CGS 9343BCAS# 109826-27-9 |
- CGH 2466 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7338
CAS No.:1177618-54-0
- Istradefylline (KW-6002)
Catalog No.:BCC3798
CAS No.:155270-99-8
- 8-Aminoadenine
Catalog No.:BCC6108
CAS No.:28128-33-8
- Preladenant
Catalog No.:BCC1868
CAS No.:377727-87-2
- ANR 94
Catalog No.:BCC7815
CAS No.:634924-89-3
- Tozadenant
Catalog No.:BCC2011
CAS No.:870070-55-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 109826-27-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 6450522 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H32N4O6 | M.Wt | 544.61 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Zaldaride maleate | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 50 mM in DMSO and to 10 mM in ethanol with gentle warming | ||
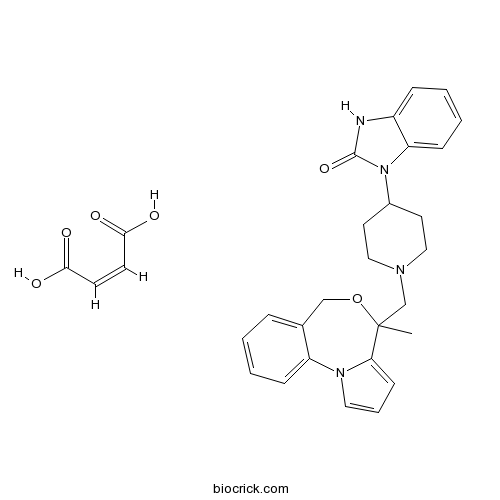
| Chemical Name | (Z)-but-2-enedioic acid;3-[1-[(4-methyl-6H-pyrrolo[1,2-a][4,1]benzoxazepin-4-yl)methyl]piperidin-4-yl]-1H-benzimidazol-2-one | ||
| SMILES | CC1(C2=CC=CN2C3=CC=CC=C3CO1)CN4CCC(CC4)N5C6=CC=CC=C6NC5=O.C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGODOSILXOFQPH-BTJKTKAUSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H28N4O2.C4H4O4/c1-26(24-11-6-14-29(24)22-9-4-2-7-19(22)17-32-26)18-28-15-12-20(13-16-28)30-23-10-5-3-8-21(23)27-25(30)31;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h2-11,14,20H,12-13,15-18H2,1H3,(H,27,31);1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b;2-1- | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Calmodulin antagonist; inhibits calmodulin-stimulated cAMP phosphodiesterase activity with an IC50 of 3.3 nM. Also prevents estrogen-induced transcription activation by ER, reversibly blocks voltage-activated Na+, Ca2+ and K+ currents in PC12 cells and inhibits nAChR. |

CGS 9343B Dilution Calculator

CGS 9343B Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8362 mL | 9.1809 mL | 18.3618 mL | 36.7235 mL | 45.9044 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3672 mL | 1.8362 mL | 3.6724 mL | 7.3447 mL | 9.1809 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1836 mL | 0.9181 mL | 1.8362 mL | 3.6724 mL | 4.5904 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0367 mL | 0.1836 mL | 0.3672 mL | 0.7345 mL | 0.9181 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0184 mL | 0.0918 mL | 0.1836 mL | 0.3672 mL | 0.459 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Kaempferol 5,7,4'-trimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN6587
CAS No.:1098-92-6
- Harmalidine
Catalog No.:BCN5889
CAS No.:109794-97-0
- ASP3026
Catalog No.:BCC1372
CAS No.:1097917-15-1
- 9R-10alpha-Hydroxyepigambogic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3079
CAS No.:1097882-33-1
- Homopahutoxin
Catalog No.:BCN1812
CAS No.:109777-68-6
- 8 beta-(4-Acetoxy-5-hydroxytigloyloxy)costunolide
Catalog No.:BCN7123
CAS No.:109770-86-7
- cis-Dehydroosthol
Catalog No.:BCN4735
CAS No.:109741-40-4
- Murraol
Catalog No.:BCN5888
CAS No.:109741-38-0
- MLN 2480
Catalog No.:BCC1771
CAS No.:1096708-71-2
- SPK-601
Catalog No.:BCC1961
CAS No.:1096687-52-3
- Neocryptotanshinone
Catalog No.:BCN3158
CAS No.:109664-02-0
- Topazolin
Catalog No.:BCN6833
CAS No.:109605-79-0
- Granisetron
Catalog No.:BCC1601
CAS No.:109889-09-0
- Sodium prasterone sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC9149
CAS No.:1099-87-2
- Kifunensine
Catalog No.:BCC7601
CAS No.:109944-15-2
- ITD 1
Catalog No.:BCC6409
CAS No.:1099644-42-4
- Succinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5890
CAS No.:110-15-6
- Maleic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8426
CAS No.:110-16-7
- Fumaric acid
Catalog No.:BCN5989
CAS No.:110-17-8
- Sorbic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2218
CAS No.:110-44-1
- 8-O-Ethylyunaconitine
Catalog No.:BCN6260
CAS No.:110011-77-3
- Taurohyodeoxycholic Acid Sodium Salt
Catalog No.:BCC8363
CAS No.:110026-03-4
- Tussilagonone
Catalog No.:BCC8365
CAS No.:110042-38-1
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
The calmodulin inhibitor CGS 9343B inhibits voltage-dependent K+ channels in rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells.[Pubmed:25796172]
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2015 Jun 15;285(3):207-13.
