XanthomicrolCAS# 16545-23-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 16545-23-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 73207 | Appearance | Yellow powder |
| Formula | C18H16O7 | M.Wt | 344.3 |
| Type of Compound | Flavonoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
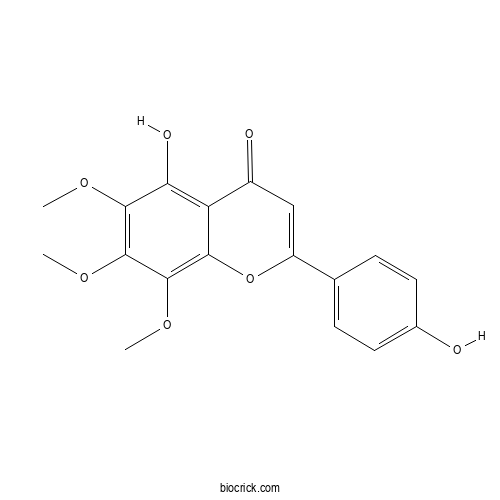
| Chemical Name | 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6,7,8-trimethoxychromen-4-one | ||
| SMILES | COC1=C(C(=C2C(=C1O)C(=O)C=C(O2)C3=CC=C(C=C3)O)OC)OC | ||
| Standard InChIKey | SAMBWAJRKKEEOR-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H16O7/c1-22-16-14(21)13-11(20)8-12(9-4-6-10(19)7-5-9)25-15(13)17(23-2)18(16)24-3/h4-8,19,21H,1-3H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Xanthomicrol Dilution Calculator

Xanthomicrol Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9044 mL | 14.5222 mL | 29.0444 mL | 58.0889 mL | 72.6111 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5809 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8089 mL | 11.6178 mL | 14.5222 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2904 mL | 1.4522 mL | 2.9044 mL | 5.8089 mL | 7.2611 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0581 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 1.1618 mL | 1.4522 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.029 mL | 0.1452 mL | 0.2904 mL | 0.5809 mL | 0.7261 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- N-Acetyl-D-mannosamine
Catalog No.:BCX0513
CAS No.:7772-94-3
- N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
Catalog No.:BCX0512
CAS No.:1811-31-0
- D-Galactosamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCX0511
CAS No.:1772-03-8
- D-Mannosamine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCX0510
CAS No.:5505-63-5
- Moracin N
Catalog No.:BCX0509
CAS No.:135248-05-4
- (S)-5-Hydroxy-1-(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-7-phenylheptan-3-one
Catalog No.:BCX0508
CAS No.:1220110-76-8
- 1β-Hydroxy-8α-methoxyeremophila-7(11),9-dien-12,8β-olide
Catalog No.:BCX0507
CAS No.:849700-45-4
- Methylconiferin
Catalog No.:BCX0506
CAS No.:883150-46-7
- Iristectorin B
Catalog No.:BCX0505
CAS No.:94396-09-5
- Vavain
Catalog No.:BCX0504
CAS No.:199996-77-5
- 6-Demethoxyirigenin
Catalog No.:BCX0503
CAS No.:1348833-10-2
- Oxyphyllenodiol A
Catalog No.:BCX0502
CAS No.:363610-30-4
- 5,7-Dihydroxy-3,8,3',4'-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0515
CAS No.:42923-42-2
- 5,4'-Dihydroxy-6,7,8,3'-tetramethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCX0516
CAS No.:16520-78-8
- Tetrahydroauroglaucin
Catalog No.:BCX0517
CAS No.:40434-07-9
- Sanggenon F
Catalog No.:BCX0518
CAS No.:85889-03-8
- 4-Hydroxyphenylpyruvic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0519
CAS No.:156-39-8
- Isodihydroauroglaucin
Catalog No.:BCX0520
CAS No.:74886-31-0
- Demethoxysudachitin
Catalog No.:BCX0521
CAS No.:4323-80-2
- Oxyphyllenodiol B
Catalog No.:BCX0522
CAS No.:363610-32-6
- Labda-12E,14-dien-16,15-olid-17-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCX0523
CAS No.:1855905-16-6
- Butyl rosmarinate
Catalog No.:BCX0524
CAS No.:222713-83-9
- Dihydroauroglaucin
Catalog No.:BCX0525
CAS No.:77102-91-1
- (E)-5-Hydroxy-6-isoprenyl-2-(pent-1-en-1-yl)benzofuran-4-carbaldehyde
Catalog No.:BCX0526
CAS No.:916602-30-7
Comparative Evaluation of Anticancer Activity of Natural Methoxylated Flavones Xanthomicrol and Eupatilin in A375 Skin Melanoma Cells.[Pubmed:38541630]
Life (Basel). 2024 Feb 26;14(3):304.
