RobustaflavoneCAS# 49620-13-5 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 49620-13-5 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5281694 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C30H18O10 | M.Wt | 538.458 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
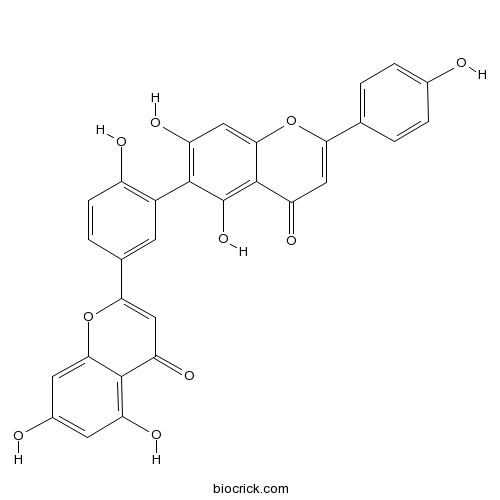
| Chemical Name | 6-[5-(5,7-dihydroxy-4-oxochromen-2-yl)-2-hydroxyphenyl]-5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)chromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=CC=C1C2=CC(=O)C3=C(C(=C(C=C3O2)O)C4=C(C=CC(=C4)C5=CC(=O)C6=C(C=C(C=C6O5)O)O)O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BORWSEZUWHQTOK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H18O10/c31-15-4-1-13(2-5-15)23-11-22(37)29-26(39-23)12-20(35)27(30(29)38)17-7-14(3-6-18(17)33)24-10-21(36)28-19(34)8-16(32)9-25(28)40-24/h1-12,31-35,38H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Robustaflavone, a naturally occurring biflavanoid isolated from Rhus succedanea, was found to be a potent inhibitor of hepatitis B virus (HBV) replication in 2.2.15 cells, with an effective concentration (EC50) of 0.25 microM, and a selectivity index (SI, IC50/EC90) of 153. | |||||

Robustaflavone Dilution Calculator

Robustaflavone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8572 mL | 9.2858 mL | 18.5716 mL | 37.1431 mL | 46.4289 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3714 mL | 1.8572 mL | 3.7143 mL | 7.4286 mL | 9.2858 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1857 mL | 0.9286 mL | 1.8572 mL | 3.7143 mL | 4.6429 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0371 mL | 0.1857 mL | 0.3714 mL | 0.7429 mL | 0.9286 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0186 mL | 0.0929 mL | 0.1857 mL | 0.3714 mL | 0.4643 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tetraethylenepentamine 5HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3867
CAS No.:4961-41-5
- Helicianeoide B
Catalog No.:BCN2487
CAS No.:496066-89-8
- Helicianeoide A
Catalog No.:BCN2486
CAS No.:496066-82-1
- Pyromeconic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7177
CAS No.:496-63-9
- Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8851
CAS No.:496-41-3
- Fenofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC4781
CAS No.:49562-28-9
- Estradiol heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8961
CAS No.:4956-37-0
- 11alpha,12alpha-Oxidotaraxerol palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN7129
CAS No.:495389-95-2
- Org 25543 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6288
CAS No.:495076-64-7
- (+)-Methysticin
Catalog No.:BCN8429
CAS No.:495-85-2
- Tigloyltropeine
Catalog No.:BCN1944
CAS No.:495-83-0
- Valtropine
Catalog No.:BCN1926
CAS No.:495-82-9
- Angelicain
Catalog No.:BCN5605
CAS No.:49624-66-0
- Isomitraphylline
Catalog No.:BCN7800
CAS No.:4963-01-3
- Simiarenol acetate
Catalog No.:BCN5606
CAS No.:4965-99-5
- ZLN005
Catalog No.:BCC4882
CAS No.:49671-76-3
- Eltrombopag
Catalog No.:BCC4968
CAS No.:496775-61-2
- Eltrombopag Olamine
Catalog No.:BCC1549
CAS No.:496775-62-3
- Crobarbatine
Catalog No.:BCN2069
CAS No.:49679-23-4
- AR-C155858
Catalog No.:BCC1367
CAS No.:496791-37-8
- HhAntag
Catalog No.:BCC1617
CAS No.:496794-70-8
- Drupacine
Catalog No.:BCN7065
CAS No.:49686-57-9
- Adarotene
Catalog No.:BCC1328
CAS No.:496868-77-0
- Arbutin
Catalog No.:BCN6307
CAS No.:497-76-7
Simultaneous quantification of five biflavonoids in rat plasma by LC-ESI-MS/MS and its application to a comparatively pharmacokinetic study of Selaginella doederleinii Hieron extract in rats.[Pubmed:29101819]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2018 Feb 5;149:80-88.
