Ro 48-8071 fumarate2,3-Oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC) inhibitor CAS# 189197-69-1 |
- BS-181
Catalog No.:BCC1439
CAS No.:1092443-52-1
- WHI-P180 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4243
CAS No.:153437-55-9
- SNS-032 (BMS-387032)
Catalog No.:BCC1152
CAS No.:345627-80-7
- Dinaciclib (SCH727965)
Catalog No.:BCC3765
CAS No.:779353-01-4
- RGB-286638
Catalog No.:BCC5519
CAS No.:784210-87-3
- AT7519 Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1376
CAS No.:902135-91-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 189197-69-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9959583 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H31BrFNO6 | M.Wt | 564.44 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 55 mg/mL (97.44 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
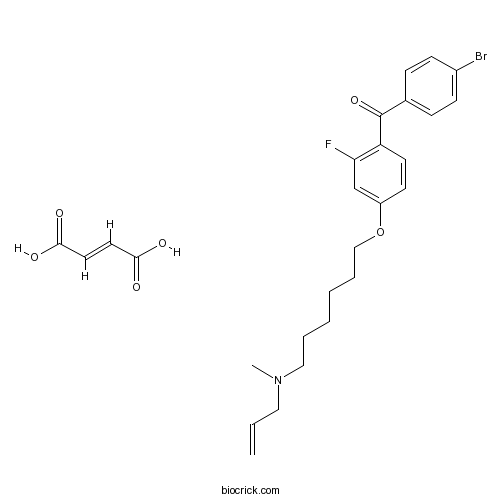
| Chemical Name | (4-bromophenyl)-[2-fluoro-4-[6-[methyl(prop-2-enyl)amino]hexoxy]phenyl]methanone;(E)-but-2-enedioic acid | ||
| SMILES | CN(CCCCCCOC1=CC(=C(C=C1)C(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)Br)F)CC=C.C(=CC(=O)O)C(=O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XCYAYLWZCRGKDS-WLHGVMLRSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27BrFNO2.C4H4O4/c1-3-14-26(2)15-6-4-5-7-16-28-20-12-13-21(22(25)17-20)23(27)18-8-10-19(24)11-9-18;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h3,8-13,17H,1,4-7,14-16H2,2H3;1-2H,(H,5,6)(H,7,8)/b;2-1+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 2,3-Oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC) inhibitor (IC50 = 6.5 nM); blocks cholesterol synthesis in HepG2 cells. Reduces viability of breast cancer cell lines. Also inhibits Ebola virus (EBOV) cell entry (IC50 = 1.74 μM). |

Ro 48-8071 fumarate Dilution Calculator

Ro 48-8071 fumarate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7717 mL | 8.8583 mL | 17.7167 mL | 35.4333 mL | 44.2917 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3543 mL | 1.7717 mL | 3.5433 mL | 7.0867 mL | 8.8583 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1772 mL | 0.8858 mL | 1.7717 mL | 3.5433 mL | 4.4292 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0354 mL | 0.1772 mL | 0.3543 mL | 0.7087 mL | 0.8858 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0177 mL | 0.0886 mL | 0.1772 mL | 0.3543 mL | 0.4429 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ro 48-8071 fumarate is an inhibitor of OSC (Oxidosqualene cyclase) with IC50 of appr 6.5 nM.
In Vitro:In HepG2 cells, Ro 48-8071 reduces cholesterol synthesis dose dependently with an IC50 value of appr 1.5 nM[1]. Ro 48-8071 (10 μM) significantly reduces the viability of PC-3 prostate cancer cells, but not normal prostate cells. Ro 48-8071 (10-30 μM) induces apoptosis of both LNCaP and C4-2 cell lines in a dose-dependent manner. And castration-resistant PC-3 and DU145 cells also demonstrate significant levels of apoptosis following 24-hour treatment with Ro 48-8071. Ro 48-8071 (10-25 μM) reduces AR protein expression in a dose-dependent manner. Ro 48-8071 (0.1-1 μM) increases ERβ protein expression dose-dependently in both hormone-dependent LNCaP and castration-resistant PC-3 cells[2]. Using mammalian cells engineered to express human ERα or ERβ protein, together with an ER-responsive luciferase promoter, Ro 48-8071 dose-dependently inhibits 17β-estradiol (E2)-induced ERα responsive luciferase activity (IC50, appr 10 µM), under conditions that are non-toxic to the cells[3].
