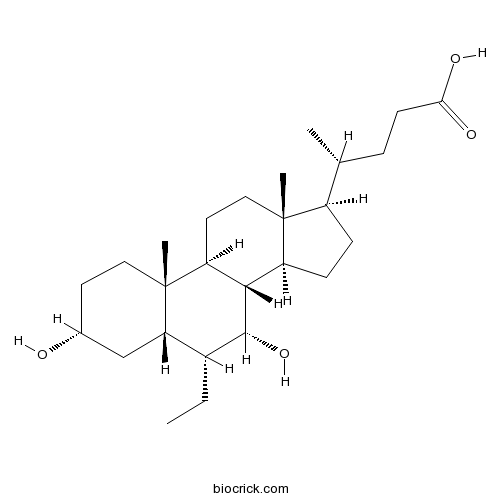
Obeticholic AcidFXR agonist with anticholeretic activity CAS# 459789-99-2 |
- GW4064
Catalog No.:BCC4500
CAS No.:278779-30-9
- Chenodeoxycholic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2620
CAS No.:474-25-9
- XL335
Catalog No.:BCC4501
CAS No.:629664-81-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 459789-99-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 447715 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H44O4 | M.Wt | 420.63 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Obeticholic acid; 6-ECDCA; 6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic acid | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (237.74 mM) Ethanol : ≥ 50 mg/mL (118.87 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4R)-4-[(3R,5S,6R,7R,8S,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CCC1C2CC(CCC2(C3CCC4(C(C3C1O)CCC4C(C)CCC(=O)O)C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ZXERDUOLZKYMJM-ZWECCWDJSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H44O4/c1-5-17-21-14-16(27)10-12-26(21,4)20-11-13-25(3)18(15(2)6-9-22(28)29)7-8-19(25)23(20)24(17)30/h15-21,23-24,27,30H,5-14H2,1-4H3,(H,28,29)/t15-,16-,17-,18-,19+,20+,21+,23+,24-,25-,26-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | INT-747 is a potent and selective FXR agonist (EC50=99 nM) endowed with anticholestatic activity.In Vitro:6-ECDCA increases the expression of FXR-regulated genes in rat hepatocytes[1]. INT-747 reduces expression of liver JNK-1 and JNK-2[2]. INT-747 (256 μg/mL) shows complete inhibition of bacterial growth in all strains tested. Intestinal permeability remains unaffected after INT-747-addition to an IFN-γ-exposed intestinal epithelium of Caco-2 cells[3].In Vivo:6-ECDCA (10 mg/kg/day) completely reverted cholestasis induced by E217α. Administration of 6-ECDCA partially prevents the impairment in total bile acid output caused by E217α by increasing the relative abundance of β-MCA and TCDCA and TDCA[1]. INT-747 (10 mg/kg) and HS increases the pulmonary congestion in the animals.INT-747 does not improve renal pathology in the HS-fed animals[2]. INT-747 (5 mg/kg) significantly increases survival in BDL rats. INT-747-treated BDL rats exhibits a significant selective ileal increase in expression of pore-closing claudin-1. Ileal expression of ZO-1 is significantly up-regulated in INT-747-treated BDL rats[3]. References: | |||||
| Cell experiment [1]: | |
| Cell lines | Rat hepatocytes |
| Preparation method | Limited solubility. General tips for obtaining a higher concentration: Please warm the tube at 37 ℃ for 10 minutes and/or shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while. Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. |
| Reacting condition | 24 h |
| Applications | In rat hepatocytes, obeticholic acid transactivates FXR and modulates FXR regulated genes, resulting in increases of Shp and bsep mRNA expression by 3- to 5-fold and reduction of cyp7a1, cyp8b1, and ntcp mRNA expression by 50 to 70% after exposure to FXR ligands. |
| Animal experiment [2]: | |
| Animal models | Male Wistar rats weighing 200-250 g |
| Dosage form | 30 mg/kg |
| Preparation method | Dissolved in 0.75-1.0 mL of freshly prepared methylcellulose (1%) |
| Application | Obeticholic acid can reactivate downstream FXR signaling pathway and reduces PP in the TAA and BDL (thioacetamide (TAA)-intoxicated and bile-duct–ligated) models without systemic hemodynamic impact. It also restores endothelial function and reduces the total IHVR in experimental cirrhosis |
| Other notes | Please test the solubility of all compounds indoor, and the actual solubility may slightly differ with the theoretical value. This is caused by an experimental system error and it is normal. |
| References: 1. Fiorucci S, Clerici C, Antonelli E et al. Protective effects of 6-ethyl chenodeoxycholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor ligand, in estrogen-induced cholestasis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005 May;313(2):604-12. Epub 2005 Jan 11. 2. Verbeke L, Farre R, Trebicka J et al. Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology. 2014 Jun;59(6):2286-98. | |

Obeticholic Acid Dilution Calculator

Obeticholic Acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3774 mL | 11.8869 mL | 23.7739 mL | 47.5477 mL | 59.4347 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4755 mL | 2.3774 mL | 4.7548 mL | 9.5095 mL | 11.8869 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2377 mL | 1.1887 mL | 2.3774 mL | 4.7548 mL | 5.9435 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0475 mL | 0.2377 mL | 0.4755 mL | 0.951 mL | 1.1887 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0238 mL | 0.1189 mL | 0.2377 mL | 0.4755 mL | 0.5943 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Obeticholic Acid (6alpha-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid, 6-ECDCA, INT-747) is a potent and selective agonist of FXR with EC50 value of 99 nM [1].
The farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a nuclear bile acid receptor involved in bile acid homeostasis, liver fibrosis, hepatic and intestinal inflammation and cardiovascular disease [2].
Obeticholic Acid is a potent and selective FXR agonist with anticholeretic activity [1]. Obeticholic Acid is a semisynthetic bile acid derivative and potent FXR ligand. In estrogen-induced cholestasis rats, 6-ECDCA protected against cholestasis induced by 17α-ethynylestradiol (E217α) [2]. In cirrhotic portal hypertension (PHT) rat models, INT-747 (30 mg/kg) reactivated the FXR downstream signaling pathway and reduced portal pressure by lowering total intrahepatic vascular resistance (IHVR) without deleterious systemic hypotension. This effect was associated with an increased eNOS activity [3]. In the Dahl rat model of salt-sensitive hypertension and insulin-resistance (IR), high salt (HS) diet significantly increased systemic blood pressure and downregulated tissue DDAH expression. INT-747 enhanced insulin sensitivity and inhibited the decrease of DDAH expression [4].
References:
[1]. Pellicciari R, Fiorucci S, Camaioni E, et al. 6alpha-ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA), a potent and selective FXR agonist endowed with anticholestatic activity. J Med Chem, 2002, 45(17): 3569-3572.
[2]. Fiorucci S, Clerici C, Antonelli E, et al. Protective effects of 6-ethyl chenodeoxycholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor ligand, in estrogen-induced cholestasis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 2005, 313(2): 604-612.
[3]. Verbeke L, Farre R, Trebicka J, et al. Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology, 2014, 59(6): 2286-2298.
[4]. Ghebremariam YT, Yamada K, Lee JC, et al. FXR agonist INT-747 upregulates DDAH expression and enhances insulin sensitivity in high-salt fed Dahl rats. PLoS One, 2013, 8(4): e60653.
- SB 452533
Catalog No.:BCC7620
CAS No.:459429-39-1
- JNJ-7777120
Catalog No.:BCC4543
CAS No.:459168-41-3
- SW033291
Catalog No.:BCC3981
CAS No.:459147-39-8
- Boc-Asn-ONp
Catalog No.:BCC3072
CAS No.:4587-33-1
- Ilicic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5505
CAS No.:4586-68-9
- Curcumin
Catalog No.:BCN5504
CAS No.:458-37-7
-
Scutebarbatine L
Catalog No.:BCN8369
CAS No.:960302-91-4
- BMS 470539 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7850
CAS No.:457893-92-4
- PA 452
Catalog No.:BCC8005
CAS No.:457657-34-0
- Pyridone 6
Catalog No.:BCC1874
CAS No.:457081-03-7
- 1alpha, 24, 25-Trihydroxy VD2
Catalog No.:BCC1298
CAS No.:457048-34-9
- 5-O-Methylgenistein
Catalog No.:BCN7714
CAS No.:4569-98-6
- PEAQX
Catalog No.:BCC5495
CAS No.:459836-30-7
- 5-[(2R)-2-Aminopropyl]-2,3-dihydro-1-[3-(phenylmethoxy)propyl]-1H-indole-7-carbonitrile
Catalog No.:BCN1438
CAS No.:459868-73-6
- Rucaparib (AG-014699,PF-01367338)
Catalog No.:BCC2207
CAS No.:459868-92-9
- Interiotherin C
Catalog No.:BCN3636
CAS No.:460090-65-7
- Larixyl acetate
Catalog No.:BCC8195
CAS No.:4608-49-5
- Eact
Catalog No.:BCC6313
CAS No.:461000-66-8
- Ko 143
Catalog No.:BCC1684
CAS No.:461054-93-3
- Dapagliflozin
Catalog No.:BCC2552
CAS No.:461432-26-8
- 4beta,12-dihydroxyguaian-6,10-diene
Catalog No.:BCN7829
CAS No.:461644-90-6
- Lactulose
Catalog No.:BCC4669
CAS No.:4618-18-2
- Gnemonol B
Catalog No.:BCN3399
CAS No.:462636-74-4
- alpha-Linolenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8319
CAS No.:463-40-1
Anti-fibrotic effects of chronic treatment with the selective FXR agonist obeticholic acid in the bleomycin-induced rat model of pulmonary fibrosis.[Pubmed:28115235]
J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2017 Apr;168:26-37.
