ThiostreptonFOXM1 inhibitor CAS# 1393-48-2 |
- Lomeguatrib
Catalog No.:BCC1133
CAS No.:192441-08-0
- 5-Azacytidine
Catalog No.:BCC1130
CAS No.:320-67-2
- Zebularine
Catalog No.:BCC1136
CAS No.:3690-10-6
- RG 108
Catalog No.:BCC1134
CAS No.:48208-26-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1393-48-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 16129666 | Appearance | Powder |
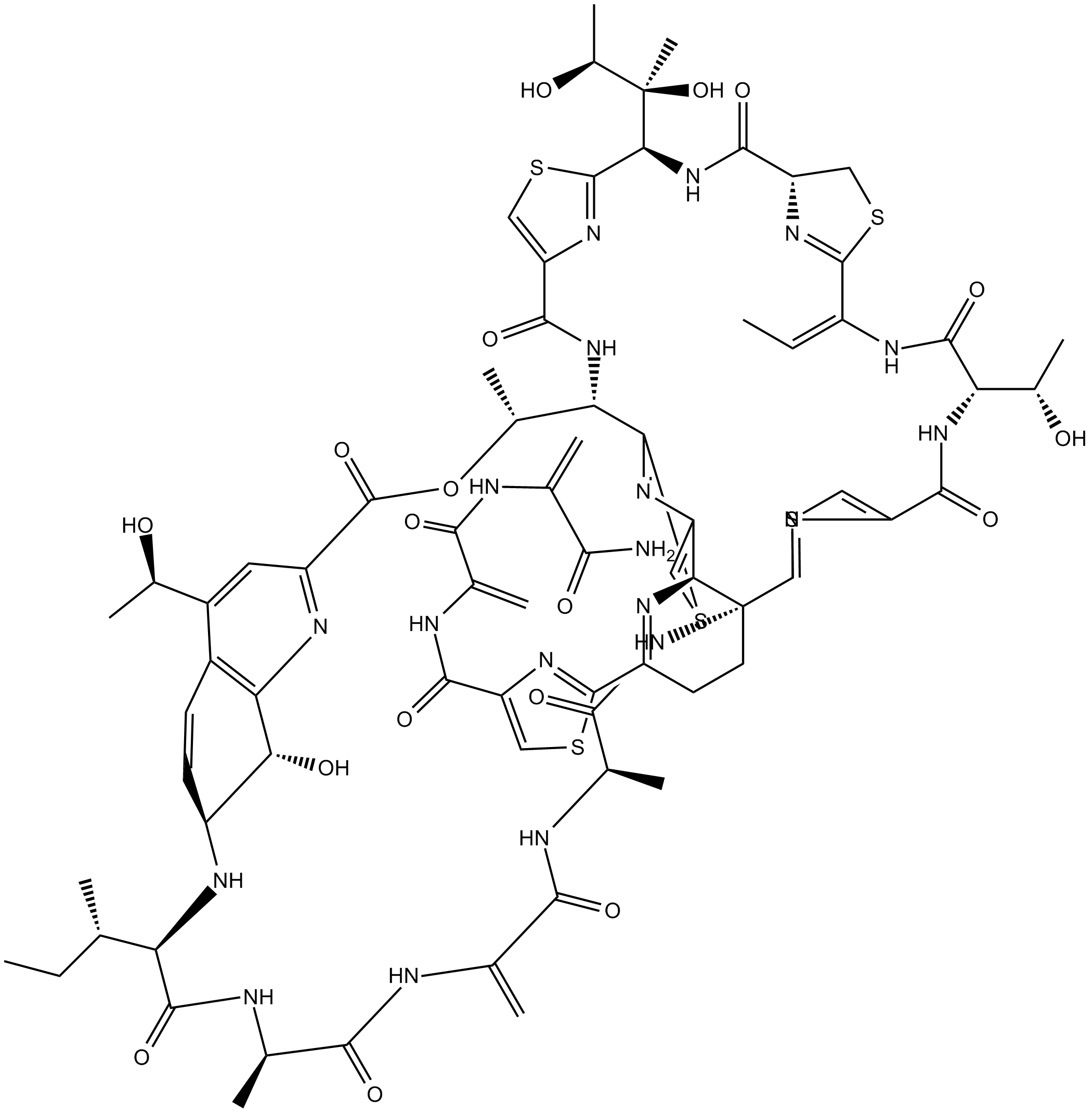
| Formula | C72H85N19O18S5 | M.Wt | 1664.89 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (60.06 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | N-[3-[(3-amino-3-oxoprop-1-en-2-yl)amino]-3-oxoprop-1-en-2-yl]-2-[(11E)-37-butan-2-yl-18-(2,3-dihydroxybutan-2-yl)-11-ethylidene-59-hydroxy-8,31-bis(1-hydroxyethyl)-26,40,46-trimethyl-43-methylidene-6,9,16,23,28,38,41,44,47-nonaoxo-27-oxa-3,13,20,56-tetrathia-7,10,17,24,36,39,42,45,48,52,58,61,62,63,64-pentadecazanonacyclo[23.23.9.329,35.12,5.112,15.119,22.154,57.01,53.032,60]tetrahexaconta-2(64),4,12(63),19(62),21,29(61),30,32(60),33,51,54,57-dodecaen-51-yl]-1,3-thiazole-4-carboxamide | ||
| SMILES | CCC(C)C1C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)NC(C(=O)NC23CCC(=NC2C4=CSC(=N4)C(C(OC(=O)C5=NC6=C(C=CC(C6O)N1)C(=C5)C(C)O)C)NC(=O)C7=CSC(=N7)C(NC(=O)C8CSC(=N8)C(=CC)NC(=O)C(NC(=O)C9=CSC3=N9)C(C)O)C(C)(C(C)O)O)C1=NC(=CS1)C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)NC(=C)C(=O)N)C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NSFFHOGKXHRQEW-DVRIZHICSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C72H85N19O18S5/c1-14-26(3)47-63(105)78-30(7)57(99)75-28(5)56(98)76-31(8)58(100)91-72-19-18-40(66-85-43(22-111-66)59(101)77-29(6)55(97)74-27(4)54(73)96)81-52(72)42-21-112