Selaginella doederleinii Hieron is a widely used as folk Chinese medicine for treatment of different cancers. Our previous investigations have confirmed that the total biflavonoids in ethyl acetate extract from S. doederleinii (SDEA) have favorable anticancer potentials. However, the in vivo process of its bioactive ingredients remains unknown. In this paper, a sensitive and reliable method was developed for simultaneous quantification of main five biflavonoids, including amentoflavone, Robustaflavone, 2'',3''-dihydro-3',3''-biapigenin, 3',3''-binaringenin and delicaflavone in the ethyl acetate extract of S. doederleinii (SDEA extract) in rat plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS/MS). Chromatographic separation was performed using an Ultimate((R)) XB-C18 (100x2.1mm, 3.5mum) with gradient elution of water (0.5% acetic acid) and acetonitrile at 0.2mL/min. All analytes with internal standard (chrysin) were detected using selective reaction monitoring (SRM) in negative ionization mode. The method showed a good linearity over a wide concentration range (r(2)>0.99). The limits of quantification for the biflavonoids were less than 10ng/mL. The developed method was applied to the comparatively pharmacokinetic study of the five biflavonoids after oral or intravenous administration of SDEA extract in rats. In addition, in silico assessments of permeability and solubility of these biflavonoids were also performed to understand their poor bioavailability. It is the first time to report the in vivo process profiles of the biflavonoids of SDEA extract in rats.
Evaluation of the diuretic activity in two Mexican medicinal species: Selaginella nothohybrida and Selaginella lepidophylla and its effects with ciclooxigenases inhibitors.[Pubmed:25645190]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Apr 2;163:167-72.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Doradilla is a plant that has a long history in the Mexican traditional system of medicine for gall and renal stones, diuresis, stomach and liver inflammation among other diseases. Major components isolated from these plants include biflavonoids as amentoflavone (1), Robustaflavone (2) and (S)-2,3-dihydroRobustaflavone (3) and the carbohydrate trehalose (4). The aim of this study was to evaluate the diuretic effect of the decoction of Selaginella nothohybrida Valdespino and Selaginella lepidophylla (Hook & Grev) Spring (Selaginellaceae), and compounds 1-4. We also explored the probable mode of action comparing the effects when using nonspecific and specific COXs inhibitors. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Three biflavonoids (1-3) were isolated from the ethyl acetate extraction of the aqueous decoction and the carbohydrate trehalose (4) from the aqueous phase. The structures of all compounds were elucidated by spectroscopic methods and comparisons were made against published data. The diuretic activity was assessed in mice by oral administration of the decoctions in doses of 1000 and 2000mg/kg and biflavonoids 1-3 and trehalose (4) in a dose range of 10mg/kg using furosemide as a standard drug. Inhibitors of COXs such as acetyl salicylic acid, sodium naproxen, indomethacin and Celebrex were also assayed to analyze the involvement of renal prostaglandins in diuresis. Water excretion rate, pH, density, conductivity, and contents of Na(+) and K(+) were measured in the urine of mice. RESULTS: Decoction of Selaginella lepidophylla showed lower effect in the urine output at doses of 1000 and 2000mg/kg, while decoction of Selaginella nothohybrida produced an increase at 2000mg/kg (P<0.05). Urinary electrolytes excretion was also affected by this last extract and pure compounds: decoction diminished urinary excretion of sodium and potassium ions, so as compounds 1 and 4; compounds 2 and 3 observed just a natriuretic effect. Pretreated mice with COXs inhibitors and then with test compounds 1, 2, 4 and decoction showed inhibition of diuresis in all cases exception for treatment with trehalose (4); natriuretic effect was observed in all cases except for biflavonoid Robustaflavone (2) which behaved as the reference compound furosemide. Selaginella nothohybrida decoction behaved similarly to COX-2 inhibitor Celebrex (8), inhibiting diuresis. CONCLUSIONS: Selaginella nothohybrida presents a moderate diuretic effect, which appears to be in partly mediated by the presence of biflavonoids and trehalose. Renal prostaglandins may be involved in the mechanism of diuresis. The present results provide a quantitative basis explaining the traditional folk medicine use of Selaginella nothohybrida as a diuretic agent by Mexican population.