Melanoma is a skin cancer caused by the malignant transformation of melanocytes and cutaneous melanoma represents the most aggressive and deadliest type of skin cancer with an increasing incidence worldwide. The main purpose of the present research was to evaluate the anticancer effects of the natural bioactive compounds Xanthomicrol (XAN) and eupatilin (EUP) in human A375 malignant skin melanoma cells, a cell line widely used as an in vitro model of cutaneous melanoma. XAN and EUP are lipophilic methoxylated flavones with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor properties. The effects of XAN and EUP on cell viability, morphology, lipid profile, oxidative status, apoptosis, and mitochondrial membrane polarization were determined and compared in A375 cells. At 24 h-incubation (MTT assay), XAN significantly reduced viability at the dose range of 2.5-200 muM, while EUP showed a significant cytotoxicity from 25 muM. Moreover, both methoxylated flavones induced (at 10 and 25 muM, 24 h-incubation) marked cell morphological alterations (presence of rounded and multi-nucleated cells), signs of apoptosis (NucView 488 assay), and a noteworthy mitochondrial membrane depolarization (MitoView 633 assay), coupled to a marked lipid profile modulation, including variations in the ratio of phospholipid/cholesterol and a decrease in the oleic, palmitic, and palmitoleic acid amounts. Moreover, a remarkable time-dependent ROS generation (2',7'-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate assay) was observed during 3 h-incubation of A375 cancer cells in the presence of XAN and EUP (10 and 25 muM). Our results confirm the potential antitumor effect of natural EUP and XAN in cutaneous melanoma by the activation of multiple anticancer mechanisms.
Preussiate, a new urease inhibitory chalcone from Dioscorea preussii Pax.[Pubmed:37599618]
Nat Prod Res. 2023 Aug 21:1-8.
The phytochemical investigation of the aqueous methanolic extract of the aerial parts of Dioscorea preussii, led to the isolation of a new chalcone preussiate (1) along with 10 other compounds including Xanthomicrol (2), cholestan-3-one (3), arjunolic acid (4), tormentic acid (5), ursolic acid (6), betulin (7), lupeol (8), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (9), isovanillin (10) and vanillic acid (11), being reported for the first time from this plant. Their structures were established by spectroscopic techniques including 2D NMR spectroscopy. All the isolates were subjected to the biological screening but only showed antioxidant and urease inhibitory properties. The compounds 1,8 and 11 displayed the most potent urease inhibitory properties with IC(50) values, 22.4(,) 33.3 and 35.7 microM, respectively, while 3 was moderately active. The compound 11 showed potent antioxidant activity among all the tested isolates with an IC(50) value of 45.3 microM.
Multi-dimensional preparation of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. by normal-phase flash chromatography coupled to counter-current chromatography.[Pubmed:37506459]
J Chromatogr A. 2023 Sep 13;1706:464238.
In this study, a multi-dimensional chromatography system was developed by integrating normal-phase flash chromatography and counter-current chromatography to isolate flavonoids, phenylpropanoids, and thymol from the aerial parts of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. In the online multi-dimensional switching system, a normal-phase flash chromatograph packed with 1.2 g of dry homogeneous silica gel mixture (containing 600 mg of methanol extract) was connected to counter-current chromatography via a six-port valve. Two two-dimensional separations were performed using n-heptane-ethyl acetate-methanol-water (6:4:6:4, v/v) and ethyl acetate-water solvent systems sequentially to separate the constituents of Thymus quinquecostatus Celak. The upper phase of the former solvent system was utilized as both elution solvent for flash chromatography and the stationary phase for counter-current chromatography, while the lower phase of the latter solvent system containing 10 mM trifluoroacetic acid was employed as elution solvent for flash chromatography and one mobile phase in pH gradient counter-current chromatography. Thymol (7) and Xanthomicrol (8), two hydrophobic ingredients, were purified in the initial two-dimensional separation. The subsequent two-dimensional separation yielded six hydrophilic compounds, namely dihydrokaempferol-7-O-D-glucopyranoside (1), lithospermic acid (2), luteolin-7-O-glucuronide (3), rosmarinic acid (4), messerschmidin (5) and apigenin-7-O-D-glucuronide (6). This study represents the first documented use of online multi-dimensional normal-phase flash chromatography coupled to counter-current chromatography for separating constituents from Thymus quinquecostatus Celak.