In Vivo:Ro 48-8071 lowers LDL-C maximally appr 60% at 150 μmol/kg per day, with no further reduction up to 300 μmol/kg per day, leaving HDL-C unchanged at all doses in hamsters. Ro 48-8071 (≥00 μmol/kg per day) increases the amount of MOS in liver of hamsters. Ro 48-8071 (300 μmol/kg per day) remarkedly and significantly reduces VLDL secretion of hamsters[1]. Ro 48-8071 (5 or 20 mg/kg) significantly reduces in vivo tumor growth in mice, without weight loss of the mice. Furthermore, Ro 48-8071 at a concentration of 20 mg/kg, completely eradicates two of the 12 tumors being monitored in the mice in the timeframe tested[2]. Ro 48-8071 (20 mg/day/kg body weight) leads to a rapid and sustained inhibition (>50%) of cholesterol synthesis in the whole small intestine of BALB/c mice. Sterol synthesis is also reduced in the large intestine and stomach[4].
References:
[1]. Morand OH, et al. Ro 48-8.071, a new 2,3-oxidosqualene:lanosterol cyclase inhibitor lowering plasma cholesterol in hamsters, squirrel monkeys, and minipigs: comparison to simvastatin. J Lipid Res. 1997 Feb;38(2):373-90.
[2]. Liang Y, et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitor RO 48-8071 suppresses growth of hormone-dependent and castration-resistant prostate cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016 May 30;9:3223-32.
[3]. Liang Y, et al. Cholesterol biosynthesis inhibitors as potent novel anti-cancer agents: suppression of hormone-dependent breast cancer by the oxidosqualene cyclase inhibitor RO 48-8071. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jul;146(1):51-62.
[4]. Chuang JC, et al. Sustained and selective suppression of intestinal cholesterol synthesis by Ro 48-8071, an inhibitor of 2,3-oxidosqualene:lanosterol cyclase, in the BALB/c mouse. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Apr 1;88(3):351-63.
- Tegaserod maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7955
CAS No.:189188-57-6
- Naringin dihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN2579
CAS No.:18916-17-1
- 3'-O-Methylmurraol
Catalog No.:BCN7471
CAS No.:1891097-17-8
- Fas C- Terminal Tripeptide
Catalog No.:BCC1019
CAS No.:189109-90-8
- Bruceantinoside C
Catalog No.:BCN1166
CAS No.:112899-35-1
- Salmefamol
Catalog No.:BCC1919
CAS No.:18910-65-1
- Hulupinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN8019
CAS No.:1891-42-5
- Oroselol
Catalog No.:BCN3907
CAS No.:1891-25-4
- [Ala92]-p16 (84-103)
Catalog No.:BCC5837
CAS No.:189064-08-2
- NGB 2904
Catalog No.:BCC7435
CAS No.:189061-11-8
- Corynantheine
Catalog No.:BCN3746
CAS No.:18904-54-6
- 1-(4-Hydroxy-2,2-dimethylchroman-6-yl)ethanone
Catalog No.:BCN7710
CAS No.:1890153-71-5
- Helioxanthin
Catalog No.:BCC5413
CAS No.:18920-47-3
- KU14R
Catalog No.:BCC1685
CAS No.:189224-48-4
- Cleroindicin C
Catalog No.:BCN1167
CAS No.:189264-44-6
- Cleroindicin D
Catalog No.:BCN1168
CAS No.:189264-45-7
- Cleroindicin F
Catalog No.:BCN1169
CAS No.:189264-47-9
- Eucalyptolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3246
CAS No.:189272-68-2
- Delafloxacin
Catalog No.:BCC1522
CAS No.:189279-58-1
- Isotanshinone IIB
Catalog No.:BCN2513
CAS No.:109664-01-9
- N-Caffeoyl-O-methyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCC8216
CAS No.:189307-47-9
- Danshenol A
Catalog No.:BCN3145
CAS No.:189308-08-5
- Danshenol B
Catalog No.:BCN2616
CAS No.:189308-09-6
- Xanthohumol B
Catalog No.:BCN8018
CAS No.:189308-10-9
Multiple cationic amphiphiles induce a Niemann-Pick C phenotype and inhibit Ebola virus entry and infection.[Pubmed:23441171]
PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56265.
