Fasudilcalcium antagonist CAS# 103745-39-7 |
- chroman 1
Catalog No.:BCC1480
CAS No.:1273579-40-0
- RKI-1447
Catalog No.:BCC1903
CAS No.:1342278-01-6
- Y-27632
Catalog No.:BCC4301
CAS No.:146986-50-7
- Y-27632 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1273
CAS No.:129830-38-2
- GSK429286A
Catalog No.:BCC2532
CAS No.:864082-47-3
- SLx-2119
Catalog No.:BCC1954
CAS No.:911417-87-3
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 103745-39-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3547 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H17N3O2S | M.Wt | 291.37 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | HA-1077; AT877 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
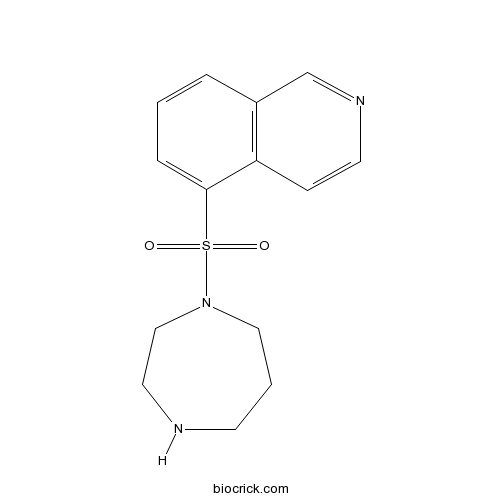
| Chemical Name | 5-(1,4-diazepan-1-ylsulfonyl)isoquinoline | ||
| SMILES | C1CNCCN(C1)S(=O)(=O)C2=CC=CC3=C2C=CN=C3 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NGOGFTYYXHNFQH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H17N3O2S/c18-20(19,17-9-2-6-15-8-10-17)14-4-1-3-12-11-16-7-5-13(12)14/h1,3-5,7,11,15H,2,6,8-10H2 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Fasudil is a potent inhibitor of ROCK1, PKA, PKC, and MLCK with Ki of 0.33 μM, 1.0 μM, 9.3 μM and 55 μM, respectively.In Vitro:Fasudil has vasodilatory action and occupies the adenine pocket of the ATP-binding site of the enzyme[1]. Fasudil produces a competitive inhibition of the Ca2+-induced contraction of the depolarized rabbit aorta. Fasudil inhibits contractile responses to KCl, phenylephnne (PHE) and prostaglandin (PG) F2a[2]. Fasudil also exhibits vasodilator actions by inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine, noradrenaline, histamine, angiotensin, and dopamine induced spiral strips contraction[3]. In addition, Fasudil induces disorganization of actin stress fiber and cell migration inhibition[4]. Fasudil inhibits hepatic stellate cells spreading, the formation of stress fibers, and expression of α-SMA with concomitant suppression of cell growth, but does not induce apoptosis. Fasudil also blocks the LPA-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2, JNK and p38 MAPK[5].In Vivo:Fasudil (30 μg) increases CBF by 50% via intra-coronary injection to dogs. Fasudil (0.01, 0.03, 0.1 and 0.3 mg/kg, bolus, i.v.) decreases MBP and increases HR, VBF, CBF, RBF, and FBF. Fasudil (1.0 ng/mL) increases cardiac output. Fasudil via i.v. produces a significant fall in MBP, left ventricular systolic pressure and total peripheral resistance with an increase in HR and cardiac output, but without obvious effect on right atrial pressure, dP/dt or left ventricular minute work in dogs[3]. Fasudil exhibits protectable effects on cardiovascular disease and reduces the activation of JNK and attenuates mitochondrial-nuclear translocation of AIF under ischemic injury[6]. Fasudil (100 mg/kg/day, p.o.) significantly reduces incidence and mean maximum clinical score of EAE in SJL/J mice immunized with PLP p139-151. Fasudil inhibits the proliferative response of splenocytes to the antigen in mice. Fasudil decreases inflammation, demyelination, axonal loss and APP positivein spinal cord of Fasudil-treated mice via p.o. administration[7]. References: | |||||

Fasudil Dilution Calculator

Fasudil Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4321 mL | 17.1603 mL | 34.3206 mL | 68.6412 mL | 85.8016 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6864 mL | 3.4321 mL | 6.8641 mL | 13.7282 mL | 17.1603 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3432 mL | 1.716 mL | 3.4321 mL | 6.8641 mL | 8.5802 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0686 mL | 0.3432 mL | 0.6864 mL | 1.3728 mL | 1.716 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0343 mL | 0.1716 mL | 0.3432 mL | 0.6864 mL | 0.858 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ki: 0.33 μM for ROCK-II
Cerebral vasospasm occurs frequently after subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) secondary to rupture of an intracranial aneurysm. The possibility that calcium entry blockers may be effective on a delayed cerebral vasospasm and the effectiveness of intrathecal administration of the calcium antagonist nifedipine and its analog nimodipine on a vasospasm has been shown from a clinical point of view. Fasudil is a class of calcium antagonists different from the calcium entry blockers.
