PukateineCAS# 81-67-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

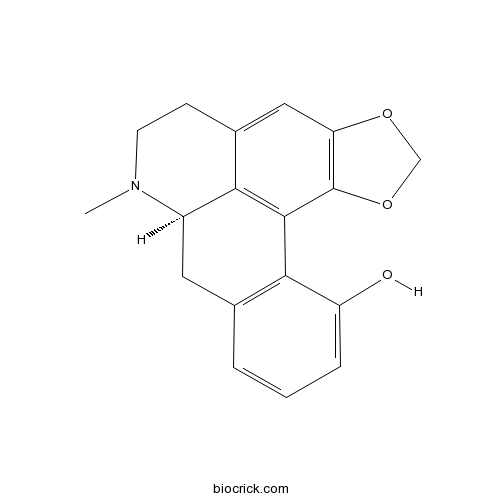
| Cas No. | 81-67-4 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442340 | Appearance | Brown powder |
| Formula | C18H17NO3 | M.Wt | 295.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (12R)-11-methyl-3,5-dioxa-11-azapentacyclo[10.7.1.02,6.08,20.014,19]icosa-1(20),2(6),7,14(19),15,17-hexaen-18-ol | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=CC3=C(C4=C2C1CC5=C4C(=CC=C5)O)OCO3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | IKMXUUHNYQWZBC-GFCCVEGCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H17NO3/c1-19-6-5-11-8-14-18(22-9-21-14)17-15(11)12(19)7-10-3-2-4-13(20)16(10)17/h2-4,8,12,20H,5-7,9H2,1H3/t12-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Pukateine Dilution Calculator

Pukateine Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3864 mL | 16.9319 mL | 33.8639 mL | 67.7277 mL | 84.6597 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6773 mL | 3.3864 mL | 6.7728 mL | 13.5455 mL | 16.9319 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3386 mL | 1.6932 mL | 3.3864 mL | 6.7728 mL | 8.466 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0677 mL | 0.3386 mL | 0.6773 mL | 1.3546 mL | 1.6932 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0339 mL | 0.1693 mL | 0.3386 mL | 0.6773 mL | 0.8466 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- 11-Methylforsythide
Catalog No.:BCN9565
CAS No.:159598-00-2
- Adoxoside
Catalog No.:BCN9564
CAS No.:42830-26-2
- 3-O-Methylellagic acid 4-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN9563
CAS No.:639089-97-7
- Quercetin 3,5,3'-trimethyl ether
Catalog No.:BCN9562
CAS No.:13459-09-1
- Aesculioside C
Catalog No.:BCN9561
CAS No.:254896-65-6
- Isoaesculioside D
Catalog No.:BCN9560
CAS No.:1184581-59-6
- Sonderianol
Catalog No.:BCN9559
CAS No.:85563-65-1
- Vanicoside B
Catalog No.:BCN9558
CAS No.:155179-21-8
- Vitisin A
Catalog No.:BCN9557
CAS No.:142449-89-6
- 3-Formylcarbazole
Catalog No.:BCN9556
CAS No.:51761-07-0
- 2,3-Dihydro-6-methylginkgetin
Catalog No.:BCN9555
CAS No.:1013649-09-6
- Acersaponin I
Catalog No.:BCN9554
CAS No.:1257940-29-6
- 3,4,5-Trihydroxyallylbenzene 3,4-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9567
CAS No.:2172431-63-7
- 3,4-Dihydroxyallylbenzene 3,4-di-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9568
CAS No.:454473-97-3
- Myricetin 3,7,3'-trimethyl ether 5'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9569
CAS No.:2170444-56-9
- Hopeaphenol
Catalog No.:BCN9570
CAS No.:388582-37-4
- Isohopeaphenol
Catalog No.:BCN9571
CAS No.:197446-77-8
- 1,7-Bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)hepta-1,4,6-trien-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN9572
CAS No.:149732-52-5
- Taraxinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN9573
CAS No.:75911-33-0
- Harringtonolide
Catalog No.:BCN9574
CAS No.:64761-48-4
- Caryatin
Catalog No.:BCN9575
CAS No.:1486-66-4
- Demethylagrimonolide 6-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN9576
CAS No.:1257408-55-1
- Momordicin IV
Catalog No.:BCN9577
CAS No.:894412-35-2
- Taikuguasin D
Catalog No.:BCN9578
CAS No.:1627163-80-7
Vascular activity of (-)-anonaine, (-)-roemerine and (-)-pukateine, three natural 6a(R)-1,2-methylenedioxyaporphines with different affinities for alpha1-adrenoceptor subtypes.[Pubmed:15254852]
Planta Med. 2004 Jul;70(7):603-9.
