ReticulineCAS# 485-19-8 |
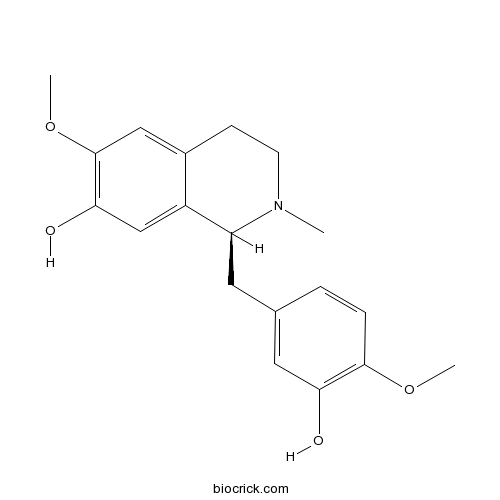
- (R)-Reticuline
Catalog No.:BCN6795
CAS No.:3968-19-2
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 485-19-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 439653 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H23NO4 | M.Wt | 329.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (1S)-1-[(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]-6-methoxy-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isoquinolin-7-ol | ||
| SMILES | CN1CCC2=CC(=C(C=C2C1CC3=CC(=C(C=C3)OC)O)O)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BHLYRWXGMIUIHG-HNNXBMFYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H23NO4/c1-20-7-6-13-10-19(24-3)17(22)11-14(13)15(20)8-12-4-5-18(23-2)16(21)9-12/h4-5,9-11,15,21-22H,6-8H2,1-3H3/t15-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Reticuline is a key compound in the biosynthetic pathway for isoquinoline alkaloids in plants, which include morphine, codeine and berberine. Reticuline possesses potent central nervous system depressant action, it (50-100 mg/kg i.p.) can produce alteration of behaviour pattern, prolongation of pentobarbital-induced sleep, reduction in motor coordination and D-amphetamine-induced hypermotility and suppression of the conditioned avoidance response. (S)-Reticuline can elicit vasorelaxation probably due to the blockade of the L-type voltage-dependent Ca(2+) current in rat aorta, the effect may contribute to the potential cardioprotective efficacy of (S)-reticuline. |
| Targets | Calcium Channel |
| In vitro | Knockdown of berberine bridge enzyme by RNAi accumulates (S)-reticuline and activates a silent pathway in cultured California poppy cells.[Pubmed: 17103244 ]Transgenic Res. 2007 Jun;16(3):363-75.Reticuline is a key compound in the biosynthetic pathway for isoquinoline alkaloids in plants, which include morphine, codeine and berberine. In vivo and in vitro L-DOPA and reticuline exposure increases ganglionic morphine levels.[Pubmed: 15874894]Med Sci Monit. 2005 May;11(5):MS1-5.Given the presence of morphine, its metabolites and precursors, i.e., Reticuline, in mammalian and invertebrate tissues, it has become imperative to determine if exposing tissues to putative opiate alkaloid and dopamine precursors would result in increasing endogenous morphine levels.
|
| In vivo | Central depressant effects of reticuline extracted from Ocotea duckei in rats and mice.[Pubmed: 9720612]J Ethnopharmacol. 1998 Aug;62(1):57-61.
|
| Kinase Assay | (S)-reticuline induces vasorelaxation through the blockade of L-type Ca(2+) channels.[Pubmed: 18825370]Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;379(2):115-25.In Brazil, various species of the genus Ocotea are used in folk medicine for treating several diseases. The chemical characterization of this plant showed the presence of alkaloids belonging to the benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline family, the major component of which is (S)-Reticuline. |

Reticuline Dilution Calculator

Reticuline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0358 mL | 15.1791 mL | 30.3582 mL | 60.7165 mL | 75.8956 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6072 mL | 3.0358 mL | 6.0716 mL | 12.1433 mL | 15.1791 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3036 mL | 1.5179 mL | 3.0358 mL | 6.0716 mL | 7.5896 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0607 mL | 0.3036 mL | 0.6072 mL | 1.2143 mL | 1.5179 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0304 mL | 0.1518 mL | 0.3036 mL | 0.6072 mL | 0.759 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Aristolochic acid C
Catalog No.:BCN2658
CAS No.:4849-90-5
- N-Nornuciferine
Catalog No.:BCN4048
CAS No.:4846-19-9
- ProTx II
Catalog No.:BCC6103
CAS No.:484598-36-9
- ProTx I
Catalog No.:BCC6255
CAS No.:484598-35-8
- Brucine sulfate
Catalog No.:BCN2460
CAS No.:4845-99-2
- DPH
Catalog No.:BCC1538
CAS No.:484049-04-9
- Okanin
Catalog No.:BCN6475
CAS No.:484-76-4
- Isodictamnine
Catalog No.:BCN7066
CAS No.:484-74-2
- Angiotensin I (human, mouse, rat)
Catalog No.:BCC1004
CAS No.:484-42-4
- Dictamnine
Catalog No.:BCN1273
CAS No.:484-29-7
- Bergapten
Catalog No.:BCN5582
CAS No.:484-20-8
- 9-Phenanthrol
Catalog No.:BCC7989
CAS No.:484-17-3
- Cytisine
Catalog No.:BCN6270
CAS No.:485-35-8
- (+)-Bicuculline
Catalog No.:BCN1238
CAS No.:485-49-4
- Cinchonidine
Catalog No.:BCC5316
CAS No.:485-71-2
- Formononetin
Catalog No.:BCN1061
CAS No.:485-72-3
- Hydrangetin
Catalog No.:BCN7439
CAS No.:485-90-5
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCC8269
CAS No.:104732-07-2
- Proanthocyanidins
Catalog No.:BCN6313
CAS No.:4852-22-6
- Choline sulphate
Catalog No.:BCN1792
CAS No.:4858-96-2
- Mirabijalone D
Catalog No.:BCN4071
CAS No.:485811-84-5
- PMX 464
Catalog No.:BCC6348
CAS No.:485842-97-5
- Isofraxidin
Catalog No.:BCN2327
CAS No.:486-21-5
- Fraxinol
Catalog No.:BCN5584
CAS No.:486-28-2
In vivo and in vitro L-DOPA and reticuline exposure increases ganglionic morphine levels.[Pubmed:15874894]
Med Sci Monit. 2005 May;11(5):MS1-5. Epub 2005 Apr 28.