In vitro: The inhibitory effects of fasudil on contractile responses to various agonists were examined on strips of rabbit aorta. The concentration-response curves to 5-hydroxytryptamine, prostaglandin F2alpha, histamine, angiotensin II, noradrenaline and dopamine were concentration-dependently shifted to the right in the presence of fasudil [1].
In vivo: Intra-coronary administration of fasudil to dog dose-dependently increased coronary blood flow, with no effect on mean blood pressure or heart rate. Intra-coronary infusion of atropine, diphenhydramine or propranolol did not modify the in vivo coronary vasodilator response to fasudil [1].
Clinical trial: The previous results suggested that fasudil was equally or more effective than nimodipine for the prevention of cerebral vasospasm and subsequent ischemic injury in patients undergoing surgery for SHA [2].
Reference:
[1] Asano T, Suzuki T, Tsuchiya M, Satoh S, Ikegaki I, Shibuya M, Suzuki Y, Hidaka H. Vasodilator actions of HA1077 in vitro and in vivo putatively mediated by the inhibition of protein kinase. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 Dec;98(4):1091-100.
[2] Zhao J, Zhou D, Guo J, Ren Z, Zhou L, Wang S, Zhang Y, Xu B, Zhao K, Wang R, Mao Y, Xu B, Zhang X; Fasudil Aneurysmal Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Study Group. Efficacy and safety of fasudil in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage: final results of a randomized trial of fasudil versus nimodipine. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2011;51(10):679-83.
- Rehmaglutin D
Catalog No.:BCN5851
CAS No.:103744-84-9
- YK-4-279
Catalog No.:BCC2065
CAS No.:1037184-44-3
- Dihydrobonducellin
Catalog No.:BCN3731
CAS No.:103680-87-1
- Mirificin
Catalog No.:BCN2783
CAS No.:103654-50-8
- 2-Carbamoyl-3-hydroxy-1,4-naphthoquinone
Catalog No.:BCC8567
CAS No.:103646-20-4
- Ondansetron hydrochloride dihydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4213
CAS No.:103639-04-9
- Catechin 3-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN5850
CAS No.:103630-03-1
- Cnidimol A
Catalog No.:BCN7167
CAS No.:103629-80-7
- Sumatriptan Succinate
Catalog No.:BCC2502
CAS No.:103628-48-4
- Sumatriptan
Catalog No.:BCC5645
CAS No.:103628-46-2
- (±)-5'-Chloro-5'-deoxy-ENBA
Catalog No.:BCC7716
CAS No.:103626-26-2
- H-Phe(2-Cl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3165
CAS No.:103616-89-3
- Shionone
Catalog No.:BCN1274
CAS No.:10376-48-4
- R428
Catalog No.:BCC3692
CAS No.:1037624-75-1
- Gimeracil
Catalog No.:BCC2296
CAS No.:103766-25-2
- Ganoderic acid C2
Catalog No.:BCN3036
CAS No.:103773-62-2
- MBX-2982
Catalog No.:BCC1732
CAS No.:1037792-44-1
- KX2-391 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC1686
CAS No.:1038395-65-1
- 7-Prenylumbelliferone
Catalog No.:BCN2938
CAS No.:10387-50-5
- 4'-O-Methyllicoflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN4827
CAS No.:1038753-13-7
- Lazabemide hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7371
CAS No.:103878-83-7
- Cycloart-25-ene-3,24-diol
Catalog No.:BCN5852
CAS No.:10388-48-4
- Procyanidin A1
Catalog No.:BCN6809
CAS No.:103883-03-0
- Lacidipine
Catalog No.:BCC4403
CAS No.:103890-78-4
RhoA/ROCK pathway inhibition by fasudil suppresses the vasculogenic mimicry of U2OS osteosarcoma cells in vitro.[Pubmed:28225457]
Anticancer Drugs. 2017 Jun;28(5):514-521.
GTPase RhoA and its downstream Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinases (ROCKs) are frequently overexpressed in human cancers. Inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK pathway blocks angiogenesis mediated by the vascular endothelial growth factor, which led us to investigate the role of this pathway in vasculogenic mimicry (VM) - a process by which aggressive cancer cells form vessel-like structures that provide adequate blood supply for tumor growth. We showed that the expression of RhoA and its effector kinases ROCK1/2 was much higher in human osteosarcoma (OS) tissues and the human OS cell line U2OS than in nontumorous tissues and cell line hFOB 1.19 using western blot analysis and real-time PCR. Inhibition of the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway by the pharmacological inhibitor Fasudil reduced vascular-like channels of U2OS cells in Matrigel. Furthermore, we used rhodamine-phalloidin immunofluorescence, wound healing assay, and transwell migration assay to examine the effect of Fasudil on tumor cell plasticity and motility, both of which play key roles in VM formation. Finally, we explored the underlying mechanisms of Fasudil-induced VM destruction. In this context, we showed that the RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway is a novel regulator in VM of U2OS OS cells and suggest that Fasudil in conjunction with established treatments may present a novel therapeutic strategy for OS.