Farnesoid X receptor (FXR) activation by Obeticholic Acid (OCA) has been demonstrated to inhibit inflammation and fibrosis development in liver, kidney and intestine in multiple disease models. FXR activation has also been demonstrated to suppress the inflammatory response and to promote lung repair after lung injury. This study investigated the protective effects of OCA treatment (3 or 10mg/kg/day) on inflammation, tissue remodeling and fibrosis in the bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis rat model. Effects of OCA treatment on morphological and molecular alterations of the lung, as well as remodeling of the alveoli and the right ventricle were also evaluated. Lung function was assessed by measuring airway resistance to inflation. In the acute phase (7days), bleomycin promoted an initial thickening and fibrosis of the lung interstitium, with upregulation of genes related to epithelial proliferation, tissue remodeling and hypoxia. At 28days, an evident increase in the deposition of collagen in the lungs was observed. This excessive deposition was accompanied by an upregulation of transcripts related to the extracellular matrix (TGFbeta1, SNAI1 and SNAI2), indicating lung fibrosis. Administration of OCA protected against bleomycin-induced lung damage by suppressing molecular mechanisms related to epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), inflammation and collagen deposition, with a dose-dependent reduction of proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-1beta and IL-6, as well as TGF-beta1 and SNAI1 expression. Pirfenidone, a recently approved treatment for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), significantly counteracted bleomycin-induced pro-fibrotic genes expression, but did not exert significant effects on IL-1beta and IL-6. OCA treatment in bleomycin-challenged rats also improved pulmonary function, by effectively normalizing airway resistance to inflation and lung stiffness in vivo. Results with OCA were similar, or even superior, to those obtained with pirfenidone. In conclusion, our results suggest an important protective effect of OCA against bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis by blunting critical mediators in the pathogenesis of IPF.
Effect of obeticholic acid on liver regeneration following portal vein embolization in an experimental model.[Pubmed:28195307]
Br J Surg. 2017 Apr;104(5):590-599.
BACKGROUND: The bile salt-activated transcription factor farnesoid X receptor (FXR) is a key mediator of proliferative bile salt signalling, which is assumed to play a role in the early phase of compensatory liver growth. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of a potent FXR agonist (Obeticholic Acid, OCA) on liver growth following portal vein embolization (PVE). METHODS: Rabbits were allocated to receive daily oral gavage with OCA (10 mg/kg) or vehicle (control group) starting 7 days before PVE (n = 18 per group), and continued until 7 days after PVE. PVE of the cranial liver lobes was performed using polyvinyl alcohol particles and coils on day 0. Caudal liver volume (CLV) was analysed by CT volumetry on days -7, -1, +3 and +7. Liver function was determined by measuring mebrofenin uptake using hepatobiliary scintigraphy. Additional parameters analysed were plasma aminotransferase levels, and histological scoring of haematoxylin and eosin- and Ki-67-stained liver sections. RESULTS: Three days after PVE of the cranial lobes, the increase in CLV was 2.2-fold greater in the OCA group than in controls (mean(s.d.) 56.1(20.3) versus 26.1(15.4) per cent respectively; P < 0.001). This increase remained greater 7 days after PVE (+1.5-fold; P = 0.020). The increase in caudal liver function at day +3 was greater in OCA-treated animals (+1.2-fold; P = 0.017). The number of Ki-67-positive hepatocytes was 1.6-fold higher in OCA-treated animals 3 days after PVE (P = 0.045). Plasma aminotransferase levels and histology did not differ significantly between groups. CONCLUSION: OCA accelerated liver regeneration after PVE in a rabbit model. OCA treatment might increase the efficacy of PVE and, thereby, resectability. Surgical relevance Liver failure is the most feared complication after liver surgery, with no effective treatment options. Liver regeneration is essential to avoid liver failure, and recently bile acid signalling was implicated in the initiation of liver regeneration through the nuclear bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor (FXR). In this study, the potent FXR agonist Obeticholic Acid accelerated liver regeneration following portal vein embolization in a rabbit model, in terms of liver volume, liver function and proliferation. Obeticholic Acid treatment could enhance the efficacy of portal vein embolization, thereby increasing resectability, and could reduce the interval to surgery. In addition, Obeticholic Acid might have a place in the prevention of liver failure after liver surgery.