-67(83-42)49(34(11)109-69(107)41-20-37(32(9)92)36-16-17-39(79-47)51(95)50(36)80-41)89-60(102)44-24-113-68(86-44)53(71(13,108)35(12)94)90-62(104)45-23-110-65(84-45)38(15-2)82-64(106)48(33(10)93)88-61(103)46-25-114-70(72)87-46/h15-17,20-22,24-26,30-35,39,45,47-49,51-53,79,92-95,108H,4-6,14,18-19,23H2,1-3,7-13H3,(H2,73,96)(H,74,97)(H,75,99)(H,76,98)(H,77,101)(H,78,105)(H,82,106)(H,88,103)(H,89,102)(H,90,104)(H,91,100)/b38-15+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis. Inhibits mRNA-tRNA translocation by GTPase elongation factor G (EF-G), EF-TU(GTP)-catalyzed aa-tRNA delivery and the activity of initiation factor 2 (IF-2). Antitumor agent; induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in breast cancer cells via downregulation of FOXM1 expression. |

Thiostrepton Dilution Calculator

Thiostrepton Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.6006 mL | 3.0032 mL | 6.0064 mL | 12.0128 mL | 15.016 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.1201 mL | 0.6006 mL | 1.2013 mL | 2.4026 mL | 3.0032 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.0601 mL | 0.3003 mL | 0.6006 mL | 1.2013 mL | 1.5016 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.012 mL | 0.0601 mL | 0.1201 mL | 0.2403 mL | 0.3003 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.006 mL | 0.03 mL | 0.0601 mL | 0.1201 mL | 0.1502 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Thiazole antibiotic thiostrepton is an inhibitor of Forkhead box M1 (FOXM1), which effectively reduces cancer cell growth through downregulation of FOXM1. FOXM1 is a transcription factors that regulate expression of genes involved in maintenance of genomic stability and cell cycle progression.
