Arginase inhibitor 1CAS# 1345808-25-4 |
- U0126-EtOH
Catalog No.:BCC1066
CAS No.:1173097-76-1
- PD98059
Catalog No.:BCC1098
CAS No.:167869-21-8
- PD184352 (CI-1040)
Catalog No.:BCC1112
CAS No.:212631-79-3
- SL-327
Catalog No.:BCC1123
CAS No.:305350-87-2
- MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162)
Catalog No.:BCC1148
CAS No.:606143-89-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1345808-25-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 66833213 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C13H27BN2O4 | M.Wt | 286.18 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 48 mg/mL (167.73 mM) H2O : ≥ 30 mg/mL (104.83 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
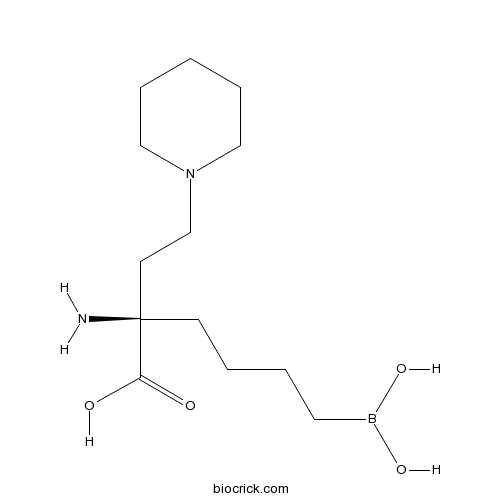
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-amino-6-borono-2-(2-piperidin-1-ylethyl)hexanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | B(CCCCC(CCN1CCCCC1)(C(=O)O)N)(O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CHPILBYRQPOXMV-CYBMUJFWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C13H27BN2O4/c15-13(12(17)18,6-2-3-8-14(19)20)7-11-16-9-4-1-5-10-16/h19-20H,1-11,15H2,(H,17,18)/t13-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Arginase inhibitor 1 is a potent inhibitor of human arginases I and II with IC50s of 223 and 509 nM, respectively.In Vitro:Arginase inhibitor 1inhibits human arginases I and II with IC50s of 223±22.3 and 509±85.1 nM, respectively, and is active in a recombinant cellular assay overexpressing human arginase I (CHO cells). Arginase inhibitor 1 is a novel second generation arginase inhibitor with significant activity in a rat model of myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury (MI/RI). Arginase inhibitor 1 is potent against hARG I in both in vitro enzyme and cellular assays. The IC50 for Arginase inhibitor 1 is 8 μM in CHO Cells Over-Expressing hArgI[1].In Vivo:A pharmacokinetic evaluation of Arginase inhibitor 1 is conducted after intravenous (i.v.) and oral (p.o.) dosing in male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=3 per dose route). Arginase inhibitor 1 is formulated in 0.9% saline and administered intravenously at 10 mg/kg by bolus through a preimplanted cannula at a dosing volume of 1 mL/kg, and orally at 10 mg/kg via gavage at a dosing volume of 2 mL/kg. Following i.v. dosing with 10 mg/kg in fasted animals, Arginase inhibitor 1has a terminal elimination half-life (t1/2) of 3.3 h with a volume of distribution and total body clearance of 1.86 L/kg and 7.89 mL/min/kg, respectively. The oral bioavailability of Arginase inhibitor 1 (10 mg/kg, p.o.) is 28% with a Cmax of 0.45 mg/L[1]. References: | |||||

Arginase inhibitor 1 Dilution Calculator

Arginase inhibitor 1 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4943 mL | 17.4715 mL | 34.943 mL | 69.8861 mL | 87.3576 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6989 mL | 3.4943 mL | 6.9886 mL | 13.9772 mL | 17.4715 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3494 mL | 1.7472 mL | 3.4943 mL | 6.9886 mL | 8.7358 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0699 mL | 0.3494 mL | 0.6989 mL | 1.3977 mL | 1.7472 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1747 mL | 0.3494 mL | 0.6989 mL | 0.8736 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Arginase inhibitor 1 is a novel and potent small molecule inhibitor of human arginases I and II with IC50s of 223 and 509 nM, respectively.