BACKGROUND: Given the presence of morphine, its metabolites and precursors, i.e., Reticuline, in mammalian and invertebrate tissues, it has become imperative to determine if exposing tissues to putative opiate alkaloid and dopamine precursors would result in increasing endogenous morphine levels. MATERIAL/METHODS: Endogenous morphine levels were determined by high performance liquid chromatography coupled to electrochemical detection and radioimmunoassay, following incubation of Mytilus edulis pedal ganglia with Reticuline or L-DOPA. Injection of L-DOPA or Reticuline into healthy animals was via the foot. RESULTS: Ganglia incubated in vitro with Reticuline or L-DOPA for 1 hour exhibited a concentration and time dependent statistically significant increase in their endogenous morphine levels (5.0 +/- 0.47, 3.6 +/- 0.45 ng/ganglion, respectively). Injection of intact, healthy animals with Reticuline or L-DOPA also results in significantly higher endogenous ganglionic morphine levels. CONCLUSIONS: Taken together, we show that L-DOPA is being converted to morphine, demonstrating that pedal ganglia can synthesize morphine from these putative precursors in vitro and in vivo. This is the first demonstration of morphine being synthesized in a normal, healthy free living animal.
Knockdown of berberine bridge enzyme by RNAi accumulates (S)-reticuline and activates a silent pathway in cultured California poppy cells.[Pubmed:17103244]
Transgenic Res. 2007 Jun;16(3):363-75.
Reticuline is a key compound in the biosynthetic pathway for isoquinoline alkaloids in plants, which include morphine, codeine and berberine. We established cultured California poppy (Eschscholzia californica) cells, in which berberine bridge enzyme (BBE) was knocked down by RNA interference, to accumulate the important key intermediate Reticuline. Both BBE mRNA accumulation and enzyme activity were effectively suppressed in transgenic cells. In these transgenic cells, end-products of isoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis, such as sanguinarine, were considerably reduced and Reticuline was accumulated at a maximum level of 310 mug/g-fresh weight. In addition, 1 g-fresh weight of these cells secreted significant amounts of Reticuline into the medium, with a maximum level of 6 mg/20 mL culture medium. These cells also produced a methylated derivative of Reticuline, laudanine, which could scarcely be detected in control cells. We discuss the potential application of RNAi technology in metabolic modification and the flexibility of plant secondary metabolism.
(S)-reticuline induces vasorelaxation through the blockade of L-type Ca(2+) channels.[Pubmed:18825370]
Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2009 Feb;379(2):115-25.
In Brazil, various species of the genus Ocotea are used in folk medicine for treating several diseases. The chemical characterization of this plant showed the presence of alkaloids belonging to the benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline family, the major component of which is (S)-Reticuline. The present study investigated whether (S)-Reticuline exerts an inhibitory effect on smooth muscle L-type Ca(2+) channels. Tension measurements and patch clamp techniques were utilized to study the effects of (S)-Reticuline. Whole-cell Ca(2+) currents were measured using the A7r5 smooth muscle cell line. (S)-Reticuline antagonized CaCl(2)- and KCl-induced contractions and elicited vasorelaxation. It also reduced the voltage-activated peak amplitude of I (Ca,L) in a concentration-dependent manner. (S)-Reticuline did not change the characteristics of current density vs. voltage relationship. (S)-Reticuline shifted leftwards the steady-state inactivation curve of I (Ca,L). The application of dibutyryl cyclic adenosine monophosphate to the cell decreased the amplitude of Ca(2+) currents. In cells pretreated with forskolin, an adenylate cyclase activator, the addition of (S)-Reticuline caused further inhibition of the Ca(2+) currents suggesting an additive effect. The results obtained show that (S)-Reticuline elicits vasorelaxation probably due to the blockade of the L-type voltage-dependent Ca(2+) current in rat aorta. The reported effect may contribute to the potential cardioprotective efficacy of (S)-Reticuline.
Central depressant effects of reticuline extracted from Ocotea duckei in rats and mice.[Pubmed:9720612]
J Ethnopharmacol. 1998 Aug;62(1):57-61.
Neuropharmacological studies were carried out with Reticuline, a benzylisoquinoline alkaloid, isolated from Ocotea duckei Vattimo. It was found that Reticuline (50-100 mg/kg i.p.) produced alteration of behaviour pattern, prolongation of pentobarbital-induced sleep, reduction in motor coordination and D-amphetamine-induced hypermotility and suppression of the conditioned avoidance response. These observations suggest that Reticuline possesses potent central nervous system depressant action.