In vitro: Thiostrepton inhibits the transcriptional activity and FOXM1 expression, and induces strong apoptosis in human cancer cells of different origin that correlates with suppression of FOXM1, including leukemia, neuroblastoma, liver cancer, melanoma and prostate cancer cells. Thiostrepton binds FOXM1 on the promoter site to inhibit transcriptional activity of FOXM1 through the FOXM1 autoregulation mechanism [1].
In vivo: Thiostrepton suppressed tumor growth in a human breast cancer xenograft model. Treatment with developed micelle-thiostrepton nanoparticles decreased xenograft tumor growth induced by the human MDA-MB-231 breast and HepG2 liver cancer cell lines. These apoptosis activities in drug-treated tumors were correlated with in vivo suppression of oncogenic FOXM1 [1].
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
Reference:
[1] Gartel AL. Suppression of the Oncogenic Transcription Factor FOXM1 by Proteasome Inhibitors. Scientifica (Cairo). 2014;2014:596528.
- KN-93
Catalog No.:BCC1683
CAS No.:139298-40-1
- MDL 100907
Catalog No.:BCC7877
CAS No.:139290-65-6
- Zolmitriptan
Catalog No.:BCC5062
CAS No.:139264-17-8
- H2L5186303
Catalog No.:BCC6315
CAS No.:139262-76-3
- Fmoc-Lys-OH.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3512
CAS No.:139262-23-0
- G-36
Catalog No.:BCC6283
CAS No.:1392487-51-2
- Musellarin C
Catalog No.:BCN7004
CAS No.:1392476-33-3
- Musellarin B
Catalog No.:BCN7192
CAS No.:1392476-32-2
- 3,4-Dihydroxy-2-O-methylanigorufone
Catalog No.:BCN7182
CAS No.:1392307-42-4
- Dodonaflavonol
Catalog No.:BCN6862
CAS No.:1392213-93-2
- 24-Hydroxy-25-ethoxy-3,4-secocycloart-4(28)-en-3-oic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCN7050
CAS No.:1392210-81-9
- Verdinexor (KPT-335)
Catalog No.:BCC5573
CAS No.:1392136-43-4
- KPT-330
Catalog No.:BCC4446
CAS No.:1393477-72-9
- TC LPA5 4
Catalog No.:BCC6267
CAS No.:1393814-38-4
- Guan-fu base A
Catalog No.:BCN8491
CAS No.:1394-48-5
- Tiotropium Bromide hydrate
Catalog No.:BCC4585
CAS No.:139404-48-1
- GNE-317
Catalog No.:BCC5655
CAS No.:1394076-92-6
- 8alpha-Hydroxyhirsutinolide
Catalog No.:BCN7111
CAS No.:1394156-45-6
- Boc-Cysteinol(Bzl)
Catalog No.:BCC3043
CAS No.:139428-96-9
- 6-O-apiosyl-5-O-Methylvisammioside
Catalog No.:BCN7858
CAS No.:139446-82-5
- Methyl 2-(((2'-cyano-[1,1'-biphenyl]-4-yl)methyl)amino)-3-nitrobenzoate
Catalog No.:BCC9033
CAS No.:139481-28-0
- Ethyl 2-ethoxy-1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC8970
CAS No.:139481-41-7
- Methyl 1-[(2'-cyanobiphenyl-4-yl)methyl]-2-ethoxy-1H-benzimidazole-7-carboxylate
Catalog No.:BCC9032
CAS No.:139481-44-0
- Candesartan ethyl ester
Catalog No.:BCC8901
CAS No.:139481-58-6
Inhibition of Sonic Hedgehog Signaling Pathway by Thiazole Antibiotic Thiostrepton Attenuates the CD44+/CD24-Stem-Like Population and Sphere-Forming Capacity in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer.[Pubmed:26963129]
Cell Physiol Biochem. 2016;38(3):1157-70.
