DelafloxacinFluoroquinolone antibiotic CAS# 189279-58-1 |
- Azelnidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4400
CAS No.:123524-52-7
- Verapamil HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4747
CAS No.:152-11-4
- Gabapentin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4502
CAS No.:60142-95-2
- Zonisamide sodium
Catalog No.:BCC4240
CAS No.:68291-98-5
- Felodipine
Catalog No.:BCC4402
CAS No.:72509-76-3
- Manidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4404
CAS No.:89226-50-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 189279-58-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 487101 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H12ClF3N4O4 | M.Wt | 440.76 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | RX-3341; WQ-3034; ABT492 | ||
| Solubility | 25℃: DMSO | ||
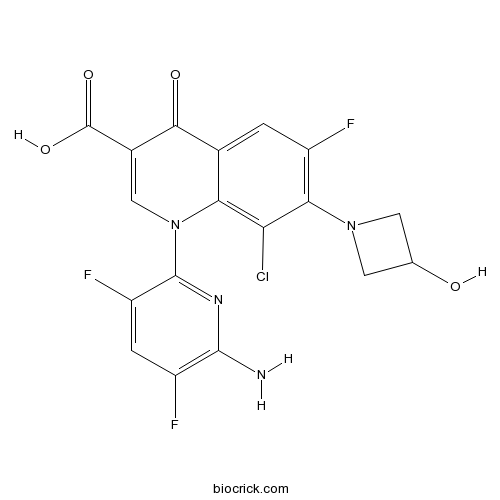
| Chemical Name | 1-(6-amino-3,5-difluoropyridin-2-yl)-8-chloro-6-fluoro-7-(3-hydroxyazetidin-1-yl)-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | C1C(CN1C2=C(C=C3C(=C2Cl)N(C=C(C3=O)C(=O)O)C4=NC(=C(C=C4F)F)N)F)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DYDCPNMLZGFQTM-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H12ClF3N4O4/c19-12-13-7(1-9(20)14(12)25-3-6(27)4-25)15(28)8(18(29)30)5-26(13)17-11(22)2-10(21)16(23)24-17/h1-2,5-6,27H,3-4H2,(H2,23,24)(H,29,30) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Delafloxacin (RX-3341, ABT-492) is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic agent.
IC50 Value: MICs ranging from 0.0078 to 0.125 micro g/ml for levofloxacin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains [1]
Target: Antibacterial
ABT-492 was more potent against quinolone-susceptible and -resistant gram-positive organisms, had activity similar to that of ciprofloxacin against certain members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, and had comparable activity against quinolone-susceptible, nonfermentative, gram-negative organisms.
in vitro: ABT-492 exhibited excellent in vitro activities against all 326 aerobic and anaerobic antral puncture sinus isolates tested with MICs (in micrograms per milliliter) at which 90% of the isolates tested were inhibited as follows: Haemophilus influenzae, 0.001; Moraxella catarrhalis, 0.008; and Streptococcus pneumoniae, 0.015 [2]. ABT-492 was as active as trovafloxacin against Chlamydia trachomatis, indicating good intracellular penetration and antibacterial activity [3].
