Pyridone 6Pan-JAK inhibitor CAS# 457081-03-7 |
- ZM 39923 HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2203
CAS No.:1021868-92-7
- CYT387 sulfate salt
Catalog No.:BCC1506
CAS No.:1056636-06-6
- NVP-BSK805
Catalog No.:BCC1815
CAS No.:1092499-93-8
- Tofacitinib (CP-690550) Citrate
Catalog No.:BCC2189
CAS No.:540737-29-9
- AZD1480
Catalog No.:BCC2191
CAS No.:935666-88-9
- XL019
Catalog No.:BCC2057
CAS No.:945755-56-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 457081-03-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5494425 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H16FN3O | M.Wt | 309.34 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | CMP 6; JAK Inhibitor | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (323.27 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
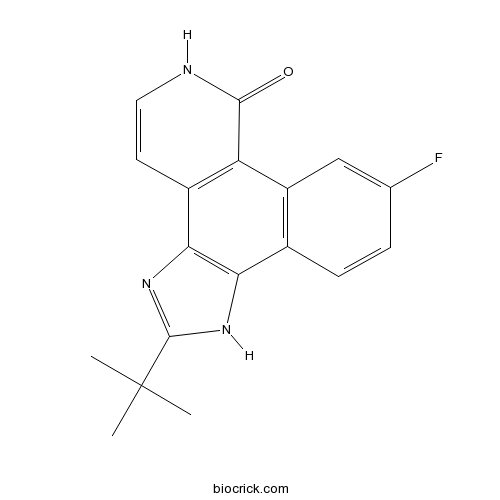
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)C1=NC2=C(N1)C3=C(C=C(C=C3)F)C4=C2C=CNC4=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VNDWQCSOSCCWIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16FN3O/c1-18(2,3)17-21-14-10-5-4-9(19)8-12(10)13-11(15(14)22-17)6-7-20-16(13)23/h4-8H,1-3H3,(H,20,23)(H,21,22) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Pyridone 6 is a pan-JAK inhibitor, which potently inhibits the JAK kinase family, with IC50s of 1 nM for JAK2 and TYK2, 5 nM for JAK3, and 15 nM for JAK1, while displaying significantly weaker affinities (130 nM to >10 mM) for other protein tyrosine kinases.In Vitro:Pyridone 6 is tested as an inhibitor of 21 other protein kinases; Pyridone 6 inhibits these kinases with IC50s ranging from 130 nM to >10 μM. Pyridone 6 inhibits IL2 driven proliferation of CTLL cells with IC50=0.1 μM and IL4 driven proliferation with IC50=0.052 μM[1]. Pyridone 6 (P6) is shown to inhibit kinase by interacting within the ATP-binding cleft of each JAK. The IC50 of Pyridone 6 is 3 nM for all of these cytokines; this is comparable to the reported IC50s of Pyridone 6 for JAK2, Tyk2, and JAK3. Pyridone 6 strongly inhibits Th2 and modestly inhibits Th1, whereas it enhances Th17 development when present within a certain range of concentrations. Pyridone 6 reduces IFN-γ and IL-13, whereas it enhances IL-17 and IL-22 expression. Pyridone 6 also inhibits both Th1 and Th2 development, whereas it promotes Th17 differentiation from naive T cells when present within a certain range of concentrations[2].In Vivo:Pyridone 6 (P6) delays the onset and reduced the magnitude of skin disease in an AD-like skin-disease model of NC/Nga mice. P6-nano strongly ameliorates atopic dermatitis (AD) in NC/Nga mice, exerting an effect comparable to that of betamethasone ointment, a commonly used drug, which also tested as a positive control. In contrast, empty polylactic acid with glycolic acid (PLGA) nanoparticles (C-nano) seemed to have no effect[2]. References: | |||||

Pyridone 6 Dilution Calculator

Pyridone 6 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.2327 mL | 16.1634 mL | 32.3269 mL | 64.6538 mL | 80.8172 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6465 mL | 3.2327 mL | 6.4654 mL | 12.9308 mL | 16.1634 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3233 mL | 1.6163 mL | 3.2327 mL | 6.4654 mL | 8.0817 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0647 mL | 0.3233 mL | 0.6465 mL | 1.2931 mL | 1.6163 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0323 mL | 0.1616 mL | 0.3233 mL | 0.6465 mL | 0.8082 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Pyridone 6 is a reversible and selective ATP-competitive inhibitor of Janus-activated kinases (JAK) with IC50 value of 1-15 nM [1].