Xanthomicrol: Effective therapy for cancer treatment.[Pubmed:37102154]
Toxicol Rep. 2023 Feb 21;10:436-440.
Cancer treatment is one of the main challenges of global health. For decades, researchers have been trying to find anti-cancer compounds with minimal side effects. In recent years, flavonoids, as a group of polyphenolic compounds, have attracted the attention of researchers due to their beneficial effects on health. Xanthomicrol is one of the flavonoids that has the ability to inhibit growth, proliferation, survival and cell invasion and ultimately tumor progression. Xanthomicrol, as active anti-cancer compounds, can be effective in the prevention and treatment of cancer. Therefore, the use of flavonoids can be suggested as a treatment along with other medicinal agents. It is obvious that additional investigations in cellular levels and animal models are still needed. In this review article, the effects of Xanthomicrol on various cancers have been reviewed.
Comparative Untargeted Metabolic Profiling of Different Parts of Citrus sinensis Fruits via Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Coupled with Multivariate Data Analyses to Unravel Authenticity.[Pubmed:36766108]
Foods. 2023 Jan 29;12(3):579.
Differences between seven authentic samples of Citrus sinensis var. Valencia peel (albedo and flavedo) and juices from Spain and Uruguay, in addition to a concentrate obtained from Brazil, were investigated by untargeted metabolic profiling. Sixty-six metabolites were detected by nano-liquid chromatography coupled to a high-resolution electrospray-ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometer (nLC-ESI-qTOF-MS) belonging to phenolic acids, coumarins, flavonoid glycosides, limonoids, terpenes, and fatty acids. Eleven metabolites were detected for the first time in Citrus sinensis and identified as citroside A, sinapic acid pentoside, apigenin-C-hexosyl-O-pentoside, chrysoeriol-C-hexoside, di-hexosyl-diosmetin, perilloside A, gingerol, ionone epoxide hydroxy-sphingenine, Xanthomicrol, and coumaryl alcohol-O-hexoside. Some flavonoids were completely absent from the juice, while present most prominently in the Citrus peel, conveying more industrial and economic prospects to the latter. Multivariate data analyses clarified that the differences among orange parts overweighed the geographical source. PCA analysis of ESI-(-)-mode data revealed for hydroxylinoleic acid abundance in flavedo peel from Uruguay the most distant cluster from all others. The PCA analysis of ESI-(+)-mode data provided a clear segregation of the different Citrus sinensis parts primarily due to the large diversity of flavonoids and coumarins among the studied samples.
Non-Volatile Terpenoids and Lipophilic Flavonoids from Achillea erba-rotta Subsp. moschata (Wulfen) I. Richardson.[Pubmed:36679115]
Plants (Basel). 2023 Jan 15;12(2):402.
Musk yarrow (Achillea erba-rotta subsp. moschata (Wulfen) I. Richardson) is endemic to the Central Alps, and is used to flavour alcoholic beverages. Despite its popularity as aromatizing agent and its alleged beneficial effects on digestion, the phytochemical profile of the plant is still largely unknown and undiscovered. As a consequence, its authentication in aromatized products is impossible beyond sensory analysis allowing forgery. To address these issues, we phytochemically characterized a sample of musk yarrow from the Italian Eastern Alps, identifying, in addition to widespread phytochemicals (taraxasterol, apigenin), the guaianolides 3, 8, 9; the seco-caryophyllane 6; and the polymethoxylated lipophilic flavonoids 1, 4, and 5. The flavonoid Xanthomicrol 1, a major constituent of the plant, was cytotoxic to HeLa cells, but only modestly affected primary 3T3 fibroblasts. On account of their stability, detectability by UV absorption, and concentration, the oxygenated flavonoids qualify as markers to validate the supply chain of the plant growers to consumers.
Xanthomicrol Activity in Cancer HeLa Cells: Comparison with Other Natural Methoxylated Flavones.[Pubmed:36677614]
Molecules. 2023 Jan 5;28(2):558.
The methoxylated flavone Xanthomicrol represents an uncommon active phenolic compound identified in herbs/plants with a long application in traditional medicine. It was isolated from a sample of Achillea erba-rotta subsp. moschata (musk yar-row) flowering tops. Xanthomicrol promising biological properties include antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and anticancer activities. This study mainly focused on the evaluation of the Xanthomicrol impact on lipid metabolism in cancer HeLa cells, together with the investigation of the treatment-induced changes in cell growth, morphology, and apoptosis. At the dose range of 5-100 muM, Xanthomicrol (24 h of incubation) significantly reduced viability and modulated lipid profile in cancer Hela cells. It induced marked changes in the phospholipid/cholesterol ratio, significant decreases in the levels of oleic and palmitic acids, and a marked increase of stearic acid, involving an inhibitory effect on de novo lipogenesis and desaturation in cancer cells. Moreover, marked cell morphological alterations, signs of apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest at the G2/M phase were observed in cancer treated cells. The bioactivity profile of Xanthomicrol was compared to that of the anticancer methoxylated flavones eupatilin and artemetin, and structure-activity relationships were underlined.
