ML 240ATP-competitive inhibitor of p97 ATPase CAS# 1346527-98-7 |
- BMN-673 8R,9S
Catalog No.:BCC1422
CAS No.:1207456-00-5
- XAV-939
Catalog No.:BCC1120
CAS No.:284028-89-3
- PJ34
Catalog No.:BCC1865
CAS No.:344458-19-1
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1346527-98-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 49830258 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H20N6O | M.Wt | 396.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (31.53 mM; Need ultrasonic) Ethanol : < 1 mg/mL (insoluble) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
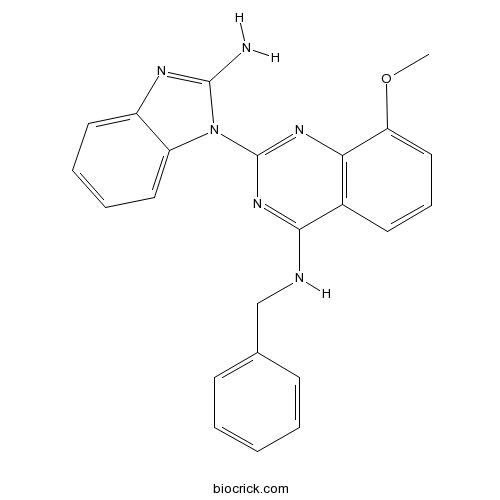
| Chemical Name | 2-(2-aminobenzimidazol-1-yl)-N-benzyl-8-methoxyquinazolin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=CC2=C1N=C(N=C2NCC3=CC=CC=C3)N4C5=CC=CC=C5N=C4N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NHAMBLRUUJAFOY-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H20N6O/c1-30-19-13-7-10-16-20(19)27-23(28-21(16)25-14-15-8-3-2-4-9-15)29-18-12-6-5-11-17(18)26-22(29)24/h2-13H,14H2,1H3,(H2,24,26)(H,25,27,28) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | ATP-competitive inhibitor of p97 ATPase (VCP, IC50 = 110 nM). Exhibits antiproliferative activity in NCI-60 cancer cell lines and rapidly induces executioner caspases 3 and 7 in multiple colon cancer cells. Promotes accumulation of LC3-II and impairs autophagosome maturation. Also impairs the endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. |

ML 240 Dilution Calculator

ML 240 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5224 mL | 12.6122 mL | 25.2245 mL | 50.449 mL | 63.0612 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5045 mL | 2.5224 mL | 5.0449 mL | 10.0898 mL | 12.6122 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2522 mL | 1.2612 mL | 2.5224 mL | 5.0449 mL | 6.3061 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0504 mL | 0.2522 mL | 0.5045 mL | 1.009 mL | 1.2612 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0252 mL | 0.1261 mL | 0.2522 mL | 0.5045 mL | 0.6306 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
ML240 is a potent p97 inhibitor, inhibiting p97 ATPase with IC50 value of 100 nM.
In Vitro:ML240 is a potent p97 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 100 nM. ML240 is active in the UbG76V-GFP stabilization assay (IC50, 0.9 μM). ML240 inhibits p97 competitively with respect to ATP with a Ki values of 0.22 μM. ML240 also inhibits labeling of only three protein kinase domains by >50% when tested at 20 μM: PIP5 K3 (belongs to phosphoinositide-3 kinase family), JAK1 JH2 (N-terminal pseudokinase domain of JAK1), and DNAPK (DNA-dependent protein kinase). ML240 (1.1, 3.3, 10, or 20 μM) induces executioner caspases 3 and 7 and triggers cell death independently of apical caspases 8 and 9[1]. ML240 is cytotoxic to HCT15 and SW403 cells, with GI50s of 0.76 and 0.5 μM after treatment for 24 h, and 0.54 and 0.5 μM after treatment for 72 h, respectively[2].
References:
[1]. Chou TF et al. Structure-activity relationship study reveals ML240 and ML241 as potent and selective inhibitors of p97 ATPase. ChemMedChem, 2013 Feb, 8(2):297-312.
[2]. Chou TF, et al. Selective, reversible inhibitors of the AAA ATPase p97. Probe Reports from the NIH Molecular Libraries Program. April 14, 2011.
- Zinc Pyrithione
Catalog No.:BCC5008
CAS No.:13463-41-7
- Eriocitrin
Catalog No.:BCN1208
CAS No.:13463-28-0
- Stavudine sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4263
CAS No.:134624-73-0
- ML 218 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6207
CAS No.:1346233-68-8
- SA 57
Catalog No.:BCC6280
CAS No.:1346169-63-8
- Planchol E
Catalog No.:BCN6882
CAS No.:1346137-02-7
- LY2795050
Catalog No.:BCC1719
CAS No.:1346133-08-1
- ML 154
Catalog No.:BCC8022
CAS No.:1345964-89-7
- 5,7-Di-O-methylquercetin
Catalog No.:BCN3386
CAS No.:13459-07-9
- CYM 50308
Catalog No.:BCC6260
CAS No.:1345858-76-5
- Altiratinib
Catalog No.:BCC6385
CAS No.:1345847-93-9
- Arginase inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4034
CAS No.:1345808-25-4
- GSK503
Catalog No.:BCC6386
CAS No.:1346572-63-1
- GSK126
Catalog No.:BCC1604
CAS No.:1346574-57-9
- GSK621
Catalog No.:BCC6517
CAS No.:1346607-05-3
- GSK343
Catalog No.:BCC1607
CAS No.:1346704-33-3
- Lamivudine
Catalog No.:BCC3801
CAS No.:134678-17-4
- Linderane
Catalog No.:BCN5023
CAS No.:13476-25-0
- A 412997 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6224
CAS No.:1347744-96-0
- 6''-O-Acetylglycitin
Catalog No.:BCN3866
CAS No.:134859-96-4
- 8-M-PDOT
Catalog No.:BCC6901
CAS No.:134865-70-6
- 4-P-PDOT
Catalog No.:BCC6900
CAS No.:134865-74-0
- SAR245409
Catalog No.:BCC2534
CAS No.:934493-76-2
- Taccalonolide AJ
Catalog No.:BCN2971
CAS No.:1349904-82-0
Prevalence and Characteristics of Exercise-Induced Bronchoconstriction in High School and College Athletes at 2,240 m Altitude.[Pubmed:28239178]
Rev Invest Clin. 2017 Jan-Feb;69(1):20-27.