JAK is a tyrosine kinase family that and a component of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway. The combination of cytokine (such as interleukin and interferon) or growth factor (such as GH and EGF) and the associated receptors leads to the dimerization of the receptors. The dimerization triggers the activation (autophosphorylation) of JAK which binds to the receptor. Subsequent phosphorylation of the receptor caused by the activated JAK attracts STAT to bind to the receptor and to be activated by JAK. At last, activated STAT enters the nucleus and regulates gene transcription. It is found that constitutive activation of JAK and STAT can promote abnormal cell proliferation. The inhibition of JAK is believed to be an effective therapy to treat for malignancies.
Pyridone 6 is a potent inhibitor of JAK. It inhibited the activities of JAK1, JAK2, JAK3 and TYK2 with IC50 values of 15 nM, 1 nM, 5 nM and 1 nM, respectively. Pyridone 6 is also a selective JAK inhibitor. It showed IC50 values of more than 130 nM when tested against other kinases [1, 2 and 3].
In B9 cells, treatment of pyridone 6 at concentration of 250 nM significantly decreased the phosphorylation of STAT3 induced by IL-6. Treatment of 1 μM almost completely inhibited the phosphorylation of STAT3. Besides that, Pyridone 6 suppressed cell proliferation with IC50 value of 250 nM. In U266 cells, pyridone 6 treatment caused a modest cell growth reduction and G1 arrest. It is consistent with that the growth of U266 is partially dependent on IL-6 signaling [1].
Pyridone 6 has low water solubility. Due to this, a polylactic acid formulation of pyridone 6 and glycolic acid has been applied in animal model. In mice model of atopic dermatitis, administration of pyridone 6 is found to have therapeutic activity through modifying Th cell differentiation and inhibiting mast cell function [2].
References:
[1]. Pedranzini L, Dechow T, Berishaj M, et al. Pyridone 6, a pan-Janus–activated kinase inhibitor, induces growth inhibition of multiple myeloma cells. Cancer research, 2006, 66(19): 9714-9721.
[2]. Nakagawa R, Yoshida H, Asakawa M, et al. Pyridone 6, a pan-JAK inhibitor, ameliorates allergic skin inflammation of NC/Nga mice via suppression of Th2 and enhancement of Th17. The Journal of Immunology, 2011, 187(9): 4611-4620.
[3]. Kwak H B, Kim H S, Lee M S, et al. Pyridone 6, A Pan-Janus-Activated Kinase Inhibitor, Suppresses Osteoclast Formation and Bone Resorption through Down-Regulation of Receptor Activator of Nuclear Factor-. KAPPA. B (NF-. KAPPA. B) Ligand (RANKL)-Induced c-Fos and Nuclear Factor of Activated T Cells (NFAT) c1 Expression. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2009, 32(1): 45-50.
- 1alpha, 24, 25-Trihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1298
CAS No.:457048-34-9
- 5-O-Methylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN7714
CAS No.:4569-98-6
- 3-Benzyl-5-(2-hydroxyethyl)-4-methylthiazolium chloride
Catalog No.:BCC8625
CAS No.:4568-71-2
- Neocnidilide
Catalog No.:BCN8174
CAS No.:4567-33-3
- H-Glu(OBzl)-OBzl.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2927
CAS No.:4561-10-8
- Zaurategrast
Catalog No.:BCC2070
CAS No.:455264-31-0
- Isovouacapenol C
Catalog No.:BCN6557
CAS No.:455255-15-9
- 4-Benzoyl-3-methyl-1-phenyl-5-pyrazolone
Catalog No.:BCC8695
CAS No.:4551-69-3
- Grossamide K
Catalog No.:BCC4547
CAS No.:
- Corosolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5503
CAS No.:4547-24-4
- Acetophenone tosylhydrazone
Catalog No.:BCC8804
CAS No.:4545-21-5
- kobe2602
Catalog No.:BCC5291
CAS No.:454453-49-7
- PA 452
Catalog No.:BCC8005
CAS No.:457657-34-0
- BMS 470539 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7850
CAS No.:457893-92-4
-
Scutebarbatine L
Catalog No.:BCN8369
CAS No.:960302-91-4
- Curcumin
Catalog No.:BCN5504
CAS No.:458-37-7
- Ilicic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5505
CAS No.:4586-68-9
- Boc-Asn-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3072
CAS No.:4587-33-1
- SW033291
Catalog No.:BCC3981
CAS No.:459147-39-8
- JNJ-7777120
Catalog No.:BCC4543
CAS No.:459168-41-3
- SB 452533
Catalog No.:BCC7620
CAS No.:459429-39-1
- Obeticholic Acid
Catalog No.:BCC5572
CAS No.:459789-99-2
- PEAQX
Catalog No.:BCC5495
CAS No.:459836-30-7
- 5-[(2R)-2-Aminopropyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-[3-(phenylmethoxy)propyl]-1H-indole-7-carbonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN1438
CAS No.:459868-73-6
Alkali metal complexes of 6-methyl-2-pyridone: simple formulae, but not so simple structures.[Pubmed:24253086]
Acta Crystallogr B Struct Sci Cryst Eng Mater. 2013 Dec;69(Pt 6):603-12.
