CalpeptinCa2+-dependent protease,calpain inhibitor CAS# 117591-20-5 |
- Calpain Inhibitor I, ALLN
Catalog No.:BCC1233
CAS No.:110044-82-1
- Acetyl-Calpastatin (184-210) (human)
Catalog No.:BCC2350
CAS No.:123714-50-1
- PD 151746
Catalog No.:BCC5485
CAS No.:179461-52-0
- PD 150606
Catalog No.:BCC2353
CAS No.:179528-45-1
- E-64
Catalog No.:BCC1222
CAS No.:66701-25-5
- MDL 28170
Catalog No.:BCC2352
CAS No.:88191-84-8
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 117591-20-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73364 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H30N2O4 | M.Wt | 362.47 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 155 mg/mL (427.63 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
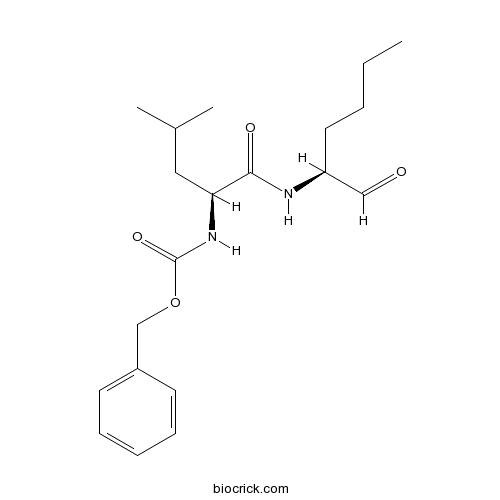
| Chemical Name | benzyl N-[(2S)-4-methyl-1-oxo-1-[[(2S)-1-oxohexan-2-yl]amino]pentan-2-yl]carbamate | ||
| SMILES | CCCCC(C=O)NC(=O)C(CC(C)C)NC(=O)OCC1=CC=CC=C1 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | PGGUOGKHUUUWAF-ROUUACIJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H30N2O4/c1-4-5-11-17(13-23)21-19(24)18(12-15(2)3)22-20(25)26-14-16-9-7-6-8-10-16/h6-10,13,15,17-18H,4-5,11-12,14H2,1-3H3,(H,21,24)(H,22,25)/t17-,18-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent, cell-permeable inhibitor of the Ca2+-dependent protease, calpain. Prevents collagen- and thrombin-induced platelet aggregation, probably by blocking calpain induced phospholipase C and thromboxane synthase activation. Potent cathepsin L inhibitor. Recently shown to preferentially inhibit a subset of protein-tyrosine phosphatases. |

Calpeptin Dilution Calculator

Calpeptin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7588 mL | 13.7942 mL | 27.5885 mL | 55.177 mL | 68.9712 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5518 mL | 2.7588 mL | 5.5177 mL | 11.0354 mL | 13.7942 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3794 mL | 2.7588 mL | 5.5177 mL | 6.8971 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5518 mL | 1.1035 mL | 1.3794 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.1379 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5518 mL | 0.6897 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 5 nM for human calpain 1
Calpeptin is a calpain inhibitor.
As a calcium-dependent intracellular cysteine protease, calpain plays an key role in various cellular processes including cell differentiation, growth and apoptosis. In rheumatoid arthritis patients, over-expression of calpains are observed in arthritic synovial fluid and are thought to play critical roles in various cellular processes.
In vitro: Calpeptin reduced production of TGF-b1, IL-6, angiopoietin-1 and collagen synthesis from lung fibroblasts. Calpeptin also reduced both angiopoietin-1-dependent migration and IL-6-dependent proliferation of the cells, which could be the underlying mechanism of the preventive effect of Calpeptin on pulmonary fibrosis [1].
In vivo: The preventive effect of calpeptin has been examined on bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Histological examinations and quantitative measurements of related proteins in bleomycin-treated mouse lung tissues with or without calpeptin were performed. Calpeptin histologically ameliorated bleomycininduced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Results showed that calpeptin decreased the expression of IL-6, TGF-b1, angiopoietin-1 and collagen type Ia1 mRNA in mouse lung tissues [1].
Clinical trial: N/A
Reference:
[1] Tabata C,Tabata R,Nakano T. The calpain inhibitor calpeptin prevents bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol.2010 Dec;162(3):560-7.
