Sumatriptan5-HT1 receptor agonist CAS# 103628-46-2 |
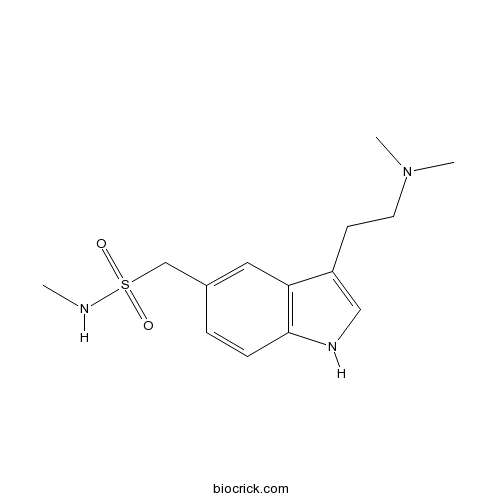
- Sumatriptan Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC2502
CAS No.:103628-48-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 103628-46-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5358 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H21N3O2S | M.Wt | 295.40 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | 1-[3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-1H-indol-5-yl]-N-methylmethanesulfonamide | ||
| SMILES | CNS(=O)(=O)CC1=CC2=C(C=C1)NC=C2CCN(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KQKPFRSPSRPDEB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H21N3O2S/c1-15-20(18,19)10-11-4-5-14-13(8-11)12(9-16-14)6-7-17(2)3/h4-5,8-9,15-16H,6-7,10H2,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Sumatriptan Dilution Calculator

Sumatriptan Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3852 mL | 16.9262 mL | 33.8524 mL | 67.7048 mL | 84.631 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.677 mL | 3.3852 mL | 6.7705 mL | 13.541 mL | 16.9262 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3385 mL | 1.6926 mL | 3.3852 mL | 6.7705 mL | 8.4631 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0677 mL | 0.3385 mL | 0.677 mL | 1.3541 mL | 1.6926 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0339 mL | 0.1693 mL | 0.3385 mL | 0.677 mL | 0.8463 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Sumatriptan succinate is a selective 5-HT1 receptor agonist with specificity towards 5-HT1D, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1A. In addition, the physicochemical properties of Sumatriptan succinate can be characterized using FT-IR, HPLC, SEM and XRD.
- (±)-5'-Chloro-5'-deoxy-ENBA
Catalog No.:BCC7716
CAS No.:103626-26-2
- H-Phe(2-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3165
CAS No.:103616-89-3
- Janolusimide
Catalog No.:BCN1840
CAS No.:103612-45-9
- RETRA hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2415
CAS No.:1036069-26-7
- 5,7-Dimethoxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN3569
CAS No.:1036-72-2
- Isookanin
Catalog No.:BCN6476
CAS No.:1036-49-3
- P005672 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6406
CAS No.:1035979-44-2
- Lansoprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1058
CAS No.:103577-45-3
- TAK-733
Catalog No.:BCC4587
CAS No.:1035555-63-5
- 3,7-O-Diacetylpinobanksin
Catalog No.:BCN5849
CAS No.:103553-98-6
- Huperzine B
Catalog No.:BCN1059
CAS No.:103548-82-9
- Apiosylskimmin
Catalog No.:BCN2455
CAS No.:103529-94-8
- Sumatriptan Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC2502
CAS No.:103628-48-4
- Cnidimol A
Catalog No.:BCN7167
CAS No.:103629-80-7
- Catechin 3-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN5850
CAS No.:103630-03-1
- Ondansetron hydrochloride dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4213
CAS No.:103639-04-9
- 2-Carbamoyl-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8567
CAS No.:103646-20-4
- Mirificin
Catalog No.:BCN2783
CAS No.:103654-50-8
- Dihydrobonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN3731
CAS No.:103680-87-1
- YK-4-279
Catalog No.:BCC2065
CAS No.:1037184-44-3
- Rehmaglutin D
Catalog No.:BCN5851
CAS No.:103744-84-9
- Fasudil
Catalog No.:BCC5262
CAS No.:103745-39-7
- Shionone
Catalog No.:BCN1274
CAS No.:10376-48-4
- R428
Catalog No.:BCC3692
CAS No.:1037624-75-1
A multicenter, open-label, long-term safety and tolerability study of DFN-02, an intranasal spray of sumatriptan 10 mg plus permeation enhancer DDM, for the acute treatment of episodic migraine.[Pubmed:28251391]
J Headache Pain. 2017 Dec;18(1):31.
BACKGROUND: DFN-02 is a novel intranasal spray formulation composed of Sumatriptan 10 mg and a permeation-enhancing excipient comprised of 0.2% 1-O-n-Dodecyl-beta-D-Maltopyranoside (DDM). This composition of DFN-02 allows Sumatriptan to be rapidly absorbed into the systemic circulation and exhibit pharmacokinetics comparable to subcutaneously administered Sumatriptan. Rapid rate of absorption is suggested to be important for optimal efficacy. The objective of this study was to evaluate the safety and tolerability of DFN-02 (10 mg) in the acute treatment of episodic migraine with and without aura over a 6-month period based on the incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events and the evaluation of results of clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, physical examination, and electrocardiograms. METHODS: This was a multi-center, open-label, repeat-dose safety study in adults with episodic migraine with and without aura. Subjects diagnosed with migraine with or without aura according to the criteria set forth in the International Classification of Headache Disorders, 2nd edition, who experienced 2 to 6 attacks per month with fewer than 15 headache days per month and at least 48 headache-free hours between attacks, used DFN-02 to treat their migraine attacks acutely over the course of 6 months. RESULTS: A total of 173 subjects was enrolled, 167 (96.5%) subjects used at least 1 dose of study medication and were evaluable for safety, and 134 (77.5%) subjects completed the 6-month study. A total of 2211 migraine attacks was reported, and 3292 doses of DFN-02 were administered; mean per subject monthly use of DFN-02 was 3.6 doses. Adverse events were those expected for triptans, as well as for nasally administered compounds. No new safety signals emerged. Dysgeusia and application site pain were the most commonly reported treatment-emergent adverse events over 6 months (21% and 30.5%, respectively). Most of the treatment-emergent adverse events were mild. There were 5 serious adverse events, all considered unrelated to the study medication; the early discontinuation rate was 22.5% over the 6-month treatment period. CONCLUSION: DFN-02 was shown to be well tolerated when used over 6 months to treat episodic migraine acutely.