- ETP-46464
Catalog No.:BCC3913
CAS No.:1345675-02-6
- AM095
Catalog No.:BCC1351
CAS No.:1345614-59-6
- Atorvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC2319
CAS No.:134523-03-8
- U 90042
Catalog No.:BCC7465
CAS No.:134516-99-7
- Gardenoin J
Catalog No.:BCN7666
CAS No.:1345109-46-7
- 1-Cinnamoyl-3-hydroxypyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCN6497
CAS No.:1344876-77-2
- Trimethylvinylammonium(1+)
Catalog No.:BCN1820
CAS No.:13448-18-5
- Richenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6185
CAS No.:134476-74-7
- BW-B 70C
Catalog No.:BCC7013
CAS No.:134470-38-5
- Discodermide
Catalog No.:BCN1834
CAS No.:134458-00-7
- CA 074
Catalog No.:BCC1141
CAS No.:134448-10-5
- Dehydroandrographolide
Catalog No.:BCN1260
CAS No.:134418-28-3
- Altiratinib
Catalog No.:BCC6385
CAS No.:1345847-93-9
- CYM 50308
Catalog No.:BCC6260
CAS No.:1345858-76-5
- 5,7-Di-O-methylquercetin
Catalog No.:BCN3386
CAS No.:13459-07-9
- ML 154
Catalog No.:BCC8022
CAS No.:1345964-89-7
- LY2795050
Catalog No.:BCC1719
CAS No.:1346133-08-1
- Planchol E
Catalog No.:BCN6882
CAS No.:1346137-02-7
- SA 57
Catalog No.:BCC6280
CAS No.:1346169-63-8
- ML 218 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6207
CAS No.:1346233-68-8
- Stavudine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4263
CAS No.:134624-73-0
- Eriocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN1208
CAS No.:13463-28-0
- Zinc Pyrithione
Catalog No.:BCC5008
CAS No.:13463-41-7
- ML 240
Catalog No.:BCC5604
CAS No.:1346527-98-7
Obesity-induced vascular inflammation involves elevated arginase activity.[Pubmed:28835451]
Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;313(5):R560-R571.
Obesity-induced vascular dysfunction involves pathological remodeling of the visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and increased inflammation. Our previous studies showed that arginase 1 (A1) in endothelial cells (ECs) is critically involved in obesity-induced vascular dysfunction. We tested the hypothesis that EC-A1 activity also drives obesity-related VAT remodeling and inflammation. Our studies utilized wild-type and EC-A1 knockout (KO) mice made obese by high-fat/high-sucrose (HFHS) diet. HFHS diet induced increases in body weight, fasting blood glucose, and VAT expansion. This was accompanied by increased arginase activity and A1 expression in vascular ECs and increased expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha), monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), interleukin-10 (IL-10), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) mRNA and protein in both VAT and ECs. HFHS also markedly increased circulating inflammatory monocytes and VAT infiltration by inflammatory macrophages, while reducing reparative macrophages. Additionally, adipocyte size and fibrosis increased and capillary density decreased in VAT. These effects of HFHS, except for weight gain and hyperglycemia, were prevented or reduced in mice lacking EC-A1 or treated with the arginase inhibitor 2-(S)-amino-6-boronohexanoic acid (ABH). In mouse aortic ECs, exposure to high glucose (25 mM) and Na palmitate (200 muM) reduced nitric oxide production and increased A1, TNF-alpha, VCAM-1, ICAM-1, and MCP-1 mRNA, and monocyte adhesion. Knockout of EC-A1 or ABH prevented these effects. HFHS diet-induced VAT inflammation is mediated by EC-A1 expression/activity. Limiting arginase activity is a possible therapeutic means of controlling obesity-induced vascular and VAT inflammation.
The role of insulin growth factor-1 on the vascular regenerative effect of MAA coated disks and macrophage-endothelial cell crosstalk.[Pubmed:28841464]
Biomaterials. 2017 Nov;144:199-210.
The IGF-1 signaling pathway and IGF-1-dependent macrophage/endothelial cell crosstalk was found to be critical features of the vascular regenerative effect displayed by implanted methacrylic acid -co-isodecyl acrylate (MAA-co-IDA; 40% MAA) coated disks in CD1 mice. Inhibition of IGF-1 signaling using AG1024 an IGF1-R tyrosine kinase inhibitor abrogated vessel formation 14 days after disk implantation in a subcutaneous pocket. Explanted tissue had increased arginase 1 expression and reduced iNOS expression consistent with the greater shift from "M1" ("pro-inflammatory") macrophages to "M2" ("pro-angiogenic") macrophages for MAA coated disks relative to control MM (methyl methacrylate-co-IDA) disks; the latter did not generate a vascular response and the polarization shift was muted with AG1024. In vitro, medium conditioned by macrophages (both human dTHP1 cells and mouse bone marrow derived macrophages) had elevated IGF-1 mRNA and protein levels, while the cells had reduced IGF1-R but elevated IGFBP-3 mRNA levels. These cells also had reduced iNOS and elevated Arg1 expression, consistent with the in vivo polarization results, including the inhibitory effects of AG1024. On the other hand, HUVEC exposed to dTHP1 conditioned medium migrated and proliferated faster suggesting that the primary target of the macrophage released IGF-1 was endothelial cells. Although further investigation is warranted, IGF-1 appears to be a key feature underpinning the observed vascularization. Why MAA based materials have this effect remains to be defined, however.
l-Arginine Uptake by Cationic Amino Acid Transporter Promotes Intra-Macrophage Survival of Leishmania donovani by Enhancing Arginase-Mediated Polyamine Synthesis.[Pubmed:28798743]
Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 26;8:839.
