ValepotriateCAS# 18296-44-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 18296-44-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442436 | Appearance | Oil |
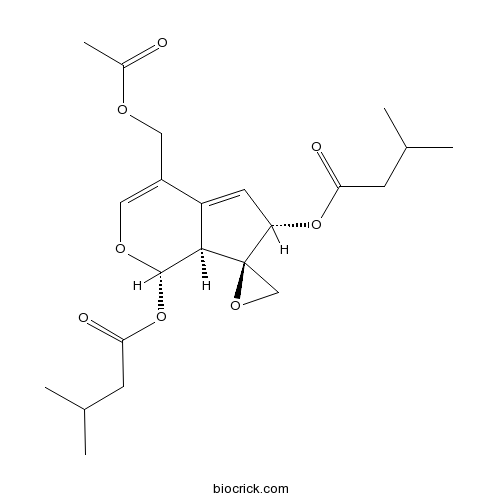
| Formula | C22H30NO8 | M.Wt | 436.5 |
| Type of Compound | Iridoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Halazuchrome B; Valepotriate; Valtratum | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in chloroform; slightly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | [(1S,6S,7R,7aS)-4-(acetyloxymethyl)-1-(3-methylbutanoyloxy)spiro[6,7a-dihydro-1H-cyclopenta[c]pyran-7,2'-oxirane]-6-yl] 3-methylbutanoate | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)CC(=O)OC1C=C2C(C13CO3)C(OC=C2COC(=O)C)OC(=O)CC(C)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BDIAUFOIMFAIPU-KVJIRVJXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C22H30O8/c1-12(2)6-18(24)29-17-8-16-15(9-26-14(5)23)10-27-21(20(16)22(17)11-28-22)30-19(25)7-13(3)4/h8,10,12-13,17,20-21H,6-7,9,11H2,1-5H3/t17-,20+,21-,22+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Valepotriates, a new class of cytotoxic and antitumor agents, they are very potent cytotoxic agents for the HTC hepatoma cells. Valepotriates may have a potential anxiolytic effect on the psychic symptoms of anxiety. Valepotriate fraction can have sedative effects and affect behavioral parameters related to recognition memory. |
| In vitro | Valepotriates, a new class of cytotoxic and antitumor agents.[Pubmed: 7232547 ]Planta Med. 1981 Jan;41(1):21-8.
|
| In vivo | A Valepotriate Fraction of Valeriana glechomifolia Shows Sedative and Anxiolytic Properties and Impairs Recognition But Not Aversive Memory in Mice.[Pubmed: 20047889]Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2010 Jan 4.Plants of the genus Valeriana (Valerianaceae) are used in traditional medicine as a mild sedative, antispasmodic and tranquilizer in many countries.
Effect of valepotriates (valerian extract) in generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled pilot study.[Pubmed: 12410546]Phytother Res. 2002 Nov;16(7):650-4.The aim of the present study was to carry out a controlled pilot study on the putative anxiolytic effect of Valepotriates.
|
| Cell Research | Valepotriate production of normal and colchicine-treated cell suspension cultures of Valeriana wallichii.[Pubmed: 4009183]J Nat Prod. 1985 Jan-Feb;48(1):17-21.
Colchicine-treated suspension cultures of Valeriana wallichii produce higher amounts of Valepotriates than did the respective untreated cultures.
|

Valepotriate Dilution Calculator

Valepotriate Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.291 mL | 11.4548 mL | 22.9095 mL | 45.819 mL | 57.2738 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4582 mL | 2.291 mL | 4.5819 mL | 9.1638 mL | 11.4548 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2291 mL | 1.1455 mL | 2.291 mL | 4.5819 mL | 5.7274 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0458 mL | 0.2291 mL | 0.4582 mL | 0.9164 mL | 1.1455 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0229 mL | 0.1145 mL | 0.2291 mL | 0.4582 mL | 0.5727 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Dibritannilactone B
Catalog No.:BCN7776
CAS No.:1829580-18-8
- (9Z,12Z)-N-Benzyloctadeca-9,12-dienamide
Catalog No.:BCN1518
CAS No.:18286-71-0
- Thalidezine
Catalog No.:BCN7763
CAS No.:18251-36-0
- SB 225002
Catalog No.:BCC8077
CAS No.:182498-32-4
- TPMPA
Catalog No.:BCC6903
CAS No.:182485-36-5
- Lomitapide
Catalog No.:BCC5570
CAS No.:182431-12-5
- Rupatadine Fumarate
Catalog No.:BCC4535
CAS No.:182349-12-8
- Baldrinal
Catalog No.:BCN2667
CAS No.:18234-46-3
- Antibiotic 2158
Catalog No.:BCN1825
CAS No.:182320-34-9
- Antibiotic ZG 1494alpha
Catalog No.:BCN1850
CAS No.:182320-33-8
- Synthalin sulfate
Catalog No.:BCC6730
CAS No.:182285-12-7
- Lirioprolioside B
Catalog No.:BCN2740
CAS No.:182284-68-0
- Didrovaltrate
Catalog No.:BCN7124
CAS No.:18296-45-2
- 3,4-O-Isopropylidene shikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1147
CAS No.:183075-03-8
- Fabiatrin
Catalog No.:BCN2920
CAS No.:18309-73-4
- Cabazitaxel
Catalog No.:BCC4966
CAS No.:183133-96-2
- Guanylin (human)
Catalog No.:BCC7204
CAS No.:183200-12-6
- Tipiracil hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC2001
CAS No.:183204-72-0
- 1,7-Dihydroxy-2,3-methylenedioxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7543
CAS No.:183210-63-1
- AM251
Catalog No.:BCC4412
CAS No.:183232-66-8
- 2-Acetoxy-3-deacetoxycaesaldekarin E
Catalog No.:BCN7476
CAS No.:18326-06-2
- 5-(1-Piperazinyl)benzofuran-2-carboxamide
Catalog No.:BCC8717
CAS No.:183288-46-2
- Erlotinib Hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC3645
CAS No.:183319-69-9
- OSI-420
Catalog No.:BCC4472
CAS No.:183320-51-6
Effect of valepotriates (valerian extract) in generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized placebo-controlled pilot study.[Pubmed:12410546]
Phytother Res. 2002 Nov;16(7):650-4.