- DMXAA (Vadimezan)
Catalog No.:BCC3644
CAS No.:117570-53-3
- threo-6'-Hydroxyustusolate C
Catalog No.:BCN6930
CAS No.:1175543-07-3
- Ustusolate E
Catalog No.:BCN7789
CAS No.:1175543-06-2
- 2alpha,9alpha,11-Trihydroxy-6-oxodrim-7-ene
Catalog No.:BCN7741
CAS No.:1175543-03-9
- Ustusol A
Catalog No.:BCN7719
CAS No.:1175543-02-8
- Neuromedin U (rat)
Catalog No.:BCC5847
CAS No.:117505-80-3
- ROX NHS ester, pure 6- isomer
Catalog No.:BCC3587
CAS No.:117491-83-5
- Sesamoside
Catalog No.:BCN6051
CAS No.:117479-87-5
- Prionitin
Catalog No.:BCN4855
CAS No.:117469-56-4
- Cefditoren Pivoxil
Catalog No.:BCC4898
CAS No.:117467-28-4
- BCECF-AM
Catalog No.:BCC5969
CAS No.:117464-70-7
- Triptonodiol
Catalog No.:BCN6782
CAS No.:117456-87-8
- Coronarin E
Catalog No.:BCN6052
CAS No.:117591-81-8
- 6-Hydroxymethylherniarin
Catalog No.:BCN3573
CAS No.:117597-79-2
- 1-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-2-methoxyphenyl)-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCN1607
CAS No.:117614-84-3
- 16-Oxocleroda-3,13E-dien-15-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7286
CAS No.:117620-72-1
- 3-Cyano-7-ethoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCC7979
CAS No.:117620-77-6
- Agomelatine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4210
CAS No.:1176316-99-6
- LY 255283
Catalog No.:BCC7290
CAS No.:117690-79-6
- DL-Syringaresinol
Catalog No.:BCN6053
CAS No.:1177-14-6
- Laxogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8434
CAS No.:1177-71-5
- Dexamethasone acetate
Catalog No.:BCC4775
CAS No.:1177-87-3
- Doramectin
Catalog No.:BCC1536
CAS No.:117704-25-3
- CKI 7 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5614
CAS No.:1177141-67-1
Neuroprotective Effect of Calpeptin on Acrylamide-Induced Neuropathy in Rats.[Pubmed:26423962]
Neurochem Res. 2015 Nov;40(11):2325-32.
Acrylamide (ACR) is a vinyl monomer with established human neurotoxic effects, which is characterized by the accumulation of neurofilaments (NFs) in the distal swellings of large axons in peripheral and central nervous systems. However, the mechanisms of neurotoxicity remain unclear. The objective is to investigate the neuroprotective effect of Calpeptin (CP) on ACR-induced neuropathy and its mechanism. Female adult Wistar rats were randomly divided into four groups (control, CP, ACR, and ACR + CP group). Control group received 0.9 % saline, ACR and ACR + CP groups received 30 mg/kg ACR by intraperitoneal injection. In addition, CP and ACR + CP groups also received 200 microg/kg CP. Gait analysis and hind limb splay were measured weekly to analyze neurobehavioral changes. The calpain activity and the changes of NFs protein levels in spinal cord are determined. Compared with control group, body weight of rats in ACR group decreased by 11.3 % (P < 0.01), while in ACR + CP group body weight increased significantly by 8.3 % (P < 0.01) compared with ACR group by the end of the 4th week; gait score of rats in both ACR and ACR + CP groups increased significantly by 167 % and 100 % (P < 0.01) compared with control group, while it decreased significantly by 25.1 % (P < 0.01) in ACR + CP group compared with ACR group; the distance of hind limb splay in both ACR and ACR + CP groups increased by 76.7 % and 49.5 % (P < 0.01) compared with control group, while it decreased by 15.4 % (P < 0.01) in ACR + CP group compared with ACR group; calpain activity of spinal cord at ACR and ACR + CP groups increased significantly by 14.9 % and 10.0 % (P < 0.01) compared with control group, while it decreased 4.2 % (P < 0.01) in ACR + CP group compared with ACR group; compared with control group, the levels of light NF (NF-L), medium NF (NF-M) and heavy NF (NF-H) subunits increased by 81.2 %, 263.6 % and 22.6 % (P < 0.01) in the supernatant of ACR group in spinal cord tissue and increased by 28.4 %, 96.6 % and 10.6 % (P < 0.01) in ACR + CP group, while the levels of NF-L, NF-M and NF-H subunits decreased by 29.1 %, 45.9 % and 9.8 % (P < 0.01) in ACR + CP group compared with ACR group. The present results suggested that CP can relieve ACR neuropathy by decrease calpain activity and NFs degradation. The changes of calpain activity and NFs may be one of the mechanisms of ACR-induced neuropathy.
