BL/6 mice release and increase MMP-9 activity, which is coupled with a decrease in release of TIMP-1 and an increase in activated cathepsin B within the extracellular space. This process occurs independently of NLRP3-inflammasome formation. Treatment with a P2X(7) receptor antagonist prevents ATP-induced MMP-9 activity, inhibition of active cathepsin B release and allows for TIMP-1 to be released from the cell. We have shown that cathepsin B degrades TIMP-1, and inhibition of cathepsin B allows for release of TIMP-1 and inhibits MMP-9 activity. We also present data that indicate that ATP or cell damage induces glial cell migration, which is inhibited by P2X(7) antagonism, depletion of MMP-9 or inhibition of cathepsin B.
(1R,2R)-N-(1-cyanocyclopropyl)-2-(6-methoxy-1,3,4,5-tetrahydropyrido[4,3-b]indole -2-carbonyl)cyclohexanecarboxamide (AZD4996): a potent and highly selective cathepsin K inhibitor for the treatment of osteoarthritis.[Pubmed:22742641]
J Med Chem. 2012 Jul 26;55(14):6363-74.
Directed screening of nitrile compounds revealed 3 as a highly potent cathepsin K inhibitor but with cathepsin S activity and very poor stability to microsomes. Synthesis of compounds with reduced molecular complexity, such as 7, revealed key SAR and demonstrated that baseline physical properties and in vitro stability were in fact excellent for this series. The tricycle carboline P3 unit was discovered by hypothesis-based design using existing structural information. Optimization using small substituents, knowledge from matched molecular pairs, and control of lipophilicity yielded compounds very close to the desired profile, of which 34 (AZD4996) was selected on the basis of pharmacokinetic profile.