Reaction of 6-methyl-2-pyridone (Hmhp) with Na or K metal, or with Rb or Cs 2-ethylhexoxide, in an appropriate single or mixed solvent, yields a series of solvated polymeric complexes with the empirical formulae M(mhp)(H2O)2 [(1), M = Na; (2), M = K], M(mhp)(H2O) [(3), M = Rb; (4), M = Cs] and Cs(mhp)(ROH) [(5), R = Me; (6), R = Et]. All of the products have been crystallographically characterized and show sheet polymeric structures, except for a double-chain structure for (2). In all of the structures, mhp(-) and solvent molecules function as bridging ligands; two metal ions are bridged (mu2) by each solvent molecule in (1), (5) and (6), while (2) contains both mu2 and mu3 triple bridges, and (3) and (4) display highly unusual mu4 quadruple bridging of metal ions by water molecules. The pyridonate O atom bridges two or three metal ions in each case. Nitrogen is also involved in coordination to the heavier metals; it bonds to a single ion in (3) and (4), but has an almost unprecedented bridging role in (5) and (6). As a result of the extensive bridging by ligands, coordination numbers between 6 and 8 are achieved for the metal ions. In each structure, all solvent OH groups form hydrogen bonds to pyridonate O and, in some cases, N atoms. With one exception, these are the first reported pyridonate complexes of the alkali metals Na-Cs that do not also include transition metals.
Crystal structure of 2,6-dimethyl-4-pyridone hemihydrate.[Pubmed:26396782]
Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2015 Jul 4;71(Pt 8):o533.
The title compound (systematic name: 2,6-dimethyl-1H-pyridin-4-one hemihydrate), C7H9NO.0.5H2O, has a single planar mol-ecule in the asymmetric unit with the non-H atoms possessing a mean deviation from planarity of 0.021 A. There is also half of a water mol-ecule present in the asymmetric unit. In the crystal, infinite (001) sheets are formed by N-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO and O-Hcdots, three dots, centeredO hydrogen bonds.
3-Cyano-6-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pyridone: two new pseudopolymorphs and two cocrystals with products of an in situ nucleophilic aromatic substitution.[Pubmed:25567570]
Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2015 Jan;71(Pt 1):19-25.
Four crystal structures of 3-cyano-6-hydroxy-4-methyl-2-pyridone (CMP), viz. the dimethyl sulfoxide monosolvate, C7H6N2O2.C2H6OS, (1), the N,N-dimethylacetamide monosolvate, C7H6N2O2.C4H9NO, (2), a cocrystal with 2-amino-4-dimethylamino-6-methylpyrimidine (as the salt 2-amino-4-dimethylamino-6-methylpyrimidin-1-ium 5-cyano-4-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridin-2-olate), C7H13N4(+).C7H5N2O2(-), (3), and a cocrystal with N,N-dimethylacetamide and 4,6-diamino-2-dimethylamino-1,3,5-triazine [as the solvated salt 2,6-diamino-4-dimethylamino-1,3,5-triazin-1-ium 5-cyano-4-methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridin-2-olate-N,N-dimethylacetamide (1/1)], C5H11N6(+).C7H5N2O2(-).C4H9NO, (4), are reported. Solvates (1) and (2) both contain the hydroxy group in a para position with respect to the cyano group of CMP, acting as a hydrogen-bond donor and leading to rather similar packing motifs. In cocrystals (3) and (4), hydrolysis of the solvent molecules occurs and an in situ nucleophilic aromatic substitution of a Cl atom with a dimethylamino group has taken place. Within all four structures, an R2(2)(8) N-H...O hydrogen-bonding pattern is observed, connecting the CMP molecules, but the pattern differs depending on which O atom participates in the motif, either the ortho or para O atom with respect to the cyano group. Solvents and coformers are attached to these arrangements via single-point O-H...O interactions in (1) and (2) or by additional R4(4)(16) hydrogen-bonding patterns in (3) and (4). Since the in situ nucleophilic aromatic substitution of the coformers occurs, the possible Watson-Crick C-G base-pair-like arrangement is inhibited, yet the cyano group of the CMP molecules participates in hydrogen bonds with their coformers, influencing the crystal packing to form chains.
Revisiting dimerization of acetoacetamide leading to 4,6-dimethyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide.[Pubmed:25099910]
J Oleo Sci. 2014;63(9):939-42. Epub 2014 Aug 5.
A commercially purchased acetoacetamide was found to dimerize during storage for several months to afford 4,6-dimethyl-2-pyridone-5-carboxamide. We successfully achieved the quantitative dimerization of acetoacetamide by using an acid catalyst. It was also found that the pyridone formed served as a self-catalyst of the dimerization.