Flavones, Flavonols, Lignans, and Caffeic Acid Derivatives from Dracocephalum moldavica and Their In Vitro Effects on Multiple Myeloma and Acute Myeloid Leukemia.[Pubmed:36430695]
Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 17;23(22):14219.
Phenolic plant constituents are well known for their health-promoting and cancer chemopreventive properties, and products containing such constituents are therefore readily consumed. In the present work, we isolated 13 phenolic constituents of four different compound classes from the aerial parts of the Moldavian dragonhead, an aromatic and medicinal plant with a high diversity on secondary metabolites. All compounds were tested for their apoptotic effect on myeloma (KMS-12-PE) and AML (Molm-13) cells, with the highest activity observed for the flavone and flavonol derivatives. While diosmetin (6) exhibited the most pronounced effects on the myeloma cell line, two polymethylated flavones, namely cirsimaritin (1) and Xanthomicrol (3), were particularly active against AML cells and therefore subsequently investigated for their antiproliferative effects at lower concentrations. At a concentration of 2.5 microM, cirsimaritin (1) reduced proliferation of Molm-13 cells by 72% while Xanthomicrol (3) even inhibited proliferation to the extent of 84% of control. In addition, both compounds were identified as potent FLT3 inhibitors and thus display promising lead structures for further drug development. Moreover, our results confirmed the chemopreventive properties of flavonoids in general, and in particular of polymethylated flavones, which have been intensively investigated especially over the last decade.
Antinociceptive activity of the ethanolic extract of Trixis angustifolia DC.[Pubmed:34963401]
Nat Prod Res. 2022 Nov;36(22):5813-5816.
The antinociceptive activity of the ethanolic extract of Trixis angustifolia DC. (EETx) was investigated using the acetic acid-induced writhing and the hot-plate tests in mice. In the acetic acid-induced writhing test, mice treated with EETx (50, 100 and 200 mg/kg, p.o.) exhibited reduced writhing (38%, 67%, and 74%, respectively). In the hot-plate test, the three doses administrated increased the nociceptive response time. The phytochemical analysis of EETx led to the isolation of three known compounds, hygric acid (1), 5,6-Dihydroxy-7,8,4'-trimethoxyflavone (2) and Xanthomicrol (3). Compound 1 was identified for the first time in this species. These results demonstrate that T. angustifolia has potential central and peripheral antinociceptive effects and support the ethnomedicinal use of this plant.
A review on the traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities of clove basil (Ocimum gratissimum L.).[Pubmed:34901489]
Heliyon. 2021 Nov 25;7(11):e08404.
In traditional medicine, Ocimum gratissimum (clove basil) is used in the treatment of various diseases such as diabetes, cancer, inflammation, anaemia, diarrhoea, pains, and fungal and bacterial infections. The present study reviewed the phytochemicals, essential oils, and pharmacological activities of O. gratissimum. The bioactive compounds extracted from O. gratissimum include phytochemicals (oleanolic acid, caffeic acid, ellagic acid, epicatechin, sinapic acid, rosmarinic acid, chlorogenic acid, luteolin, apigenin, nepetoidin, Xanthomicrol, nevadensin, salvigenin, gallic acid, catechin, quercetin, rutin, and kaempfero) and essential oils (camphene, beta-caryophyllene, alpha- and beta-pinene, alpha-humulene, sabinene, beta-myrcene, limonene, 1,8-cineole, trans-beta-ocimene, linalool, alpha- and delta-terpineol, eugenol, alpha-copaene, beta-elemene, p-cymene, thymol, and carvacrol). Various in vivo and in vitro studies have shown that O. gratissimum and its bioactive constituents possess pharmacological properties such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, hepatoprotective, antidiabetic, antihypertensive, antidiarrhoeal, and antimicrobial properties. This review demonstrated that O. gratissimum has a strong preventive and therapeutic effect against several diseases. The effectiveness of O. gratissimum to ameliorate various diseases may be attributed to its antimicrobial and antioxidant properties as well as its capacity to improve the antioxidant systems. However, despite the widespread pharmacological activities of O. gratissimum, further experiments in human clinical trial studies are needed to establish effective and safe doses for the treatment of various diseases.
