SAGHh and Smo agonist CAS# 912545-86-9 |
- Mibefradil
Catalog No.:BCC1748
CAS No.:116644-53-2
- Mibefradil dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1749
CAS No.:116666-63-8
- Cilnidipine
Catalog No.:BCC1083
CAS No.:132203-70-4
- NNC 55-0396
Catalog No.:BCC1803
CAS No.:357400-13-6
- NP118809
Catalog No.:BCC1807
CAS No.:41332-24-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 912545-86-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5284330 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C28H28ClN3OS | M.Wt | 490.06 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 38 mg/mL (77.54 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
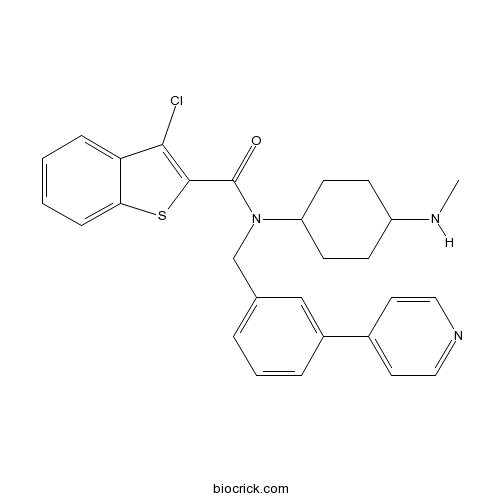
| Chemical Name | 3-chloro-N-[4-(methylamino)cyclohexyl]-N-[(3-pyridin-4-ylphenyl)methyl]-1-benzothiophene-2-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CNC1CCC(CC1)N(CC2=CC=CC(=C2)C3=CC=NC=C3)C(=O)C4=C(C5=CC=CC=C5S4)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | VFSUUTYAEQOIMW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C28H28ClN3OS/c1-30-22-9-11-23(12-10-22)32(28(33)27-26(29)24-7-2-3-8-25(24)34-27)18-19-5-4-6-21(17-19)20-13-15-31-16-14-20/h2-8,13-17,22-23,30H,9-12,18H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent Smoothened (Smo) receptor agonist (Kd = 59 nM); antagonizes Cyclopamine action at the Smo receptor. Potently activates the Hedgehog signaling pathway in Shh-light 2 cells (EC50 ~ 3 nM). Induces pathway activation independently of Ptch proteins. Putative inhibitor of a cellular component required for Hedgehog signaling. Enhances neuronal differentiation of iPSCs into dopaminergic neurons. |

SAG Dilution Calculator

SAG Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0406 mL | 10.2028 mL | 20.4057 mL | 40.8113 mL | 51.0142 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4081 mL | 2.0406 mL | 4.0811 mL | 8.1623 mL | 10.2028 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2041 mL | 1.0203 mL | 2.0406 mL | 4.0811 mL | 5.1014 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0408 mL | 0.2041 mL | 0.4081 mL | 0.8162 mL | 1.0203 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0204 mL | 0.102 mL | 0.2041 mL | 0.4081 mL | 0.5101 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
SAG is a synthetic chlorobenzothiophene-containing Hh pathway agonist that regulates smo activity. It is a SMO agonist at EC50 of 3 nM and but inhibits hedgehog signaling at >1 μM. [1]
Smoothened (SMO) is a GPCR-like receptor that mediates hedgehog signaling with Patched to regulate gene expression through the Gli transcription factors. It is plays an important role for embryogenesis and adults tissue homeostasis
In a mouse cultured cell assay (Shh-LIGHT2), SAG induces pathway activation (EC50 ≈3 nM). It differs in that pathway activity decreases dramatically as SAG concentration surpasses 1 μM. [1] SAG binds directly to the SMO heptahelical bundle. SAG dose dependently blocks this association and produces apparent dissociation constant (KD) of 59 nM for the SAG/SMO complex. [2]
SAG also antagonizes GC’s antiproliferative effects in CGNP P4 wild-type mice primary cultures. At 15-240 nM, SAG prevents the neurotoxic effects of glucocorticoids without interfering with the beneficial effects of glucocorticoids on lung maturation. [2]
References:
1. Chen JK, Taipale J, Young KE et al. Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14071-6.
2. Heine VM, Griveau A, Chapin C et al. A small-molecule smoothened agonist prevents glucocorticoid-induced neonatal cerebellar injury. Sci Transl Med. 2011 Oct 19;3(105):105ra104.
