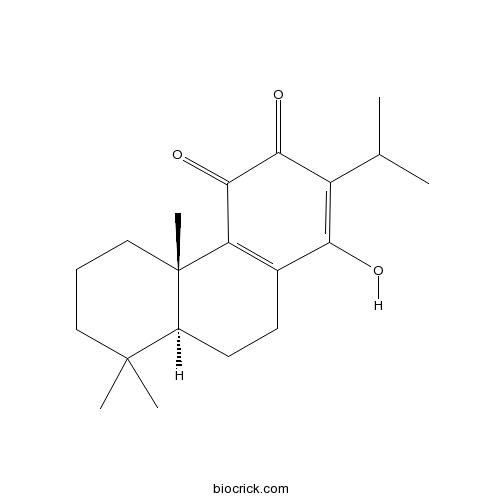
RoyleanoneCAS# 6812-87-9 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 6812-87-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442084 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C20H28O3 | M.Wt | 316.4 |
| Type of Compound | Quinones | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4bS,8aS)-1-hydroxy-4b,8,8-trimethyl-2-propan-2-yl-5,6,7,8a,9,10-hexahydrophenanthrene-3,4-dione | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=C(C2=C(C(=O)C1=O)C3(CCCC(C3CC2)(C)C)C)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | XBJOAZYNSZDFSF-RBZFPXEDSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H28O3/c1-11(2)14-16(21)12-7-8-13-19(3,4)9-6-10-20(13,5)15(12)18(23)17(14)22/h11,13,21H,6-10H2,1-5H3/t13-,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Royleanone possesses cytotoxic activity against the human pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2. |

Royleanone Dilution Calculator

Royleanone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1606 mL | 15.8028 mL | 31.6056 mL | 63.2111 mL | 79.0139 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6321 mL | 3.1606 mL | 6.3211 mL | 12.6422 mL | 15.8028 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3161 mL | 1.5803 mL | 3.1606 mL | 6.3211 mL | 7.9014 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0632 mL | 0.3161 mL | 0.6321 mL | 1.2642 mL | 1.5803 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0316 mL | 0.158 mL | 0.3161 mL | 0.6321 mL | 0.7901 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Roburic acid
Catalog No.:BCN5385
CAS No.:6812-81-3
- JNJ-1661010
Catalog No.:BCC2315
CAS No.:681136-29-8
- AICAR phosphate
Catalog No.:BCC4220
CAS No.:681006-28-0
- 13-Dehydroxyindaconintine
Catalog No.:BCN8403
CAS No.:681-18-9
- Bepridil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7864
CAS No.:68099-86-5
- 4',5,7-Trihydroxy-6-prenylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN4238
CAS No.:68097-13-2
- Boc-Phe(4-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3172
CAS No.:68090-88-0
- Norfloxacin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4230
CAS No.:68077-27-0
- Trifolirhizin
Catalog No.:BCN4237
CAS No.:6807-83-6
- Megastigm-7-ene-3,5,6,9-tetraol
Catalog No.:BCN5169
CAS No.:680617-50-9
- EMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6226
CAS No.:680590-49-2
- Platyconic acid A
Catalog No.:BCN3239
CAS No.:68051-23-0
- Chonglou Saponin VII
Catalog No.:BCN4239
CAS No.:68124-04-9
- Astressin 2B
Catalog No.:BCC5906
CAS No.:681260-70-8
- Diosgenyl-3-di-β-O-glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCC8168
CAS No.:68127-19-5
- Humic acid sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCN1284
CAS No.:68131-04-4
- Jujuboside B1
Catalog No.:BCN3881
CAS No.:68144-21-8
- 1-O-Acetyl britannilactone
Catalog No.:BCN2365
CAS No.:681457-46-5
- Nortetraphyllicine
Catalog No.:BCN4240
CAS No.:68160-76-9
- Isoliensinine
Catalog No.:BCN6331
CAS No.:6817-41-0
- BRL 44408 maleate
Catalog No.:BCC6948
CAS No.:681806-46-2
- 6,8-Diprenylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN3000
CAS No.:68236-11-3
- 6-Prenylnaringenin
Catalog No.:BCN2999
CAS No.:68236-13-5
- 2-Hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)anthraquinone
Catalog No.:BCN1380
CAS No.:68243-30-1
Abietane diterpenes induce cytotoxic effects in human pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2 through different modes of action.[Pubmed:22436445]
Phytochemistry. 2012 Jun;78:107-19.