Cocktail of Superoxide Dismutase and Fasudil Encapsulated in Targeted Liposomes Slows PAH Progression at a Reduced Dosing Frequency.[Pubmed:28165252]
Mol Pharm. 2017 Mar 6;14(3):830-841.
Currently, two or more pulmonary vasodilators are used to treat pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH), but conventional vasodilators alone cannot reverse disease progression. In this study, we tested the hypothesis that a combination therapy comprising a vasodilator plus a therapeutic agent that slows pulmonary arterial remodeling and right heart hypertrophy is an efficacious alternative to current vasodilator-based PAH therapy. Thus, we encapsulated a cocktail of superoxide dismutase (SOD), a superoxide scavenger, and Fasudil, a specific rho-kinase inhibitor, into a liposomal formulation equipped with a homing peptide, CAR. We evaluated the effect of the formulations on pulmonary hemodynamics in monocrotaline-induced PAH rats (MCT-induced PAH) and assessed the formulation's efficacy in slowing the disease progression in Sugen-5416/hypoxia-induced PAH rats (SU/hypoxia-induced PAH). For acute studies, we monitored both mean pulmonary and systemic arterial pressures (mPAP and mSAP) for 2 to 6 h after a single dose of the plain drugs or formulations. In chronic studies, PAH rats received plain drugs every 48 h and the formulations every 72 h for 21 days. In MCT-induced PAH rats, CAR-modified liposomes containing Fasudil plus SOD elicited a more pronounced, prolonged, and selective reduction in mPAP than unmodified liposomes and plain drugs did. In SU/hypoxia-induced PAH rats, the formulation produced a >50% reduction in mPAP and slowed right ventricular hypertrophy. When compared with individual plain drugs or combination, CAR-modified-liposomes containing both drugs reduced the extent of collagen deposition, muscularization of arteries, increased SOD levels in the lungs, and decreased the expression of pSTAT-3 and p-MYPT1. Overall, CAR-modified-liposomes of SOD plus Fasudil, given every 72 h, was as efficacious as plain drugs, given every 48 h, suggesting that the formulation can reduce the total drug intake, systemic exposures, and dosing frequency.
Rho Kinase Inhibition with Fasudil in the SOD1(G93A) Mouse Model of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis-Symptomatic Treatment Potential after Disease Onset.[Pubmed:28197100]
Front Pharmacol. 2017 Jan 31;8:17.
Despite an improved understanding of the genetic background and the pathomechanisms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) no novel disease-modifying therapies have been successfully implemented in clinical routine. Riluzole still remains the only clinically approved substance in human ALS treatment with limited efficacy. We have previously identified pharmacological rho kinase (ROCK) inhibitors as orally applicable substances in SOD1.G93A transgenic ALS mice (SOD1(G93A)), which are able to extend survival time and improve motor function after presymptomatic treatment. Here, we have evaluated the therapeutic effect of the orally administered ROCK inhibitor Fasudil starting at a symptomatic disease stage, more realistically reflecting the clinical situation. Oral Fasudil treatment was initiated at a symptomatic stage at 80 days of life (d80) with 30 or 100 mg/kg body weight in both female and male mice. While baseline neurological scoring and survival were not influenced, Fasudil significantly improved motor behavior in male mice. Spinal cord pathology of motoneurons (MN) and infiltrating microglial cells (MG) at disease end-stage were not significantly modified. Although treatment after symptom onset was less potent than treatment in asymptomatic animals, our study shows the therapeutic benefits of this well-tolerated substance, which is already in clinical use for other indications.
Aldehyde oxidase-dependent species difference in hepatic metabolism of fasudil to hydroxyfasudil.[Pubmed:28166443]
Xenobiotica. 2018 Feb;48(2):170-177.
1. An investigation on the metabolic mechanism of Fasudil to hydroxyFasudil was conducted in vitro using liver subcellular fractions of different species. HydroxyFasudil was generated in large amounts by rat liver S9 and to a similar extent by human liver S9 but was not detected in dog liver S9 incubations. 2. Studies with various molybdenum hydroxylase inhibitors demonstrated that aldehyde oxidase (AO), but not xanthine oxidase (XO), selectively catalyzed Fasudil to hydroxyFasudil in both rat and human liver cytosol. In addition, the oxygen atom incorporated into hydroxyFasudil was derived from water rather than atmospheric oxygen, which further corroborated AO involvement. 3. Enzyme kinetics experiments revealed that Fasudil had a higher affinity to human hepatic AO than to rat hepatic AO. Besides, significantly different in vivo pharmacokinetic parameters observed between male and female rats indicated that the AO activity in rats was gender-dependent. 4. The present study provided first evidences that AO causes differences in Fasudil metabolism between species.