- Veliparib dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2076
CAS No.:912445-05-7
- ABT-888 (Veliparib)
Catalog No.:BCC1267
CAS No.:912444-00-9
- TCB-2
Catalog No.:BCC7421
CAS No.:912342-28-0
- Karavilagenin A
Catalog No.:BCN4455
CAS No.:912329-03-4
- Spantide I
Catalog No.:BCC5808
CAS No.:91224-37-2
- Noscapine HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3819
CAS No.:912-60-7
- H-Met-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2996
CAS No.:91183-71-0
- Ophiopogonin C
Catalog No.:BCN5379
CAS No.:911819-08-4
- Lucyoside B
Catalog No.:BCN7811
CAS No.:91174-19-5
- Chrysothol
Catalog No.:BCN4454
CAS No.:911714-91-5
- 17-AAG Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1297
CAS No.:911710-03-7
- Terbinafine
Catalog No.:BCC3865
CAS No.:91161-71-6
- Melilotigenin B
Catalog No.:BCN4456
CAS No.:91269-84-0
- Sarafloxacin HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4713
CAS No.:91296-87-6
- AT13387
Catalog No.:BCC2122
CAS No.:912999-49-6
- ELN441958
Catalog No.:BCC6452
CAS No.:913064-47-8
- LY 2087101
Catalog No.:BCC7869
CAS No.:913186-74-0
- Almorexant hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5123
CAS No.:913358-93-7
- AMG-458
Catalog No.:BCC3721
CAS No.:913376-83-7
- Brexpiprazole
Catalog No.:BCC4118
CAS No.:913611-97-9
- 1''-Hydroxyerythrinin C
Catalog No.:BCN4066
CAS No.:913690-46-7
- Ropinirole HCl
Catalog No.:BCC4939
CAS No.:91374-20-8
- SC75741
Catalog No.:BCC5448
CAS No.:913822-46-5
- CS 2100
Catalog No.:BCC6221
CAS No.:913827-99-3
SAG-QC: quality control of single amplified genome information by subtracting non-target sequences based on sequence compositions.[Pubmed:28259144]
BMC Bioinformatics. 2017 Mar 4;18(1):152.
BACKGROUND: Whole genome amplification techniques have enabled the analysis of unexplored genomic information by sequencing of single-amplified genomes (SAGs). Whole genome amplification of single bacteria is currently challenging because contamination often occurs in experimental processes. Thus, to increase the confidence in the analyses of sequenced SAGs, bioinformatics approaches that identify and exclude non-target sequences from SAGs are required. Since currently reported approaches utilize sequence information in public databases, they have limitations when new strains are the targets of interest. Here, we developed a software SAG-QC that identify and exclude non-target sequences independent of database. RESULTS: In our method, "no template control" sequences acquired during WGA were used. We calculated the probability that a sequence was derived from contaminants by comparing k-mer compositions with the no template control sequences. Based on the results of tests using simulated SAG datasets, the accuracy of our method for predicting non-target sequences was higher than that of currently reported techniques. Subsequently, we applied our tool to actual SAG datasets and evaluated the accuracy of the predictions. CONCLUSIONS: Our method works independently of public sequence information for distinguishing SAGs from non-target sequences. This method will be effective when employed against SAG sequences of unexplored strains and we anticipate that it will contribute to the correct interpretation of SAGs.
Influence of Irradiation on Leukodepleted Small Unit Red Blood Cell (RBC) Bags for Infant Transfusion in Additive Solution SAG-M.[Pubmed:28164645]
Clin Lab. 2016 Jul 1;62(7):1295-1301.
BACKGROUND: To reduce transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease irradiation of blood products is widely accepted. There is little data about the effect of gamma-irradiation on leukoreduced RBCs stored in SAG-M that are subdivided for use in transfusion to preterm infants and small children. METHODS: We studied 30 leukoreduced SAG-M preserved RBC bags. All RBCs were leukoreduced on the collection day. The 30 units were divided into two groups. Every unit was divided into three bags. One of these bags served as nonirradiated control (group 1A, group 2A), the other two were gamma-irradiated at different times. In vitro evaluation of irradiated and nonirradiated units was performed on the days +3, +7, +14, +21, and +28 from the day of collection. RESULTS: Gamma irradiation induced a higher increase of extracellular hemoglobin, LDH, and potassium than non-irradiated storage over the time. No irradiated or non-irradiated unit showed a hemolysis rate over the recommended limit of 0.8% over the 28 day period. CONCLUSIONS: Our findings show that subdivision of RBCs does not have an appreciable influence on the storage of leukoreduced, irradiated RBCs in AS SAG-M. Our "worst case scenario" was irradiation on day +3 after donation and subsequent storage until day +28. Especially for infant use, it is important to have the possibility to irradiate even late after donation, because this procedure offers the possibility to use one RBC bag over a longer period of time and to reduce the donor exposure for infants. Therefore, subdivided leukoreduced RBCs can be safely irradiated until day +14 and subsequently stored until day +28 after donation.
Combining Smoothened Agonist and NEL-Like Protein-1 Enhances Bone Healing.[Pubmed:28198775]
Plast Reconstr Surg. 2017 Jun;139(6):1385-1396.