We investigated the effects of the calmodulin inhibitor CGS 9343B on voltage-dependent K(+) (Kv) channels using whole-cell patch clamp technique in freshly isolated rabbit coronary arterial smooth muscle cells. CGS 9343B inhibited Kv currents in a concentration-dependent manner, with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) value of 0.81muM. The decay rate of Kv channel inactivation was accelerated by CGS 9343B. The rate constants of association and dissociation for CGS 9343B were 2.77+/-0.04muM(-1)s(-1) and 2.55+/-1.50s(-1), respectively. CGS 9343B did not affect the steady-state activation curve, but shifted the inactivation curve toward to a more negative potential. Train pulses (1 or 2Hz) application progressively increased the CGS 9343B-induced Kv channel inhibition. In addition, the inactivation recovery time constant was increased in the presence of CGS 9343B, suggesting that CGS 9343B-induced inhibition of Kv channel was use-dependent. Another calmodulin inhibitor, W-13, did not affect Kv currents, and did not change the inhibitory effect of CGS 9343B on Kv current. Our results demonstrated that CGS 9343B inhibited Kv currents in a state-, time-, and use-dependent manner, independent of calmodulin inhibition.
Influence of CGS 9343B, an inhibitor of calmodulin activity, on histamine release from isolated rat mast cells.[Pubmed:1382372]
Agents Actions. 1992 Jul;36(3-4):192-9.
Investigations of calmodulin involvement in cell responses has been complicated by the lack of selective calmodulin antagonists. A novel inhibitor, CGS 9343B, reportedly without influence on protein kinase C, is used in the present study of mast cell responses. The histamine release induced by antigen and compound 48/80 in the presence of calcium was enhanced by 10-20 microM CGS 9343B and inhibited by higher concentrations. Only inhibitory effects on the response to compound 48/80 in the absence of calcium and to the ionophore A23187 were observed, the latter being inhibited by 20 microM CGS 9343B. The influence on responses to combinations of the phorbol ester TPA and the ionophore A23187 was more complex, giving rise to enhancement at lower and inhibition at higher concentrations of CGS 9343B in a manner which depended on the experimental conditions. Unlike previously used calmodulin antagonists, CGS 9343B is devoid of detergent effects and without serious metabolic interference. The inhibitor seems useful to reveal differences in the mechanisms involved in responses to various histamine liberators. Our results conform with an inhibition of calmodulin by CGS 9343B but are at present inconclusive.
Effects of CGS 9343B (a putative calmodulin antagonist) on isolated skeletal muscle. Dissociation of signaling pathways for insulin-mediated activation of glycogen synthase and hexose transport.[Pubmed:7592735]
J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 27;270(43):25613-8.
The role of calmoudulin in control of carbohydrate metabolism in the absence and presence of insulin in isolated mouse soleus muscle was investigated. The calmodulin antagonist CGS 9343B had no effect on basal glycogen synthase activity, the contents of high energy phosphates, glucose-6-P, or glycogen synthesis. However, CGS 9343B inhibited the basal rates of 2-deoxyglucose uptake and 3-O-methylglucose transport by 30% (p < 0.05) and 40% (p < 0.001), respectively. Insulin activated glycogen synthase by almost 40% (p < 0.01) and this increase was not altered in the presence of CGS 9343B. Insulin increased the muscle content of glucose-6-P (approximately equal to 2-fold), as well as glycogen synthesis (approximately equal to 8-fold), 2-deoxyglucose uptake (approximately equal to 3-fold), and 3-O-methylglucose transport (approximately equal to 2-fold), and these increases were inhibited by CGS 9343B. In additional experiments on isolated rat epitrochlearis muscle, it was found that the hypoxia-mediated activation of 3-O-methylglucose transport was also inhibited by CGS 9343B. These data demonstrate that: 1) hexose transport, both in the absence and presence of external stimuli (insulin and hypoxia), requires functional calmodulin; and 2) insulin-mediated activation of glycogen synthase does not require functional calmodulin, nor can it be accounted for by increases in glucose transport or glucose-6-P.
