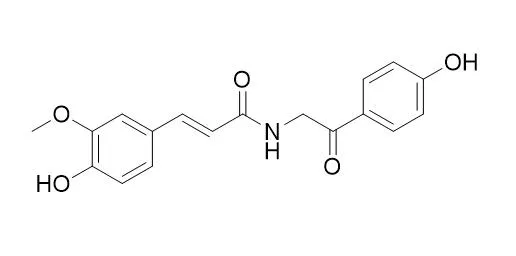
TerrestriamideCAS# 157536-49-7 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 157536-49-7 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C18H17NO5 | M.Wt | 327.3 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Terrestriamide Dilution Calculator

Terrestriamide Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0553 mL | 15.2765 mL | 30.553 mL | 61.106 mL | 76.3825 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6111 mL | 3.0553 mL | 6.1106 mL | 12.2212 mL | 15.2765 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3055 mL | 1.5277 mL | 3.0553 mL | 6.1106 mL | 7.6383 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0611 mL | 0.3055 mL | 0.6111 mL | 1.2221 mL | 1.5277 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0306 mL | 0.1528 mL | 0.3055 mL | 0.6111 mL | 0.7638 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Quercetin-5-O-glucoside-3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCX2138
CAS No.:1478622-04-6
- Praeroside I
Catalog No.:BCX2137
CAS No.:121064-73-1
- Cryptostigmin II
Catalog No.:BCX2136
CAS No.:50906-57-5
- Davidigenin
Catalog No.:BCX2135
CAS No.:23130-26-9
- Pinocembrin 7-O-neohesperidoside
Catalog No.:BCX2134
CAS No.:13241-31-1
- Gerardianin A
Catalog No.:BCX2133
CAS No.:137171-31-4
- Euphopiloside A
Catalog No.:BCX2132
CAS No.:1610615-04-7
- Graciliflorin F
Catalog No.:BCX2131
CAS No.:1413941-67-9
- Eugenol 4-O-beta-D-(6'-O-galloyl) glucopyranoside
Catalog No.:BCX2130
CAS No.:152041-15-1
- Plumbagic acid
Catalog No.:BCX2129
CAS No.:75640-06-1
- Etuycomanol
Catalog No.:BCX2128
CAS No.:84633-28-3
- Ellagic acid glucoside
Catalog No.:BCX2127
CAS No.:163774-64-9
- Auranamide
Catalog No.:BCX2140
CAS No.:740813-53-0
- 5-Allyl-1-methoxy-2,3-dihydroxybenzene
Catalog No.:BCX2141
CAS No.:4055-72-5
- Notoginsenoside E
Catalog No.:BCX2142
CAS No.:193976-50-0
- Hydrastinine
Catalog No.:BCX2143
CAS No.:5936-29-8
- 15-O-Methylgraciliflorin F
Catalog No.:BCX2144
CAS No.:1411994-51-8
- 4-Hydroxy-2-methoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX2145
CAS No.:90111-34-5
- Mangostanin
Catalog No.:BCX2146
CAS No.:463342-39-4
- Monoisovalerate
Catalog No.:BCX2147
CAS No.:95486-32-1
- Ajugamarin A1
Catalog No.:BCX2148
CAS No.:78798-40-0
- Obtusichromoneside B
Catalog No.:BCX2149
CAS No.:2414481-39-1
- 3,4-Dihydroxy-5-methoxybenzoic acidmethylester
Catalog No.:BCX2150
CAS No.:3934-86-9
- Leonoside F
Catalog No.:BCX2151
CAS No.:1360075-79-1
In silico study of medicinal plants with cyclodextrin inclusion complex as the potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M(pro)) and spike (S) receptor.[Pubmed:34189252]
Inform Med Unlocked. 2021;25:100645.