BACKGROUND/AIM: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) represents a particular clinical challenge because these cancers do not respond to endocrine therapy or other available targeted agents. The lack of effective agents and obvious targets are major challenges in treating TNBC. In this study we explored the cytostatic effect of thiazole ring containing antibiotic drug Thiostrepton on TNBC cell lines and investigated the molecular mechanism. METHODS: Cell viability was measured by MTT assay. Cell surface marker was monitored by FCM. Western blot was applied to assess the protein expression levels of target genes. RESULTS: We found that Thiostrepton remarkably suppressed the CD44+/CD24- stem-like population and sphere forming capacity of TNBC cell lines. Notably, we showed for the first time that Thiostrepton exerted its pharmacological action by targeting sonic hedgehog (SHH) signaling pathway. Thiostrepton repressed SHH ligand expression and reduced Gli-1 nuclear localization in TNBC cell line. Furthermore, the downstream target of SHH signaling undergone dose-dependent, rapid, and sustained loss of mRNA transcript level after Thiostrepton treatment. Finally, we showed that SHH ligand was essential for maintaining CD44+/CD24- stem-like population in TNBC cell line. CONCLUSION: We conclude that Thiostrepton suppresses the CD44+/CD24- stem-like population through inhibition of SHH signaling pathway. Our results give a new insight into the mechanism of Thiostrepton anti-tumor activity and suggest Thiostrepton as a promising agent that targets hedgehog signaling pathway in TNBC.
Precursor-Directed Mutational Biosynthesis Facilitates the Functional Assignment of Two Cytochromes P450 in Thiostrepton Biosynthesis.[Pubmed:27560135]
ACS Chem Biol. 2016 Oct 21;11(10):2673-2678.
Side-ring-modified Thiostrepton (TSR) derivatives that vary in their quinaldic acid (QA) substitution possess more potent biological activities and better pharmaceutical properties than the parent compound. In this work, we sought to introduce fluorine onto C-7' or C-8' of the TSR QA moiety via precursor-directed mutational biosynthesis to obtain new TSR variants. Unexpectedly, instead of the target product, the exogenous chemical feeding of 7-F-QA into the DeltatsrT mutant strain resulted in a unique TSR analog with an incomplete side-ring structure and an unoxidized QA moiety (1). Accordingly, two cytochrome P450 genes, tsrP and tsrR, were in-frame deleted to elucidate the candidate responsible for the monooxidation of the QA moiety in TSR. The unfluorinated analog of compound 1 that was thus isolated from DeltatsrP (2) and the abolishment of TSR production in DeltatsrR revealed not only the biosynthetic logic of the TSR side-ring but also the essential checkpoint in TSR maturation before macro-ring closure.
Complete Genome Sequence of Thiostrepton-Producing Streptomyces laurentii ATCC 31255.[Pubmed:27257211]
Genome Announc. 2016 Jun 2;4(3). pii: 4/3/e00360-16.
Streptomyces laurentii ATCC 31255 produces Thiostrepton, a thiopeptide class antibiotic. Here, we report the complete genome sequence for this strain, which contains a total of 8,032,664 bp, 7,452 predicted coding sequences, and a G+C content of 72.3%.
An alpha/beta-hydrolase fold protein in the biosynthesis of thiostrepton exhibits a dual activity for endopeptidyl hydrolysis and epoxide ring opening/macrocyclization.[Pubmed:27911800]
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Dec 13;113(50):14318-14323.