in vivo:
Clinical trial: N/A References: | |||||

Delafloxacin Dilution Calculator

Delafloxacin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2688 mL | 11.344 mL | 22.6881 mL | 45.3762 mL | 56.7202 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4538 mL | 2.2688 mL | 4.5376 mL | 9.0752 mL | 11.344 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2269 mL | 1.1344 mL | 2.2688 mL | 4.5376 mL | 5.672 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0454 mL | 0.2269 mL | 0.4538 mL | 0.9075 mL | 1.1344 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0227 mL | 0.1134 mL | 0.2269 mL | 0.4538 mL | 0.5672 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Description: IC50 Value: MICs ranging from 0.0078 to 0.125 micro g/ml for levofloxacin-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae strains [1] ABT-492 was more potent against quinolone-susceptible and -resistant gram-positive organisms, had activity similar to that of ciprofloxacin against certain members of the family Enterobacteriaceae, and had comparable activity against quinolone-susceptible, nonfermentative, gram-negative organisms. in vitro: ABT-492 exhibited excellent in vitro activities against all 326 aerobic and anaerobic antral puncture sinus isolates tested with MICs (in micrograms per milliliter) at which 90% of the isolates tested were inhibited as follows: Haemophilus influenzae, 0.001; Moraxella catarrhalis, 0.008; and Streptococcus pneumoniae, 0.015 [2]. ABT-492 was as active as trovafloxacin against Chlamydia trachomatis, indicating good intracellular penetration and antibacterial activity [3]. in vivo: N/A Clinical trial: N/A
- Eucalyptolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3246
CAS No.:189272-68-2
- Cleroindicin F
Catalog No.:BCN1169
CAS No.:189264-47-9
- Cleroindicin D
Catalog No.:BCN1168
CAS No.:189264-45-7
- Cleroindicin C
Catalog No.:BCN1167
CAS No.:189264-44-6
- KU14R
Catalog No.:BCC1685
CAS No.:189224-48-4
- Helioxanthin
Catalog No.:BCC5413
CAS No.:18920-47-3
- Ro 48-8071 fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC5546
CAS No.:189197-69-1
- Tegaserod maleate
Catalog No.:BCC7955
CAS No.:189188-57-6
- Naringin dihydrochalcone
Catalog No.:BCN2579
CAS No.:18916-17-1
- 3'-O-Methylmurraol
Catalog No.:BCN7471
CAS No.:1891097-17-8
- Fas C- Terminal Tripeptide
Catalog No.:BCC1019
CAS No.:189109-90-8
- Bruceantinoside C
Catalog No.:BCN1166
CAS No.:112899-35-1
- Isotanshinone IIB
Catalog No.:BCN2513
CAS No.:109664-01-9
- N-Caffeoyl-O-methyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCC8216
CAS No.:189307-47-9
- Danshenol A
Catalog No.:BCN3145
CAS No.:189308-08-5
- Danshenol B
Catalog No.:BCN2616
CAS No.:189308-09-6
- Xanthohumol B
Catalog No.:BCN8018
CAS No.:189308-10-9
- 3'-Hydroxyrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN1170
CAS No.:189322-67-6
- 3'-Methoxyrocaglamide
Catalog No.:BCN1171
CAS No.:189322-69-8
- Fmoc-Thr(tBu)-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2576
CAS No.:189337-28-8
- Corchoionol C
Catalog No.:BCN1172
CAS No.:189351-15-3
- Endomorphin-1
Catalog No.:BCC1008
CAS No.:189388-22-5
- Triptinin B
Catalog No.:BCN6785
CAS No.:189389-05-7
- Chebulinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN3263
CAS No.:18942-26-2
Delafloxacin: design, development and potential place in therapy.[Pubmed:28356714]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2017 Mar 20;11:881-891.
Delafloxacin (DLX) is a new fluoroquinolone pending approval, which has shown a good in vitro and in vivo activity against major pathogens associated with skin and soft tissue infections and community-acquired respiratory tract infections. DLX also shows good activity against a broad spectrum of microorganisms, including those resistant to other fluoroquinolones, as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Its pharmacokinetic properties and excellent activity in acidic environments make DLX an alternative in the treatment of these and other infections. In this manuscript, a detailed analysis of this new fluoroquinolone is performed, from its chemical structure to its in vivo activity in recently published clinical trials. Its possible place in the current antimicrobial outlook and in other infectious models is also discussed.
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic profiling of delafloxacin in a murine lung model against community-acquired respiratory tract pathogens.[Pubmed:27742208]
Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2016 Nov;48(5):535-541.