The current outbreak of novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) causes an alarming number of deaths in 221 countries around the world. Nowadays, there is no specific and effective drug regimen for curing COVID-19. Since the COVID-19 pandemic, several medicinal plants with promising results in the previous SARS-CoV could be used to treat SARS-CoV-2 infected patients. This work assesses proven medicinal plants as potential inhibitors against SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) and spike (S) receptors by employing in silico methods. Molecular docking studies and 3D structure-based pharmacophore modeling were performed to identify the molecular interactions of potential active molecules with the Mpro and (S) receptor of SARS-CoV-2. The drug-likeness and ADME properties were also predicted to support the drug-like nature of the selected active molecules. The results indicated that the most favorable ligand was Terrestriamide with (DeltaG: horizontal line 8.70 kcal/mol; Ki: 0.417 muM) and (DeltaG: horizontal line 7.02 kcal/mol; Ki: 7.21 muM) for Mpro and (S) receptor, respectively. Terrestriamide is also supported with a high drug-likeness value and appropriate ADME profile. Furthermore, to improve drug delivery, the cyclodextrin inclusion complex was calculated based on semi-empirical quantum mechanical methods. Terrestriamide/gamma-cyclodextrin is the most favorable pathway of inclusion complex formation and could be used to treat COVID-19.
Phenolic amides from Tribulus terrestris and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 cells.[Pubmed:29177586]
Arch Pharm Res. 2018 Feb;41(2):192-195.
A new phenolic amide, named cis-Terrestriamide (7), together with ten known compounds (1-6, 8-11), were isolated from the methanolic extract of the fruits of Tribulus terrestris. The structure of 7 was elucidated on the basis of extensive analyses of 1D and 2D nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopic and high resolution mass spectrometry data. Compounds 1, 2, 5, 6, 8, 9, and 11 exhibited inhibitory effects on the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 cells, with IC(50) values of 18.7-49.4 muM.
Tribuli fructus constituents protect against tacrine-induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells.[Pubmed:20191345]
Arch Pharm Res. 2010 Jan;33(1):67-70.
A new phenolic amide, tribulusimide D (4-hydroxy-N-[3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-1-oxo-2-propen-1-yl]-3-methoxybenzamide) (1), together with a known phenolic amide, Terrestriamide ((E)-3-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-N-[2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-oxoethyl]-prop-2-enamide) (2) and a flavonol glycoside, quercetin-3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3) were isolated from the H2O extract of Tribuli Fructus. Compounds 1 and 3 showed significant hepatoprotective activities, with EC50 values of 13.46 +/- 0.2 and 7.06 +/- 0.7 microM, respectively, against tacrine-induced cytotoxicity in HepG2 cells.
One new cinnamic imide dervative from the fruits of Tribulus terrestris.[Pubmed:18629718]
Nat Prod Res. 2008;22(11):1007-1010.
One new cinnamic imide derivative, named tribulusimide C (1), was isolated from the fruits of Tribulus terrestris, together with three known compounds, N-p-coumaroyltyramine (2), Terrestriamide (3), N-trans-caffeoyltyramine (4). The structure of 1 was elucidated based on chemical analysis and spectral methods (IR, 1D and 2D NMR, HR-FAB-MS, EI-MS).
Tribulusamide A and B, new hepatoprotective lignanamides from the fruits of Tribulus terrestris: indications of cytoprotective activity in murine hepatocyte culture.[Pubmed:9810268]
Planta Med. 1998 Oct;64(7):628-31.
Tribulusamides A (1) and B (2), new lignanamides embracing two cinnamic amide parts joined in a cis configuration, were isolated from the fruits of Tribulus terrestris, together with four known compounds, N-trans-feruloyltyramine (3), Terrestriamide (4), N-trans-coumaroyltyramine (5), and beta-sitosterol. The structures were elucidated by 2D-NMR spectroscopy. Addition of compounds 1-5, especially 1 and 2, to primary cultured mouse hepatocytes significantly prevented cell death induced by D-galactosamine (D-GalN)/tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-alpha).