New flavonoid C-O-C dimers and other chemical constituents from Garcinia brevipedicellata stem heartwood.[Pubmed:27343472]
Z Naturforsch C. 2016;71(7-8):233-41.
The methanol extract of the stem heartwood of Garcinia brevipedicellata has furnished three new flavonoid C-O-C dimers, brevipedicilones A (6), B (8) and C (10), along with five previously reported flavonoid dimers, viz. amentoflavone (1), 4'''-O-methylamentoflavone (2), Robustaflavone (3), 4'-O-methyl Robustaflavone (4) and tetrahinokiflavone (5). The new structures, which are composed of flavanone-flavanonol or flavanonol-flavanonol sub-units, were established based on spectroscopic analysis including 1D and 2D NMR (1H-1H COSY, HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY) spectroscopy, and by comparing their spectral data with those reported for related compounds.
Chemical constituents of the leaves of Campylospermum elongatum.[Pubmed:27295334]
Z Naturforsch C. 2017 Jan 1;72(1-2):71-75.
The leaves of Campylospermum elongatum have furnished the cyano-glycoside (lithospermoside), nine isomeric biflavonoid derivatives among which five are I3-II6 linked (Robustaflavone; 4'-O-methyl Robustaflavone; 4',4'''-di-O-methyl Robustaflavone; 7,4',4''-tri-O-methyl Robustaflavone; 4',7''-di-O-methyl Robustaflavone) and four I3-II8 linked (amentoflavone; 7-O-methyl amentoflavone; 7,7''-di-O-methyl amentoflavone; 7, 4',7''-tri-O-methyl amentoflavone) and a flavone glycoside, 4''-O-methyl-7-O-beta-d-galactosylapigenin. All structures were established from a complete spectroscopic analysis (MS, IR, 1D, and 2D NMR, including HSQC, HMBC, and NOESY) as well as by comparing the obtained spectroscopic data with literature. This is the first report on the characterization of 4'-O-methyl-7-O-beta-d-galactosylapigenin from the genus campylospermum and thus has important chemotaxonomic implications.
Probing the Antiallergic and Anti-inflammatory Activity of Biflavonoids and Dihydroflavonols from Dietes bicolor.[Pubmed:29381070]
J Nat Prod. 2018 Feb 23;81(2):243-253.
Dietes bicolor (Iridaceae) is an ornamental plant used by African local healers to treat diarrhea and dysentery. A new dihydroflavonol, (2R,3R)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-8-methoxyflavanone (1); two known dihydroflavonols, trans-3-hydroxy-5-methoxy-6,7-methylenedioxyflavanone (2) and trans-3-hydroxy-5,7-dimethoxyflavanone (3); the known isoflavone orobol 7,3'-di-O-methyl ether (4); the known biflavones lanaroflavone (5), Robustaflavone (6), and amentoflavone (7); and beta-sitosterol (8) were isolated from the CH2Cl2 fraction of D. bicolor leaves. The extract showed potent activity in antiallergic and anti-inflammatory assays. The structures of the isolates were identified by spectroscopic and spectrometric methods. Compounds 6 and 7 (400 muM) exhibited antiallergic activity by inhibiting antigen-induced beta-hexosaminidase release at 45.7% and 46.3%, respectively. Moreover, 6 and 7 exerted anti-inflammatory activity as demonstrated by the inhibition of superoxide anion generation with an IC50 value of 1.0 muM as well as the inhibition of elastase release with IC50 values of 0.45 and 0.75 muM, respectively. The anti-inflammatory activity was further explained by the virtual docking of the isolated compounds to the binding sites in the human neutrophil elastase (HNE) crystal structure using Discovery Studio 2.5. It was concluded that the biflavonoids bind directly to HNE and inhibit its enzymatic activity based on the CDOCKER algorithm. The data provided evidence for the potential use of D. bicolor against certain diseases related to allergy and inflammation.