Calpeptin, not calpain, directly inhibits an ion channel of the inner mitochondrial membrane.[Pubmed:26108743]
Protoplasma. 2016 May;253(3):835-43.
The permeability transition pore (PTP) of inner mitochondrial membranes is a large conductance pathway for ions up to 1500 Da which opening is responsible for ion equilibration and loss of membrane potential in apoptosis and thus in several neurodegenerative diseases. The PTP can be regulated by the Ca(2+)-activated mitochondrial K channel (BK). Calpains are Ca(2+)-activated cystein proteases; Calpeptin is an inhibitor of calpains. We wondered whether calpain or Calpeptin can modulate activity of PTP or BK. Patch clamp experiments were performed on mitoplasts of rat liver (PTP) and of an astrocytoma cell line (BK). Channel-independent open probability (P(o)) was determined (PTP) and, taking into account the number of open levels, NP(o) by single channel analysis (BK). We find that PTP in the presence of Ca(2+) (200 muM) is uninfluenced by calpain (13 nM) and shows insignificant decrease by the calpain inhibitor Calpeptin (1 muM). The NP(o) of the BK is insensitive to calpain (54 nM), too. However, it is significantly and reversibly inhibited by the calpain inhibitor Calpeptin (IC50 = 42 muM). The results agree with Calpeptin-induced activation of the PTP via inhibition of the BK. Screening experiments with respirometry show Calpeptin effects, fitting to inhibition of the BK by Calpeptin, and strong inhibition of state 3 respiration.
Calpeptin Prevents Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma Cell Proliferation via the Angiopoietin1/Tie2 System.[Pubmed:27509983]
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2016;17(7):3405-9.
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM), an aggressive malignant tumor of mesothelial origin associated with asbestos exposure, shows a limited response to conventional chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Therefore, the overall survival of MPM patients remains very poor. Progress in the development of therapeutic strategies for MPM has been limited. We recently reported that the calpain inhibitor, Calpeptin exerted inhibitory effects on pulmonary fibrosis by inhibiting the proliferation of lung fibroblasts. In the present study, we examined the preventive effects of Calpeptin on the cell growth of MPM, the origin of which is mesenchymal cells, similar to lung fibroblasts. Calpeptin inhibited the proliferation of MPM cells, but not mesothelial cells. It also prevented 1) the expression of angiopoietin (Ang)1 and Tie2 mRNA in MPM cells, but not mesothelial cells and 2) the Ang1induced proliferation of MPM cells through an NFkB dependent pathway, which may be the mechanism underlying the preventive effects of Calpeptin on the growth of MPM cells. These results suggest potential clinical use of Calpeptin for the treatment of MPM.
Calpain inhibitor calpeptin suppresses pancreatic cancer by disrupting cancer-stromal interactions in a mouse xenograft model.[Pubmed:27487486]
Cancer Sci. 2016 Oct;107(10):1443-1452.
Desmoplasia contributes to the aggressive behavior of pancreatic cancer. However, recent clinical trials testing several antifibrotic agents on pancreatic cancer have not shown clear efficacy. Therefore, further investigation of desmoplasia-targeting antifibrotic agents by another mechanism is needed. Calpeptin, an inhibitor of calpains, suppressed fibroblast function and inhibited fibrosis. In this study, we investigated the anticancer effects of Calpeptin on pancreatic cancer. We investigated whether Calpeptin inhibited tumor progression using a mouse xenograft model. We used quantitative RT-PCR to evaluate the expression of calpain-1 and calpain-2 mRNA in pancreatic cancer cells (PCCs) and pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs). We also undertook functional assays, including proliferation, migration, and invasion, to evaluate the inhibitory effects of Calpeptin on PCCs and PSCs. Quantitative RT-PCR indicated that PCCs and PSCs expressed calpain-2 mRNA. Calpeptin reduced tumor volume (P = 0.0473) and tumor weight (P = 0.0471) and inhibited the tumor desmoplastic reaction (P < 0.001) in xenograft tumors in nude mice. Calpeptin also inhibited the biologic functions of PCCs and PSCs including proliferation (P = 0.017), migration (P = 0.027), and invasion (P = 0.035) in vitro. Furthermore, Calpeptin reduced the migration of PCCs and PSCs by disrupting the cancer-stromal interaction (P = 0.0002). Our findings indicate that Calpeptin is a promising antitumor agent for pancreatic cancer, due not only to its suppressive effect on PCCs and PSCs but also its disruption of the cancer-stromal interaction.