The survival of intracellular protozoan parasite, Leishmania donovani, the causative agent of Indian visceral leishmaniasis (VL), depends on the activation status of macrophages. l-Arginine, a semi-essential amino acid plays a crucial regulatory role for activation of macrophages. However, the role of l-arginine transport in VL still remains elusive. In this study, we demonstrated that intra-macrophage survival of L. donovani depends on the availability of extracellular l-arginine. Infection of THP-1-derived macrophage/human monocyte-derived macrophage (hMDM) with Leishmania, resulted in upregulation of l-arginine transport. While investigating the involvement of the transporters, we observed that Leishmania survival was greatly impaired when the transporters were blocked either using inhibitor or siRNA-mediated downregulation. CAT-2 was found to be the main isoform associated with l-arginine transport in L. donovani-infected macrophages. l-arginine availability and its transport regulated the host arginase in Leishmania infection. Arginase and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression were reciprocally regulated when assayed using specific inhibitors and siRNA-mediated downregulation. Interestingly, induction of iNOS expression and nitric oxide production were observed in case of inhibition of arginase in infected macrophages. Furthermore, inhibition of l-arginine transport as well as arginase resulted in decreased polyamine production, limiting parasite survival inside macrophages. l-arginine availability and transport regulated Th1/Th2 cytokine levels in case of Leishmania infection. Upregulation of l-arginine transport, induction of host arginase, and enhanced polyamine production were correlated with increased level of IL-10 and decreased level of IL-12 and TNF-alpha in L. donovani-infected macrophages. Our findings provide clear evidence for targeting the metabolism of l-arginine and l-arginine-metabolizing enzymes as an important therapeutic and prophylactic strategy to treat VL.
Entinostat Neutralizes Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Enhances the Antitumor Effect of PD-1 Inhibition in Murine Models of Lung and Renal Cell Carcinoma.[Pubmed:28698201]
Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 1;23(17):5187-5201.
PURPOSE: Recent advances in immunotherapy highlight the antitumor effects of immune checkpoint inhibition despite a relatively limited subset of patients receiving clinical benefit. The selective class I histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat has been reported to have immunomodulatory activity including targeting of immune suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment. Thus, we decided to assess whether entinostat could enhance anti-PD-1 treatment and investigate those alterations in the immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment that contribute to the combined antitumor activity. EXPERIMENTAL DESIGN: We utilized syngeneic mouse models of lung (LLC) and renal cell (RENCA) carcinoma and assessed immune correlates, tumor growth, and survival following treatment with entinostat (5 or 10 mg/kg, p.o.) and a PD-1 inhibitor (10 and 20 mg/kg, s.c.). RESULTS: Entinostat enhanced the antitumor effect of PD-1 inhibition in two syngeneic mouse tumor models by reducing tumor growth and increasing survival. Entinostat inhibited the immunosuppressive function of both polymorphonuclear (PMN)- and monocytic-myeloid derived suppressor cell (M-MDSC) populations. Analysis of MDSC response to entinostat revealed significantly reduced arginase-1, iNOS, and COX-2 levels, suggesting potential mechanisms for the altered function. We also observed significant alterations in cytokine/chemokine release in vivo with a shift toward a tumor-suppressive microenvironment. CONCLUSIONS: Our results demonstrate that entinostat enhances the antitumor effect of PD-1 targeting through functional inhibition of MDSCs and a transition away from an immune-suppressive tumor microenvironment. These data provide a mechanistic rationale for the clinical testing and potential markers of response of this novel combination in solid tumor patients.
Arginase Inhibition Reverses Monocrotaline-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension.[Pubmed:28757567]
Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Jul 25;18(8). pii: ijms18081609.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a heterogeneous disorder associated with a poor prognosis. Thus, the development of novel treatment strategies is of great interest. The enzyme arginase (Arg) is emerging as important player in PH development. The aim of the current study was to determine the expression of ArgI and ArgII as well as the effects of Arg inhibition in a rat model of PH. PH was induced in 35 Sprague-Dawley rats by monocrotaline (MCT, 60 mg/kg as single-dose). There were three experimental groups: sham-treated controls (control group, n = 11), MCT-induced PH (MCT group, n = 11) and MCT-induced PH treated with the Arg inhibitor Nomega-hydroxy-nor-l-arginine (nor-NOHA; MCT/NorNoha group, n = 13). ArgI and ArgII expression was determined by immunohistochemistry and Western blot. Right ventricular systolic pressure (RVPsys) was measured and lung tissue remodeling was determined. Induction of PH resulted in an increase in RVPsys (81 +/- 16 mmHg) compared to the control group (41 +/- 15 mmHg, p = 0.002) accompanied by a significant elevation of histological sum-score (8.2 +/- 2.4 in the MCT compared to 1.6 +/- 1.6 in the control group, p < 0.001). Both, ArgI and ArgII were relevantly expressed in lung tissue and there was a significant increase in the MCT compared to the control group (p < 0.01). Arg inhibition resulted in a significant reduction of RVPsys to 52 +/- 19 mmHg (p = 0.006) and histological sum-score to 5.8 +/- 1.4 compared to the MCT group (p = 0.022). PH leads to increased expression of Arg. Arg inhibition leads to reduction of RVPsys and diminished lung tissue remodeling and therefore represents a potential treatment strategy in PH.