Thiostrepton (TSR), an archetypal bimacrocyclic thiopeptide antibiotic that arises from complex posttranslational modifications of a genetically encoded precursor peptide, possesses a quinaldic acid (QA) moiety within the side-ring system of a thiopeptide-characteristic framework. Focusing on selective engineering of the QA moiety, i.e., by fluorination or methylation, we have recently designed and biosynthesized biologically more active TSR analogs. Using these analogs as chemical probes, we uncovered an unusual indirect mechanism of TSR-type thiopeptides, which are able to act against intracellular pathogens through host autophagy induction in addition to direct targeting of bacterial ribosome. Herein, we report the accumulation of 6'-fluoro-7', 8'-epoxy-TSR, a key intermediate in the preparation of the analog 6'-fluoro-TSR. This unexpected finding led to unveiling of the TSR maturation process, which involves an unusual dual activity of TsrI, an alpha/beta-hydrolase fold protein, for cascade C-N bond cleavage and formation during side-ring system construction. These two functions of TsrI rely on the same catalytic triad, Ser72-His200-Asp191, which first mediates endopeptidyl hydrolysis that occurs selectively between the residues Met-1 and Ile1 for removal of the leader peptide and then triggers epoxide ring opening for closure of the QA-containing side-ring system in a regio- and stereo-specific manner. The former reaction likely requires the formation of an acyl-Ser72 enzyme intermediate; in contrast, the latter is independent of Ser72. Consequently, C-6' fluorination of QA lowers the reactivity of the epoxide intermediate and, thereby, allows the dissection of the TsrI-associated enzymatic process that proceeds rapidly and typically is difficult to be realized during TSR biosynthesis.
Thiostrepton selectively targets breast cancer cells through inhibition of forkhead box M1 expression.[Pubmed:18645012]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2008 Jul;7(7):2022-32.
Elevated expression or activity of the transcription factor forkhead box M1 (FOXM1) is associated with the development and progression of many malignancies, including breast cancer. In this study, we show that the thiazole antibiotic Thiostrepton selectively induces cell cycle arrest and cell death in breast cancer cells through down-regulating FOXM1 expression. Crucially, our data show that Thiostrepton treatment reduced FOXM1 expression in a time- and dose-dependent manner, independent of de novo protein synthesis and predominantly at transcriptional and gene promoter levels. Our results indicate that Thiostrepton can induce cell death through caspase-dependent intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways as well as through caspase-independent death mechanisms, as observed in MCF-7 cells, which are deficient of caspase-3 and caspase-7. Cell cycle analysis showed that Thiostrepton induced cell cycle arrest at G(1) and S phases and cell death, concomitant with FOXM1 repression in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, Thiostrepton also shows efficacy in repressing breast cancer cell migration, metastasis, and transformation, which are all downstream functional attributes of FOXM1. We also show that overexpression of a constitutively active FOXM1 mutant, DeltaN-FOXM1, can abrogate the antiproliferative effects of Thiostrepton. Interestingly, Thiostrepton has no affect on FOXM1 expression and proliferation of the untransformed MCF-10A breast epithelial cells. Collectively, our data show that FOXM1 is one of the primary cellular targets of Thiostrepton in breast cancer cells and that Thiostrepton may represent a novel lead compound for targeted therapy of breast cancer with minimal toxicity against noncancer cells.
Thiostrepton inhibition of tRNA delivery to the ribosome.[Pubmed:17951333]
RNA. 2007 Dec;13(12):2091-7.
Ribosome-stimulated hydrolysis of guanosine-5'-triphosphate (GTP) by guanosine triphosphatase (GTPase) translation factors drives protein synthesis by the ribosome. Allosteric coupling of GTP hydrolysis by elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu) at the ribosomal GTPase center to messenger RNA (mRNA) codon:aminoacyl-transfer RNA (aa-tRNA) anticodon recognition at the ribosomal decoding site is essential for accurate and rapid aa-tRNA selection. Here we use single-molecule methods to investigate the mechanism of action of the antibiotic Thiostrepton and show that the GTPase center of the ribosome has at least two discrete functions during aa-tRNA selection: binding of EF-Tu(GTP) and stimulation of GTP hydrolysis by the factor. We separate these two functions of the GTPase center and assign each to distinct, conserved structural regions of the ribosome. The data provide a specific model for the coupling between the decoding site and the GTPase center during aa-tRNA selection as well as a general mechanistic model for ribosome-stimulated GTP hydrolysis by GTPase translation factors.