Ebola virus (EBOV) is an enveloped RNA virus that causes hemorrhagic fever in humans and non-human primates. Infection requires internalization from the cell surface and trafficking to a late endocytic compartment, where viral fusion occurs, providing a conduit for the viral genome to enter the cytoplasm and initiate replication. In a concurrent study, we identified clomiphene as a potent inhibitor of EBOV entry. Here, we screened eleven inhibitors that target the same biosynthetic pathway as clomiphene. From this screen we identified six compounds, including U18666A, that block EBOV infection (IC(50) 1.6 to 8.0 microM) at a late stage of entry. Intriguingly, all six are cationic amphiphiles that share additional chemical features. U18666A induces phenotypes, including cholesterol accumulation in endosomes, associated with defects in Niemann-Pick C1 protein (NPC1), a late endosomal and lysosomal protein required for EBOV entry. We tested and found that all six EBOV entry inhibitors from our screen induced cholesterol accumulation. We further showed that higher concentrations of cationic amphiphiles are required to inhibit EBOV entry into cells that overexpress NPC1 than parental cells, supporting the contention that they inhibit EBOV entry in an NPC1-dependent manner. A previously reported inhibitor, compound 3.47, inhibits EBOV entry by blocking binding of the EBOV glycoprotein to NPC1. None of the cationic amphiphiles tested had this effect. Hence, multiple cationic amphiphiles (including several FDA approved agents) inhibit EBOV entry in an NPC1-dependent fashion, but by a mechanism distinct from that of compound 3.47. Our findings suggest that there are minimally two ways of perturbing NPC1-dependent pathways that can block EBOV entry, increasing the attractiveness of NPC1 as an anti-filoviral therapeutic target.
An inverse docking approach for identifying new potential anti-cancer targets.[Pubmed:21315634]
J Mol Graph Model. 2011 Apr;29(6):795-9.
Inverse docking is a relatively new technique that has been used to identify potential receptor targets of small molecules. Our docking software package MDock is well suited for such an application as it is both computationally efficient, yet simultaneously shows adequate results in binding affinity predictions and enrichment tests. As a validation study, we present the first stage results of an inverse-docking study which seeks to identify potential direct targets of PRIMA-1. PRIMA-1 is well known for its ability to restore mutant p53's tumor suppressor function, leading to apoptosis in several types of cancer cells. For this reason, we believe that potential direct targets of PRIMA-1 identified in silico should be experimentally screened for their ability to inhibit cancer cell growth. The highest-ranked human protein of our PRIMA-1 docking results is oxidosqualene cyclase (OSC), which is part of the cholesterol synthetic pathway. The results of two followup experiments which treat OSC as a possible anti-cancer target are promising. We show that both PRIMA-1 and Ro 48-8071, a known potent OSC inhibitor, significantly reduce the viability of BT-474 and T47-D breast cancer cells relative to normal mammary cells. In addition, like PRIMA-1, we find that Ro 48-8071 results in increased binding of p53 to DNA in BT-474 cells (which express mutant p53). For the first time, Ro 48-8071 is shown as a potent agent in killing human breast cancer cells. The potential of OSC as a new target for developing anticancer therapies is worth further investigation.
Ro 48-8.071, a new 2,3-oxidosqualene:lanosterol cyclase inhibitor lowering plasma cholesterol in hamsters, squirrel monkeys, and minipigs: comparison to simvastatin.[Pubmed:9162756]
J Lipid Res. 1997 Feb;38(2):373-90.
2,3-Oxidosqualene:lanosterol cyclase (OSC, E.C. 5.4.99.7) represents a unique target for a cholesterol lowering drug. Partial inhibition of OSC should reduce synthesis of lanosterol and subsequent sterols, and also stimulate the production of epoxysterols that repress HMG-CoA reductase expression, generating a synergistic, self-limited negative regulatory loop. Hence, the pharmacological properties of Ro 48-8.071, a new OSC inhibitor, were compared to that of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin. Ro 48-8.071 blocked human liver OSC and cholesterol synthesis in HepG2 cells in the nanomolar range; in cells it triggered the production of monooxidosqualene, dioxidosqualene, and epoxycholesterol. It was safe in hamsters, squirrel monkeys and Gottingen minipigs at pharmacologically active doses, lowering LDL approximately 60% in hamsters, and at least 30% in the two other species, being at least as efficacious as safe doses of simvastatin. The latter was hepatotoxic in hamsters at doses > 30 mumol/kg/day limiting its window of efficacy. Hepatic monooxidosqualene increased dose-dependently after treatment with Ro 48-8.071, up to approximately 20 micrograms/g wet liver or less than 1% of hepatic cholesterol, and it was inversely correlated with LDL levels. Ro 48-8.071 did not reduce coenzyme Q10 levels in liver and heart of hamsters, and importantly did not trigger an overexpression of hepatic HMG-CoA reductase, squalene synthase, and OSC itself. In strong contrast, simvastatin stimulated these enzymes dramatically, and reduced coenzyme Q10 levels in liver and heart. Altogether these findings clearly differentiate the OSC inhibitor Ro 48-8.071 from simvastatin, and support the view that OSC is a distinct key component in the regulation of the cholesterol synthesis pathway.