In vitro activity of the hydroethanolic extract and biflavonoids isolated from Selaginella sellowii on Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis.[Pubmed:25591109]
Mem Inst Oswaldo Cruz. 2014 Dec;109(8):1050-6.
This study is the first phytochemical investigation of Selaginella sellowii and demonstrates the antileishmanial activity of the hydroethanolic extract from this plant (SSHE), as well as of the biflavonoids amentoflavone and Robustaflavone, isolated from this species. The effects of these substances were evaluated on intracellular amastigotes of Leishmania (Leishmania) amazonensis, an aetiological agent of American cutaneous leishmaniasis. SSHE was highly active against intracellular amastigotes [the half maximum inhibitory concentration (IC50) = 20.2 microg/mL]. Fractionation of the extract led to the isolation of the two bioflavonoids with the highest activity: amentoflavone, which was about 200 times more active (IC50 = 0.1 mug/mL) and less cytotoxic than SSHE (IC50 = 2.2 and 3 mug/mL, respectively on NIH/3T3 and J774.A1 cells), with a high selectivity index (SI) (22 and 30), Robustaflavone, which was also active against L. amazonensis (IC50 = 2.8 microg/mL), but more cytotoxic, with IC50 = 25.5 microg/mL (SI = 9.1) on NIH/3T3 cells and IC50 = 3.1 microg/mL (SI = 1.1) on J774.A1 cells. The production of nitric oxide (NO) was lower in cells treated with amentoflavone (suggesting that NO does not contribute to the leishmanicidal mechanism in this case), while NO release was higher after treatment with Robustaflavone. S. sellowii may be a potential source of biflavonoids that could provide promising compounds for the treatment of cutaneous leishmaniasis.
Rapid Screening and Structural Characterization of Antioxidants from the Extract of Selaginella doederleinii Hieron with DPPH-UPLC-Q-TOF/MS Method.[Pubmed:25792983]
Int J Anal Chem. 2015;2015:849769.
2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl-ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-Q-time-of-flight mass spectrometry (DPPH-UPLC-Q-TOF/MS), as a rapid and efficient means, now was used for the first time to screen antioxidants from Selaginella doederleinii. The nine biflavone compounds were screened as potential antioxidants. The biflavones were structurally identified and divided into the three types, that is, amentoflavone-type, Robustaflavone-type, and hinokiflavone-type biflavonoids. Among the compounds bilobetin (3) and putraflavone (8) were found from Selaginella doederleinii for the first time and others including amentoflavone (1), Robustaflavone (2), 4'-methoxy Robustaflavone (4), podocarpusflavone A (5), hinokiflavone (6), ginkgetin (7), and heveaflavone (9) were identified previously in the plant. Moreover, nine biflavones possessed a good antioxidant activity via their DPPH free radical scavenging. It demonstrates that DPPH-UPLC-Q-TOF/MS exhibits strong capacity in separation and identification for small molecule. The method is suitable for rapid screening of antioxidants without the need for complicated systems and additional instruments.
[Flavonoids from Selaginella uncinata].[Pubmed:26677701]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2015 Aug;40(15):3005-8.
In the current study, nine flavonoids were isolated and purified from 75% ethanol extract of Selaginella uncinata (Desv.) Spring by column chromatographic techniques over macroporous resin, polyamide, silica gel, Sephadex LH-20 and pre-HPLC. On the basis of their physico-chemical properties and spectroscopic data analyses, these compounds were elucidated as cirsimarin (1), nepitrin (2), apigenin-6-C-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-8-C-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), apigenin-6-C-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-8-C-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (4), apigenin-7-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (5), 2,3-dihydroamentoflavone (6), 4'-O-methylamentoflavone (7), 2,3-dihydro-4'-O-methyl-amentoflavone (8), and 2,3,2",3"-tetrahydron-4'-O-methyl-Robustaflavone (9). Compounds 1-5 belong to flavonoid glycosides and were isolated from the genus Selaginella for the first time.