BACKGROUND: Athletes practicing strenuous physical activities may develop exercise-induced bronchoconstriction (EIB). We aimed to determine the prevalence and features of this condition in Mexico City (altitude, 2,240 m). METHODS: In the present study, 208 high school and college athletes performed a standardized EIB test on a treadmill. RESULTS: Responses to exercise had large between-subject variability in all physiological parameters (forced expiratory volume in one second [FEV1], heart rate, blood oxygen saturation level [SpO2], blood pressure), with nearly similar proportions of subjects in whom FEV1 increased or decreased. According to the recommended cut-off value of 10% FEV1 decrease, only 15 (7.2%) athletes had a positive EIB test. Weight lifters were more prone to develop EIB (three out of seven athletes; p = 0.01). Subjects with a positive EIB test already had a lower baseline forced expiratory volume in one second/forced vital capacity (FEV1/FVC) ratio (96.4 vs. 103.2% of predicted, respectively; p = 0.047), and developed more respiratory symptoms after exercise than subjects with a negative test. There were no differences with respect to age, gender, body mass index, history of asthma or atopic diseases, smoking habit, and exposure to potential indoor allergens. CONCLUSIONS: The relatively low prevalence of EIB in athletes from Mexico City raises the possibility that high altitude constitutes a protective factor for EIB. In contrast, weight lifters were especially prone to develop EIB, which suggests that repetitive Valsalva maneuvers could be a novel risk factor for EIB. There was a large between-subject variability of all physiological responses to exercise.
Case 240: Meckel Diverticulitis.[Pubmed:28318437]
Radiology. 2017 Apr;283(1):303-307.
History A previously healthy 28-year-old man developed right lower quadrant pain while traveling. The pain progressed over the course of 2-3 days, and his family took him to a local emergency department. He was found to have an elevated white blood cell count of 12.2 x 10(9)/L (reference range, [3.9-10.3] x 10(9)/L), with a predominance of neutrophils. Contrast material-enhanced computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis was performed, and findings were abnormal. The patient elected to leave the emergency department without undergoing treatment, and he returned home via airplane. He presented to his primary care physician for further evaluation later that same day. His physician noted a mildly distended abdomen that was diffusely tender on palpation, with rebound tenderness in the right lower quadrant. The patient was admitted to our hospital, and the general surgery department was consulted. The CT images that were obtained at the outside institution were submitted to our radiology department for interpretation.
Surface-dominated conduction up to 240 K in the Kondo insulator SmB6 under strain.[Pubmed:28369051]
Nat Mater. 2017 Jul;16(7):708-711.
SmB6 is a strongly correlated mixed-valence Kondo insulator with a newly discovered surface state, proposed to be of non-trivial topological origin. However, the surface state dominates electrical conduction only below T( *) approximately 4 K (ref. ), limiting its scientific investigation and device application. Here, we report the enhancement of T( *) in SmB6 under the application of tensile strain. With 0.7% tensile strain we report surface-dominated conduction at up to a temperature of 240 K, persisting even after the strain has been removed. This can be explained in the framework of strain-tuned temporal and spatial fluctuations of f-electron configurations, which might be generally applied to other mixed-valence materials. We note that this amount of strain can be induced in epitaxial SmB6 films via substrate in potential device applications.
Structure-activity relationship study reveals ML240 and ML241 as potent and selective inhibitors of p97 ATPase.[Pubmed:23316025]
ChemMedChem. 2013 Feb;8(2):297-312.
To discover more potent p97 inhibitors, we carried out a structure-activity relationship study of the quinazoline scaffold previously identified from our HTS campaigns. Two improved inhibitors, ML240 and ML241, inhibit p97 ATPase with IC(50) values of 100 nM. Both compounds inhibited degradation of a p97-dependent but not a p97-independent proteasome substrate in a dual-reporter cell line. They also impaired the endoplasmic-reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) pathway. Unexpectedly, ML240 potently stimulated accumulation of LC3-II within minutes, inhibited cancer cell growth, and rapidly mobilized the executioner caspases 3 and 7, whereas ML241 did not. The behavior of ML240 suggests that disruption of the protein homeostasis function of p97 leads to more rapid activation of apoptosis than is observed with a proteasome inhibitor. Further characterization revealed that ML240 has broad antiproliferative activity toward the NCI-60 panel of cancer cell lines, but slightly lower activity toward normal cells. ML240 also synergizes with the proteasome inhibitor MG132 to kill multiple colon cancer cell lines. Meanwhile, both probes have low off-target activity toward a panel of protein kinases and central nervous system targets. Our results nominate ML240 as a promising starting point for the development of a novel agent for the chemotherapy of cancer, and provide a rationale for developing pathway-specific p97 inhibitors.