Evidence for a calpeptin-sensitive protein-tyrosine phosphatase upstream of the small GTPase Rho. A novel role for the calpain inhibitor calpeptin in the inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatases.[Pubmed:10318859]
J Biol Chem. 1999 May 14;274(20):14359-67.
Activation of the thiol protease calpain results in proteolysis of focal adhesion-associated proteins and severing of cytoskeletal-integrin links. We employed a commonly used inhibitor of calpain, Calpeptin, to examine a role for this protease in the reorganization of the cytoskeleton under a variety of conditions. Calpeptin induced stress fiber formation in both forskolin-treated REF-52 fibroblasts and serum-starved Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Surprisingly, Calpeptin was the only calpain inhibitor of several tested with the ability to induce these effects, suggesting that Calpeptin may act on targets besides calpain. Here we show that Calpeptin inhibits tyrosine phosphatases, enhancing tyrosine phosphorylation particularly of paxillin. Calpeptin preferentially inhibits membrane-associated phosphatase activity. Consistent with this observation, in vitro phosphatase assays using purified glutathione S-transferase fusion proteins demonstrated a preference for the transmembrane protein-tyrosine phosphatase-alpha over the cytosolic protein-tyrosine phosphatase-1B. Furthermore, unlike wide spectrum inhibitors of tyrosine phosphatases such as pervanadate, Calpeptin appeared to inhibit a subset of phosphatases. Calpeptin-induced assembly of stress fibers was inhibited by botulinum toxin C3, indicating that Calpeptin is acting on a phosphatase upstream of the small GTPase Rho, a protein that controls stress fiber and focal adhesion assembly. Not only does this work reveal that Calpeptin is an inhibitor of protein-tyrosine phosphatases, but it suggests that Calpeptin will be a valuable tool to identify the phosphatase activity upstream of Rho.
Cell-penetrating inhibitors of calpain.[Pubmed:1877091]
Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):150-3.
Inhibitors of the calcium-dependent cysteine protease calpain are described that are new analogs of the naturally-occurring compounds E-64 and leupeptin. These new derivatives, unlike the parent compounds, can inhibit calpain within cells. Their lack of charged groups probably accounts for this improved membrane permeability. These new inhibitors are proving useful in exploration of the role of calpain in many cellular processes, including platelet activation.
Inhibitory effect of di- and tripeptidyl aldehydes on calpains and cathepsins.[Pubmed:2079636]
J Enzyme Inhib. 1990;3(3):195-201.
Eight different di- and tripeptidyl aldehyde derivatives, each having at its C-terminus an aldehyde analog of L-norleucine, L-methionine, or L-phenylalanine with a preceding L-leucine residue, were synthesized and tested for their inhibitory effects on several serine and cysteine endopeptidases. These compounds showed almost no inhibition of trypsin, and only weak inhibition of alpha-chymotrypsin and cathepsin H, while they exhibited marked inhibition of cathepsin B less than calpain II congruent to calpain I less than cathepsin L, being stronger in this order. The mode of inhibition of these cysteine proteinases was competitive for the peptide substrate used and inhibitor constants (Ki) were calculated from the Dixon plot. The best inhibitors found were: 4-phenyl-butyryl-Leu-Met-H for calpain I (Ki, 36 nM) and calpain II (Ki, 50 nM); acetyl-Leu-Leu-nLeu-H for cathepsin L (Ki, 0.5 nM); acetyl-Leu-Leu-Met-H for cathepsin B (Ki, 100 nM).
Synthesis of a new cell penetrating calpain inhibitor (calpeptin).[Pubmed:2839170]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jun 30;153(3):1201-8.
N-terminal of Leu-norleucinal or Leu-methioninal was modified to obtain a cell penetrative peptide inhibitor against calpain. Benzyloxycarbonyl (Z) derivatives had less active against papain than phenylbutyryl derivatives and leupeptin. Z-Leu-nLeu-H (Calpeptin) was more sensitive to calpain I than Z-Leu-Met-H and leupeptin. Calpeptin was most potent among synthesized inhibitors in terms of preventing the Ca2+-ionophore induced degradation of actin binding protein and P235 in intact platelets. After 30 min incubation with intact platelets, Calpeptin completely abolished calpain activity in platelets but no effect was observed in case of leupeptin. Calpeptin also inhibited 20K phosphorylation in platelets stimulated by thrombin, ionomycin or collagen. Thus Calpeptin was found to be a useful cell-penetrative calpain inhibitor.