Increasing antimicrobial resistance in community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) pathogens has contributed to infection-related morbidity and mortality. Delafloxacin is a novel fluoroquinolone with broad-spectrum activity against Gram-positive and -negative organisms, including Streptococcus pneumoniae and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). This study aimed to define the pharmacodynamic profile of Delafloxacin against CAP pathogens using a neutropenic murine lung infection model. Five S. pneumoniae, 2 methicillin-susceptible S. aureus (MSSA), 2 MRSA and 2 Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates were studied. Delafloxacin doses varied from 0.5 mg/kg/day to 640 mg/kg/day and were given as once-daily to every 3 h regimens over the 24-h treatment period. Efficacy was measured as the change in log10 CFU at 24 h compared with 0-h controls. Plasma and bronchopulmonary pharmacokinetic studies were conducted. Delafloxacin demonstrated potent in vitro and in vivo activity. Delafloxacin demonstrated high penetration into the lung compartment, as epithelial lining fluid concentrations were substantially higher than free drug in plasma. The ratio of the area under the free drug concentration-time curve to the minimum inhibitory concentration of the infecting organism (fAUC/MIC) was the parameter that best correlated with the efficacy of the drug, and the magnitude required to achieve 1 log10 CFU reduction was 31.8, 24.7, 0.4 and 9.6 for S. pneumoniae, MRSA, MSSA and K. pneumoniae, respectively. The observed in vivo efficacy of Delafloxacin was supported by the high pulmonary disposition of the compound. The results derived from this pre-clinical lung model support the continued investigation of Delafloxacin for the treatment of community-acquired lower respiratory tract infections.
Clinical Pharmacology of Delafloxacin in Patients With Hepatic Impairment.[Pubmed:27570245]
J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Mar;57(3):328-335.
Delafloxacin is a novel anionic fluoroquinolone with robust activity against Gram-positive, Gram-negative, atypical, and anaerobic bacteria, including methicillin-resistant S aureus. Delafloxacin is currently being studied for the treatment of acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections and community-acquired pneumonia. This was a phase 1, open-label pharmacokinetic and safety study of a single intravenous dose of 300 mg Delafloxacin in subjects with mild, moderate, and severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh class A, B, and C, respectively) compared with matched healthy controls. The effects of hepatic impairment were assessed by ANOVA of log-transformed values for AUC0-infinity , Cmax , and systemic clearance, with hepatic group as a fixed effect. Mean AUC0-infinity and Cmax in each impairment group were not significantly different from those of the pooled healthy subjects (P > 0.05). The 90% confidence interval (CI) of the percentage ratios of least-squares means of AUC0-infinity did not indicate significant differences between the impairment groups and pooled healthy controls: Child-Pugh class A (mild) 114.4 (CI: 95.6, 137.0), Child-Pugh class B (moderate) 114.8 (CI: 95.9, 137.4), and Child-Pugh class C (severe) 115.1 (CI: 96.1, 137.8). A single IV infusion of Delafloxacin was generally well tolerated in all treatment groups. The exposure and clearance of Delafloxacin in subjects with mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment did not significantly differ from those of pooled, matched healthy subjects. Based on these pharmacokinetic data, dose adjustment of Delafloxacin in the presence of hepatic impairment is not needed.
In Vitro Activity of Delafloxacin against Contemporary Bacterial Pathogens from the United States and Europe, 2014.[Pubmed:28167542]
Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2017 Mar 24;61(4). pii: AAC.02609-16.
The in vitro activities of Delafloxacin and comparator antimicrobial agents against 6,485 bacterial isolates collected from medical centers in Europe and the United States in 2014 were tested. Delafloxacin was the most potent agent tested against methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA), methicillin-resistant S. aureus, Streptococcus pneumoniae, viridans group streptococci, and beta-hemolytic streptococci and had activity similar to that of ciprofloxacin and levofloxacin against certain members of the Enterobacteriaceae Overall, the broadest coverage of the tested pathogens (Gram-positive cocci and Gram-negative bacilli) was observed with meropenem and tigecycline in both Europe and the United States. Delafloxacin was shown to be active against organisms that may be encountered in acute bacterial skin and skin structure infections, respiratory infections, and urinary tract infections.