Subcutaneous sumatriptan delivery devices: comparative ease of use and preference among migraineurs.[Pubmed:28176899]
Patient Prefer Adherence. 2017 Jan 19;11:121-129.
BACKGROUND: Several Sumatriptan subcutaneous autoinjector devices for acute treatment of migraine patients are available, each device differs with respect to design and features. Determining device preference and ease of use is important because patients experiencing a migraine attack are often functionally impaired. OBJECTIVE: The objective of this human factors study was to compare migraine patients' device use performance and preferences for three Sumatriptan subcutaneous autoinjectors: a disposable two-step device (Zembrace((R)) SymTouch((R))), a disposable three-step device (Sumavel((R)) DosePro((R))), and a multistep reloadable device (Imitrex((R)) STATdose((R))), using simulated injections. METHODS: Each study subject performed two unaided simulated injections with each of three different drug delivery devices, which were presented in counterbalanced order. The participants were then asked to rate the three devices on various subjective measures. The primary end point was overall device preference using a visual analog scale. RESULTS: A total of 54 subjects participated and each subject performed two simulated injections with each of the three devices. Most subjects preferred the two-step device (88.9%) to the three-step (13.0%) and the reloadable (1.9%). The two-step device had higher mean overall preference ratings (F (2, 159)=56.6, P<0.01) and higher ratings for ease of use, intuitiveness, convenience, portability, and control. The two-step device had a first injection full-dose delivery success rate of 44.4%, higher than both the reloadable (24.1%) and the three-step (3.7%) devices. The number of errors with the two-step device (n=3) was ~90% lower than the three-step (n=49) and reloadable (n=44) devices. CONCLUSION: In this human factors study, 54 migraineurs used simulated injections to compare three Sumatriptan subcutaneous delivery devices. Zembrace SymTouch, a two-step device, was most preferred compared with Sumavel DosePro and Imitrex STATdose. It also ranked highest for ease of use and various other measures. In this study, migraine patients preferred the autoinjector that they rated as simpler and more intuitive.
Randomized, double-blind, crossover study comparing DFN-11 injection (3 mg subcutaneous sumatriptan) with 6 mg subcutaneous sumatriptan for the treatment of rapidly-escalating attacks of episodic migraine.[Pubmed:28176235]
J Headache Pain. 2017 Dec;18(1):17.
BACKGROUND: A 6-mg dose of SC Sumatriptan is the most efficacious and fast-acting acute treatment for migraine, but a 3-mg dose of SC Sumatriptan may improve tolerability while maintaining efficacy. METHODS: This randomized, double-blind, crossover study compared the efficacy and tolerability of 3 mg subcutaneous (SC) Sumatriptan (DFN-11) with 6 mg SC Sumatriptan in 20 adults with rapidly-escalating migraine attacks. Eligible subjects were randomized (1:1) to treat 1 attack with DFN-11 and matching placebo autoinjector consecutively or 2 DFN-11 autoinjectors consecutively and a second attack similarly but with the alternative dose (3 mg or 6 mg). RESULTS: The proportions of subjects who were pain-free at 60 min postdose, the primary endpoint, were similar following treatment with 3 mg SC Sumatriptan and 6 mg SC Sumatriptan (50% vs 52.6%, P = .87). The proportions of subjects experiencing pain relief (P >/= .48); reductions in migraine pain intensity (P >/= .78); and relief from nausea, photophobia, or phonophobia (P >/= .88) with 3 mg SC Sumatriptan and 6 mg SC Sumatriptan were similar, as were the mean scores for satisfaction with treatment (M = 2.6 vs M = 2.4, P = .81) and the mean number of rescue medications used (M = .11 vs M = .26, P = .32). The most common adverse events with the 3- and 6-mg doses were triptan sensations - paresthesia, neck pain, flushing, and involuntary muscle contractions of the neck - and the incidence of adverse events with both doses was similar (32 events total: 3 mg, n = 14 [44%]; 6 mg, n = 18 [56%], P = .60). Triptan sensations affected 4 subjects with the 6-mg dose only, 1 subject with the 3-mg dose only, and 7 subjects with both Sumatriptan doses. Chest pain affected 2 subjects (10%) treated with the 6-mg dose and no subjects (0%) treated with the 3-mg dose of DFN-11. There were no serious adverse events. CONCLUSIONS: The 3-mg SC dose of Sumatriptan in DFN-11 provided relief of migraine pain and associated symptoms comparable to a 6-mg SC dose of Sumatriptan. Tolerability was similar with both study medications; DFN-11 treatment was associated with fewer triptan sensations than the 6-mg dose. DFN-11, with its 3-mg dose of Sumatriptan, may be a clinically useful alternative to higher-dose autoinjectors.