The aim of the present study was to carry out a controlled pilot study on the putative anxiolytic effect of Valepotriates. Thirty-six outpatients with generalized anxiety disorder (DSM III-R), after a 2-week wash-out, were randomized to one of the following three treatments for 4 weeks (n = 12 per group): Valepotriates (mean daily dose: 81.3 mg), diazepam (mean daily dose: 6.5 mg), or placebo. A parallel, double-blind, flexible-dose, placebo-controlled design was employed. No significant difference was observed among the three groups at baseline or in the change from baseline on the Hamilton anxiety scale (HAM-A) or in the trait part of the state-trait anxiety inventory (STAI-trait). Moreover, the three groups presented a significant reduction in the total HAM-A scores. On the other hand, only the diazepam and Valepotriates groups showed a significant reduction in the psychic factor of HAM-A. The diazepam group also presented a significant reduction of the STAI-trait. Although the principal analysis (HAM-A between group comparison) found negative results (probably due to the small sample size in each group), the preliminary data obtained in the present study suggest that the Valepotriates may have a potential anxiolytic effect on the psychic symptoms of anxiety. However, since the number of subjects per group was very small, the present results must be viewed as preliminary. Thus, further studies addressing this issue are warranted.
A Valepotriate Fraction of Valeriana glechomifolia Shows Sedative and Anxiolytic Properties and Impairs Recognition But Not Aversive Memory in Mice.[Pubmed:20047889]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2011;2011:720853.
Plants of the genus Valeriana (Valerianaceae) are used in traditional medicine as a mild sedative, antispasmodic and tranquilizer in many countries. This study was undertaken to explore the neurobehavioral effects of systemic administration of a Valepotriate extract fraction of known quantitative composition of Valeriana glechomifolia (endemic of southern Brazil) in mice. Adult animals were treated with a single intraperitoneal injection of Valepotriate fraction (VF) in the concentrations of 1, 3 or 10 mg kg(-1), or with vehicle in the pre-training period before each behavioral test. During the exploration of an open field, mice treated with 10 mg kg(-1) of VF showed reduced locomotion and exploratory behavior. Although overall habituation sessions for locomotion and exploratory behavior among vehicle control and doses of VF were not affected, comparison between open-field and habituation sessions within each treatment showed that VF administration at 1 and 10 mg kg(-1) impaired habituation. In the elevated plus-maze test, mice treated with VF (10 mg kg(-1)) showed a significant increase in the percentage of time spent in the open arms without significant effects in the number of total arm entries. VF at 3 mg kg(-1) produced an impairment of novel-object recognition memory. In contrast, VF did not affect fear-related memory assessed in an inhibitory avoidance task. The results indicate that VF can have sedative effects and affect behavioral parameters related to recognition memory.
Valepotriate content in different in vitro cultures of Valerianaceae and characterization of Valeriana officinalis L. callus during a growth period.[Pubmed:6646985]
Pharm Weekbl Sci. 1983 Oct 21;5(5):205-9.
Different in vitro cultures of Valerianaceae were analysed for Valepotriate content [(iso)valtrate, acevaltrate, didrovaltrate] in a study on properties of production in vitro (plant species, growth conditions, differentiation level, Valepotriate content of the medium after growth). The in vitro cultures were: callus cultures of Valeriana officinalis L., Valerianella locusta L. and Centranthus ruber L.DC.; a suspension culture of Valeriana officinalis L. and a root organ culture of Centranthus ruber L.DC. All of the cultures produced Valepotriates in vitro in different amounts. None of the media that had served for growth contained any Valepotriates. In order to characterize the in vitro growth more precisely different parameters were analysed at different time intervals during a growth period in one of the cultures (callus culture of Valeriana officinalis L.). These different parameters were: fresh and dry weight, lipid and nitrogen content and (iso)valtrate content. This study during a growth period was performed on two media differing in plant hormone content.
Valepotriate production of normal and colchicine-treated cell suspension cultures of Valeriana wallichii.[Pubmed:4009183]
J Nat Prod. 1985 Jan-Feb;48(1):17-21.
Colchicine-treated suspension cultures of Valeriana wallichii produce higher amounts of Valepotriates than did the respective untreated cultures. The ability to produce Valepotriates in the treated culture remains in the absence of colchicine even if the chromosome status returns to normal. When the colchicine treatment is repeated, a further increase in Valepotriate production can be obtained. Besides known Valepotriates, a series of fourteen new compounds, hitherto not described for the parent plant, were isolated from the cell suspension culture. Eight of them are also found in plant parts in minor amounts, but six seem to be present only in tissue cultures of V. wallichii.


