ML 154Potent neuropeptide S receptor (NPSR) antagonist CAS# 1345964-89-7 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1345964-89-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 46930969 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C29H26BrN2PS | M.Wt | 545.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 100 mM in DMSO and to 50 mM in ethanol | ||
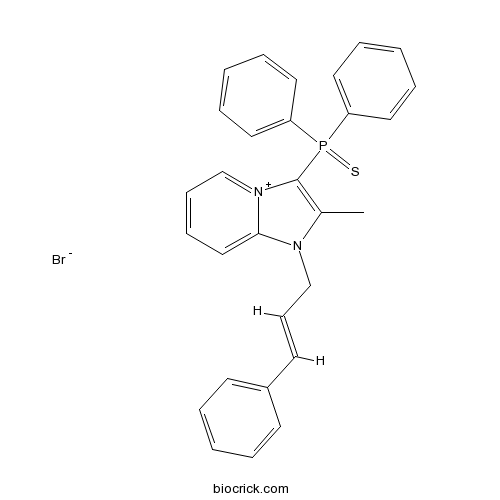
| Chemical Name | [2-methyl-1-[(E)-3-phenylprop-2-enyl]imidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-4-ium-3-yl]-diphenyl-sulfanylidene-$l^{5}-phosphane;bromide | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C([N+]2=CC=CC=C2N1CC=CC3=CC=CC=C3)P(=S)(C4=CC=CC=C4)C5=CC=CC=C5.[Br-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | CJAQCMBWGUOBIX-ZUQRMPMESA-M | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C29H26N2PS.BrH/c1-24-29(32(33,26-17-7-3-8-18-26)27-19-9-4-10-20-27)31-22-12-11-21-28(31)30(24)23-13-16-25-14-5-2-6-15-25;/h2-22H,23H2,1H3;1H/q+1;/p-1/b16-13+; | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent neuropeptide S receptor (NPSR) antagonist (pA2 = 9.98). Inhibits neuropeptide S-induced ERK phosphorylation over cAMP responses and calcium responses (IC50 values are 9.3, 22.1 and 36.5 nM, respectively). Appears to modulate addictive behavior in vivo. Displays no activity against vasopressin V1B receptors. Brain penetrant. |

ML 154 Dilution Calculator

ML 154 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8333 mL | 9.1664 mL | 18.3328 mL | 36.6656 mL | 45.832 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3667 mL | 1.8333 mL | 3.6666 mL | 7.3331 mL | 9.1664 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1833 mL | 0.9166 mL | 1.8333 mL | 3.6666 mL | 4.5832 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1833 mL | 0.3667 mL | 0.7333 mL | 0.9166 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0183 mL | 0.0917 mL | 0.1833 mL | 0.3667 mL | 0.4583 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 5,7-Di-O-methylquercetin
Catalog No.:BCN3386
CAS No.:13459-07-9
- CYM 50308
Catalog No.:BCC6260
CAS No.:1345858-76-5
- Altiratinib
Catalog No.:BCC6385
CAS No.:1345847-93-9
- Arginase inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4034
CAS No.:1345808-25-4
- ETP-46464
Catalog No.:BCC3913
CAS No.:1345675-02-6
- AM095
Catalog No.:BCC1351
CAS No.:1345614-59-6
- Atorvastatin Calcium
Catalog No.:BCC2319
CAS No.:134523-03-8
- U 90042
Catalog No.:BCC7465
CAS No.:134516-99-7
- Gardenoin J
Catalog No.:BCN7666
CAS No.:1345109-46-7
- 1-Cinnamoyl-3-hydroxypyrrolidine
Catalog No.:BCN6497
CAS No.:1344876-77-2
- Trimethylvinylammonium(1+)
Catalog No.:BCN1820
CAS No.:13448-18-5
- Richenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6185
CAS No.:134476-74-7
- LY2795050
Catalog No.:BCC1719
CAS No.:1346133-08-1
- Planchol E
Catalog No.:BCN6882
CAS No.:1346137-02-7
- SA 57
Catalog No.:BCC6280
CAS No.:1346169-63-8
- ML 218 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6207
CAS No.:1346233-68-8
- Stavudine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4263
CAS No.:134624-73-0
- Eriocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN1208
CAS No.:13463-28-0
- Zinc Pyrithione
Catalog No.:BCC5008
CAS No.:13463-41-7
- ML 240
Catalog No.:BCC5604
CAS No.:1346527-98-7
- GSK503
Catalog No.:BCC6386
CAS No.:1346572-63-1
- GSK126
Catalog No.:BCC1604
CAS No.:1346574-57-9
- GSK621
Catalog No.:BCC6517
CAS No.:1346607-05-3
- GSK343
Catalog No.:BCC1607
CAS No.:1346704-33-3
Clinical features, long-term clinical outcomes, and prognostic factors of tuberculous meningitis in West China: a multivariate analysis of 154 adults.[Pubmed:28343419]
Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017 Jun;15(6):629-635.