Abietane diterpenes, especially those containing quinone moieties, are often reported to have cytotoxic effects on cancer cell lines. They deserve greater attention because several cancer chemotherapeutic agents also possess the quinone structural feature. To date, very little is known about their cytotoxic molecular modes of action. In the present study, five diterpenes, 7 alpha-acetoxyRoyleanone, horminone, Royleanone, 7-ketoRoyleanone and sugiol which have been previously isolated from the medicinal plant Peltodon longipes were shown to possess cytotoxic activity against the human pancreatic cancer cell line MIA PaCa-2. 7 alpha-AcetoxyRoyleanone, horminone and Royleanone were demonstrated to possess alkylating properties using the nucleophile 4-(4-nitrobenzyl)pyridine. However, no clear correlation between the alkylating properties and cytotoxicity of these diterpenes was observed. Furthermore, the relaxation activity of human DNA topoisomerases I and II was found to be influenced by these compounds, with 7-ketoRoyleanone and sugiol being the most active. These two diterpenes preferentially inhibited topoisomerase I and exhibited lower IC(50) values than the classical topoisomerase I inhibitor camptothecin. Molecular docking studies revealed possible interactions of diterpenes with topoisomerase I, indicating that these compounds do not form the drug-enzyme-DNA covalent ternary complex as observed with camptothecin. A binding pocket located at the surface of the DNA-interaction site was proposed. Moreover, the ability of the five diterpenes to generate DNA-strand breaks in single cells was confirmed using the alkaline comet assay. As expected, these diterpenes also influenced cell cycle progression and arrested cells in different phases of the cell cycle, primarily the G1/G0 and S-phases. Interestingly, the diterpenes only exhibited a slight ability to induce apoptotic cell death and failed to generate intracellular reactive oxygen species. These results provide additional understanding of the cytotoxic effects of abietane diterpenes. Depending on their functional groups, we propose that abietane diterpenes utilise different mechanisms to induce cell death.
Bioactivity-guided study of antiproliferative activities of Salvia extracts.[Pubmed:21615011]
Nat Prod Commun. 2011 May;6(5):575-9.
The cytotoxic activities of the n-hexane, chloroform and aqueous methanolic fractions prepared from the methanolic extract of the leaves of 23 Salvia taxa were studied for their cell growth-inhibitory activity against human cervix adenocarcinoma (HeLa), skin carcinoma (A431) and breast adenocarcinoma (MCF7) cells using the MTT assay. The n-hexane fractions of six Salvia taxa (S. hispanica, S. nemorosa, S. nemorosa 1. albiflora, S. pratensis, S. recognita and S. ringens) and the chloroform fraction ofS. officinalis 1. albiflora produced over 50% growth inhibition of the skin carcinoma cell line. None of the tested extracts showed substantial (above 50%) antiproliferative effects against HeLa and MCF7 cells. S. ringens was the most powerful among the studied Salvia species with a 61.8% cell growth inhibitory activity on A431 cells. In the case of S. ringens, other plant parts were also tested for antiproliferative effect, and the highest activities were recorded for the root extract. This was subjected to bioactivity-guided fractionation, which yielded four abietane diterpenes (Royleanone, horminone, 7-O-methyl-horminone and 7-acetyl-horminone), one triterpene (erythrodiol-3-acetate) and beta-sitosterol. Horminone, 7-acetyl-horminone and erythrodiol-3-acetate displayed marked concentration-dependent antiproliferative effects, while Royleanone and 7-O-methyl-horminone produced weaker activities.
Antioxidant diterpenoids from the roots of Salvia barrelieri.[Pubmed:19402189]
Phytochem Anal. 2009 Jul-Aug;20(4):320-7.
INTRODUCTION: The phytochemical and biological studies carried out on Salvia species showed that their extracts and constituents have various biological activities. OBJECTIVE: The aim of this study was the isolation of diterpenoids from the roots of Salvia barrelieri Ettling and the determination of the antioxidant activity. METHODOLOGY: Chromatographic methods were used for fractionation and isolation, respectively. Structure elucidation was established by spectroscopic methods. Five antioxidant assays were performed. RESULTS: Three new abietane diterpenoids barreliol, Royleanone 12-methyl ether and 7-epi-salviviridinol, and six known diterpenoids, with a known dammarane triterpenoid, pyxinol were isolated. The absolute stereochemistry of pyxinol was confirmed by X-ray analysis. CONCLUSION: Taxodione exhibited the highest antioxidant activity among the tested compounds.