Inhibition of mechanotransducer currents in crayfish sensory neuron by CGS 9343B, a calmodulin antagonist.[Pubmed:10844093]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2000 May 26;397(1):11-7.
The effects of CGS 9343B (zaldaride maleate), a calmodulin antagonist, on mechanosensitive channels were examined in crayfish slowly adapting sensory neurons using the two-electrode voltage clamp technique. In addition to its inhibition of voltage-gated Na(+) and K(+) currents, CGS 9343B (<30 microM) blocked reversibly the receptor current in a dose-dependent and voltage-dependent manner with a dissociation constant (K(d)) of 26.8 microM. The time course of the block was 265 s. Within the extension range of 3-30%, the reduction in receptor current was stimulus-independent and the gating mechanisms were not affected. Extracellular Ca(2+) was not necessary for its blocking effects. No changes in passive muscle tension were observed in the presence of 20 microM CGS 9343B. These results suggest that CGS 9343B, as a calmodulin antagonist, can also block mechanosensitive channels, possibly by being incorporated into the lipid membrane and/or interacting with the channel protein.
Calmodulin regulates the transcriptional activity of estrogen receptors. Selective inhibition of calmodulin function in subcellular compartments.[Pubmed:12419798]
J Biol Chem. 2003 Jan 10;278(2):1195-200.
The steroid hormone estrogen elicits biological effects in cells by binding to and activating the estrogen receptor (ER). Estrogen binding induces a conformational change in the receptor, inducing nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation of ER. The ubiquitous Ca(2+)-binding protein calmodulin has been shown to interact directly with ER and enhance its stability. To further elucidate the functional sequelae of the association between calmodulin and ER, we examined the effect on ER transcriptional activation of specifically inhibiting calmodulin. The cell-permeable calmodulin antagonist CGS9343B prevented estrogen-induced transcriptional activation by ER, without altering basal transcription. The inhibition was dose-dependent and independent of the time of estrogen stimulation. To validate these findings, calmodulin function was also neutralized by targeted expression of a specific inhibitor peptide. By inserting localization signals, the inhibitor peptide was selectively targeted to different subcellular domains. Inactivation of calmodulin function in the nucleus virtually eliminated estrogen-stimulated ER transcriptional activation. By contrast, when membrane calmodulin was specifically neutralized, estrogen-stimulated transcriptional activation by ER was only slightly attenuated. Importantly, the inhibitor peptides did not significantly reduce the amount of ER in the cells. Together, these data demonstrate that calmodulin is a fundamental component of ER transcriptional activation.
Inhibition of membrane currents and rises of intracellular Ca2+ in PC12 cells by CGS 9343B, a calmodulin inhibitor.[Pubmed:1379190]
Eur J Pharmacol. 1992 Jun 5;226(2):183-5.
The calmodulin inhibitor 1,3-dihydro-1-[1-((4-methyl-4H,6H-pyrrolo[1,2-a]-[4,1]benzoxazepin - 4-yl)methyl)-4-piperidinyl]-2H-benzimidazol-2-one maleate (CGS 9343B) caused a reversible block of voltage-activated Ca2+, Na+, and K+ currents in differentiated rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells. The drug also inhibited nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) channel currents but not inward currents evoked by extracellular ATP. Depolarization-induced intracellular Ca2+ transients were almost completely inhibited in growth cones and cell bodies by CGS 9343B. Our results suggest actions of CGS 9343B on ion fluxes unrelated to calmodulin inhibition.
CGS 9343B, a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of calmodulin activity.[Pubmed:3033469]
Mol Pharmacol. 1987 May;31(5):535-40.
1,3-Dihydro-1-[1-[(4-methyl-4H,6H-pyrrolo[1,2-a][4,1]- benzoxazepin-4-yl)methyl]-4-piperidinyl]-2H-benzimidazol-2-o ne (1:1) maleate was synthesized in six steps from methyl anthranilate and designated CGS 9343B. CGS 9343B inhibited calmodulin-stimulated cAMP phosphodiesterase activity with an IC50 value of 3.3 microM. CGS 9343B was 3.8 times more potent than trifluoperazine (IC50 = 12.7 microM) as an inhibitor of calmodulin activity. CGS 9343B did not inhibit protein kinase C activity at concentrations up to 100 microM, whereas trifluoperazine inhibited protein kinase C activity with an IC50 value of 43.9 microM. CGS 9343B weakly displaced [3H]spiperone from postsynaptic dopamine receptors with an IC50 value of 4.8 microM while the value for trifluoperazine, a potent antipsychotic agent, was 0.018 microM. It is concluded that CGS 9343B is a novel, potent, and selective inhibitor of calmodulin activity. Unlike trifluoperazine, CGS 9343B does not inhibit protein kinase C activity and does not possess potential antidopaminergic activity.