BACKGROUND: Tuberculosis is prevalent in China, which is the second greatest contributor to the global tuberculosis burden. Tuberculosis meningitis (TBM) is the most severe disease form but few reports describe long-term clinical outcomes and prognostic factors. Thus, we studied these features in Chinese TBM patients. METHODS: A retrospective follow-up study was used to collect clinical features and outcomes of adult TB meningitis at the First Affiliated Hospital of Chongqing Medical University from June 2012 to August 2015. Univariate analysis and multivariate analysis were used to identify predictive factors associated with outcomes at discharge and follow-up. RESULTS: TBM patients (N = 154) were a median age of 41 years (range: 16-82 years). Median time to follow-up was 26.4 months (range: 9.3-46.5 months) and 31% had poor outcomes at follow-up and limb weakness (p = 0.016), lower GCS scores (p < 0.001), cranial-nerve palsy (p = 0.024), and hydrocephalus (p = 0.009) were closely associated with these poor outcomes. Furthermore, a high neutrophil to lymphocytes ratio, high D-dimer, a low albumin to globulin ratio and slow background of EEG associated with poor outcomes as well. CONCLUSIONS: Mortality and disability associated with TBM are high in China. Limb weakness, GCS scores, cranial-nerve palsy and hydrocephalus were independent predictors of poor outcomes, and AGR, NLR, D-dimer, and EEG abnormalities may be prognostic factors of TBM.
Structure-activity relationship of imidazopyridinium analogues as antagonists of neuropeptide s receptor.[Pubmed:24171469]
J Med Chem. 2013 Nov 27;56(22):9045-56.
The discovery and characterization of a novel chemical series of phosphorothioyl-containing imidazopyridines as potent neuropeptide S receptor antagonists is presented. The synthesis of analogues and their structure-activity relationship with respect to the Gq, Gs, and ERK pathways is detailed. The pharmacokinetics and in vivo efficacy of a potent analogue in a food intake rodent model are also included, underscoring its potential therapeutic value for the treatment of sleep, anxiety, and addiction disorders.
A novel brain penetrant NPS receptor antagonist, NCGC00185684, blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the central amygdala and decreases operant alcohol self-administration in rats.[Pubmed:23761908]
J Neurosci. 2013 Jun 12;33(24):10132-42.
The Neuropeptide S receptor, a Gs/Gq-coupled GPCR expressed in brain regions involved in mediating drug reward, has recently emerged as a candidate therapeutic target in addictive disorders. Here, we describe the in vitro and in vivo pharmacology of a novel, selective and brain penetrant NPSR antagonist with nanomolar affinity for the NPSR, NCGC00185684. In vitro, NCGC00185684 shows biased antagonist properties, and preferentially blocks ERK-phosphorylation over intracellular cAMP or calcium responses to NPS. In vivo, systemic NCGC00185684 blocks alcohol-induced ERK-phosphorylation in the rat central amygdala, a region involved in regulation of alcohol intake. NCGC00185684 also decreases operant alcohol self-administration, and lowers motivation for alcohol reward as measured using progressive ratio responding. These effects are behaviorally specific, in that they are observed at doses that do not influence locomotor activity or reinstatement responding following extinction. Together, these data provide an initial validation of the NPSR as a therapeutic target in alcoholism.