BACKGROUND: Nonhealing bone defects represent an immense biomedical burden. Despite recent advances in protein-based bone regeneration, safety concerns over bone morphogenetic protein-2 have prompted the search for alternative factors. Previously, the authors examined the additive/synergistic effects of hedgehog and Nel-like protein-1 (NELL-1) on the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. In this study, the authors sought to leverage their previous findings by applying the combination of Smoothened agonist (SAG), hedgehog signal activator, and NELL-1 to an in vivo critical-size bone defect model. METHODS: A 4-mm parietal bone defect was created in mixed-gender CD-1 mice. Treatment groups included control (n = 6), SAG (n = 7), NELL-1 (n = 7), and SAG plus NELL-1 (n = 7). A custom fabricated poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) disk with hydroxyapatite coating was used as an osteoinductive scaffold. RESULTS: Results at 4 and 8 weeks showed increased bone formation by micro-computed tomographic analyses with either stimulus alone (SAG or NELL-1), but significantly greater bone formation with both components combined (SAG plus NELL-1). This included greater bone healing scores and increased bone volume and bone thickness. Histologic analyses confirmed a significant increase in new bone formation with the combination therapy SAG plus NELL-1, accompanied by increased defect vascularization. CONCLUSIONS: In summary, the authors' results suggest that combining the hedgehog signaling agonist SAG and NELL-1 has potential as a novel therapeutic strategy for the healing of critical-size bone defects. Future directions will include optimization of doSAGe and delivery strategy for an SAG and NELL-1 combination product.
Early gamma-irradiation and subsequent storage of red cells in SAG-M additive solution potentiate energy imbalance, microvesiculation and susceptibility to stress-induced apoptotic cell death.[Pubmed:28378415]
Vox Sang. 2017 Jul;112(5):480-483.
gamma-Irradiation of red blood cell (RBC) concentrates prevents transfusion-associated graft-versus-host disease but may diminish RBC quality. Herein, we show that early gamma-irradiation (25 Gy) of RBC units and their subsequent storage in SAG-M additive solution altered membrane microvesiculation, supernatant haemoglobin and cytosolic ATP. gamma-Irradiation did not influence phosphatidylserine externalization, a marker of erythrocyte apoptotic cell death (eryptosis), in RBC stored for 42 days. However, shorter periods (4-21 days) of storage accentuated eryptosis in gamma-irradiated RBC versus untreated RBCs following energy depletion, suggesting that gamma-irradiated RBC is primed for stress-induced eryptosis during storage.
Small molecules greatly improve conversion of human-induced pluripotent stem cells to the neuronal lineage.[Pubmed:22567022]
Stem Cells Int. 2012;2012:140427.
Efficient in vitro differentiation into specific cell types is more important than ever after the breakthrough in nuclear reprogramming of somatic cells and its potential for disease modeling and drug screening. Key success factors for neuronal differentiation are the yield of desired neuronal marker expression, reproducibility, length, and cost. Three main neuronal differentiation approaches are stromal-induced neuronal differentiation, embryoid body (EB) differentiation, and direct neuronal differentiation. Here, we describe our neurodifferentiation protocol using small molecules that very efficiently promote neural induction in a 5-stage EB protocol from six induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC) lines from patients with Parkinson's disease and controls. This protocol generates neural precursors using Dorsomorphin and SB431542 and further maturation into dopaminergic neurons by replacing sonic hedgehog with purmorphamine or smoothened agonist. The advantage of this approach is that all patient-specific iPSC lines tested in this study were successfully and consistently coaxed into the neural lineage.
A small molecule that binds Hedgehog and blocks its signaling in human cells.[Pubmed:19151731]
Nat Chem Biol. 2009 Mar;5(3):154-6.
Small-molecule inhibition of extracellular proteins that activate membrane receptors has proven to be extremely challenging. Diversity-oriented synthesis and small-molecule microarrays enabled the discovery of robotnikinin, a small molecule that binds the extracellular Sonic hedgehog (Shh) protein and blocks Shh signaling in cell lines, human primary keratinocytes and a synthetic model of human skin. Shh pathway activity is rescued by small-molecule agonists of Smoothened, which functions immediately downstream of the Shh receptor Patched.
Small molecule modulation of Smoothened activity.[Pubmed:12391318]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Oct 29;99(22):14071-6.
Smoothened (Smo), a distant relative of G protein-coupled receptors, mediates Hedgehog (Hh) signaling during embryonic development and can initiate or transmit ligand-independent pathway activation in tumorigenesis. Although the cellular mechanisms that regulate Smo function remain unclear, the direct inhibition of Smo by cyclopamine, a plant-derived steroidal alkaloid, suggests that endogenous small molecules may be involved. Here we demonstrate that SAG, a chlorobenzothiophene-containing Hh pathway agonist, binds to the Smo heptahelical bundle in a manner that antagonizes cyclopamine action. In addition, we have identified four small molecules that directly inhibit Smo activity but are structurally distinct from cyclopamine. Functional and biochemical studies of these compounds provide evidence for the small molecule modulation of Smo through multiple mechanisms and yield insights into the physiological regulation of Smo activity. The mechanistic differences between the Smo antagonists may be useful in the therapeutic manipulation of Hh signaling.