We have studied the mechanism of action of three 6a( R)-1,2-methylenedioxyaporphines as vasorelaxant compounds. The alkaloids assayed showed different affinities for the three human cloned alpha (1)-adrenoceptor (AR) subtypes stably expressed in rat-1 fibroblasts, showing lower affinity for alpha(1B)-AR with regard to the alpha(1A)- or alpha(1D)-subtypes. These three natural compounds are more potent inhibitors of [ (3)H]-prazosin binding than of [ (3)H]-diltiazem binding to rat cerebral cortical membranes. As all these alkaloids inhibited noradrenaline (NA)-induced [ (3)H]-inositol phosphate formation in cerebral cortex and rat tail artery, they may be safely viewed as alpha (1)-AR antagonists, as is demonstrated by the vasorelaxant responses observed in isolated rat tail artery and/or aorta precontracted with NA. The alkaloids also inhibited the contractile response evoked by KCl (80 mM) but with a lower potency than that shown against NA-induced contraction. We have also examined their ability to inhibit the different forms of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases (PDE) isolated from bovine aortic smooth muscle and endothelial cells, with negative results. We conclude that N-methylation favours the interaction of (R)-aporphines with all alpha (1)-AR subtypes, and that the topography of the binding site recognizing the basic or protonated nitrogen atom is similar in all three alpha (1)-AR subtypes. The presence of a hydroxy group at C-11 has different effects on the affinity for each alpha (1)-AR subtype but decreases the affinity for Ca (2+) channels. These results confirm and extend the view that subtle changes in the hydroxylation patterns on the aromatic ring of the aporphine structure affect the interactions of these compounds with the three alpha (1)-AR subtypes in different ways, suggesting that the binding site recognizing the aporphine skeleton is different in each of the three subtypes.
Dopaminergic pharmacology and antioxidant properties of pukateine, a natural product lead for the design of agents increasing dopamine neurotransmission.[Pubmed:10211594]
Gen Pharmacol. 1999 Mar;32(3):373-9.
The dopaminergic and antioxidant properties of Pukateine [(R)-11-hydroxy-1,2-methylenedioxyaporphine, PUK], a natural aporphine derivative, were analyzed in the rat central nervous system. At dopamine (DA) D1 ([3H]-SCH 23390) and D2 ([3H]-raclopride) binding sites, PUK showed IC50 values in the submicromolar range (0.4 and 0.6 microM, respectively). When the uptake of tritiated dopamine was assayed by using a synaptosomal preparation, PUK showed an IC50 = 46 microM. In 6-hydroxydopamine unilaterally denervated rats, PUK (8 mg/kg but not 4 mg/kg) elicited a significant contralateral circling, a behavior classically associated with a dopaminergic agonist action. When perfused through a microdialysis probe inserted into the striatum, PUK (340 microM) induced a significant increase in dopamine levels. In vitro experiments with a crude rat brain mitochondrial suspension showed that PUK did not affect monoamine oxidase activities, at concentrations as high as 100 microM. PUK potently (IC50 = 15 microM) and dose-dependently inhibited the basal lipid peroxidation of a rat brain membrane preparation. As a whole, PUK showed a unique profile of action, comprising an increase in extracellular DA, an agonist-like interaction with DA receptors, and antioxidant activity. Thus, PUK may be taken as a lead compound for the development of novel therapeutic strategies for Parkinson disease.
Structure elucidation of norlaureline and puterine, new noraporphine alkaloids from Guatteria elata.[Pubmed:927039]
Lloydia. 1977 Sep-Oct;40(5):505-7.
The structures of norlaureline (1) and puterine (4), new noraporphine alkaloids isolated from Guatteria elata (Annonaceae), were established by interpretation of the optical rotation, uv, ir, pmr, and mass spectral data of their N-acetyl derivatives. Proposed structures were confirmed by transformation of 1 and 4 to laureline (3) and Pukateine methyl ether (6), respectively.