Inductive effect of titanium dioxide nanoparticles on the anticancer compounds production and expression of rosmarinic acid biosynthesis genes in Dracocephalum kotschyi transformed roots.[Pubmed:34555667]
Plant Physiol Biochem. 2021 Oct;167:934-945.
Methoxylated flavonoids, mainly Xanthomicrol and cirsimaritin that can be extracted from Dracocephalum kotschyi Boiss, have anticancer, antispasmodic and antiplatelet effects. The production of these valuable pharmaceutical compounds is one of the major goals of biotechnology studies. In this work, induced transformed roots were influenced by various concentrations of titanium dioxide nanoparticles (TiO(2) NPs) at 24 or 48 h exposure time. The effects of TiO(2) NPs were assessed on growth rate, activity of antioxidant enzymes, total phenol and flavonoid content (TPC and TFC) and rosmarinic acid (RA) and some flavonoids accumulation. The gene expression level of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase (pal) and rosmarinic acid synthase (ras) genes were assessed by real time PCR analysis. The transformed roots biomass was substantially increased in elicited roots in comparison with the control. The TPC, TFC and antioxidant enzymes activitywere affected by TiO(2) NPs concentration and exposure time. Valuable flavonoids with anticancer characteristics along with Xanthomicrol, cirsimaritin and isokaempferide exhibited an increase (70, 34.28 and 7.81-fold, respectively) versus the control. The maximum content of RA (530.5 mug g(-1) FW), which was 4.30 times as great as that of control was detected in samples treated with TiO(2) NPs (50 mg L(-1)) 24 h after elicitation. Real-time PCR analysis revealed a considerable increase in pal and ras expression rate engaged by TiO(2) NPs levels and exposure time. Overall D. kotschyi transformed roots elicitation by TiO(2) NPs led to a massive increment in the production of valuable anticancer flavonoids such as Xanthomicrol, cirsimaritin and RA as polyphenol.
Xanthomicrol suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma cells migration and invasion ability via Muu-opioid receptor.[Pubmed:34355768]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2022 Jan 5;74(1):139-146.
BACKGROUND: Xanthomicrol is one of the methoxylated flavones and a promising cancer chemopreventive agent, but its anti-migration and anti-invasion ability on human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unknown. OBJECTIVES: This study aims to explore Xanthomicrol's effects on migration and invasion ability of the human HCC Huh7 cell line. METHODS: Viability of Huh7 cells was measured by cell counting kit-8 (CCK8) assay. Cell apoptosis was assayed with flow cytometry analysis. The ability of migration and invasion of Huh7 cells was then detected through Transwell assays. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT)-related proteins were also detected through Western blot. KEY FINDINGS: Xanthomicrol inhibits the migration and invasion of Huh7 cells. The overexpression of Muu-opioid receptor (MOR) increases Huh7 cells' proliferation and enhances migration and invasion ability, while Xanthomicrol treatment decreases the expression of MOR. Moreover, Xanthomicrol can reverse migration, invasion and EMT-related protein expression by overexpressed MOR. CONCLUSIONS: These results suggest that Xanthomicrol is a potential MOR antagonist, and it possesses potent anti-migration and anti-invasion ability on Huh7 cells.
Breast cancer cell line toxicity of a flavonoid isolated from Baccharis densiflora.[Pubmed:34215226]
BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jul 2;21(1):188.
BACKGROUND: Flavonoids are compounds of interest in the search for new anti-cancer therapies. We have previously isolated the methoxyflavones 5,4'-dihydroxy-6,7,8,3'-tetramethoxyflavone (8-methoxycirsilineol), 5,4'-dihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (Xanthomicrol), and 5,4,'3'-trihydroxy-6,7,8-trimethoxyflavone (sideritoflavone) from Baccharis densiflora. Herein, we investigate the toxicity of these methoxyflavones in human breast-derived cell line. Our main aim was to focus on the cancer stem cell (CSC) sub-population of JIMT-1 breast cancer cells. METHODS: Initially, dose response experiments yielding inhibitory concentration 50 (IC(50)) values were performed using MCF-7, HCC1937, and JIMT-1 breast cancer, and the MCF-10A normal-like breast cell lines to get an understanding of toxic ranges. Due to a clear difference in the toxicity of the flavones, only sideritoflavone was selected for further studies using the JIMT-1 cell line. Effects on the CSC sub-population was investigated using flow cytometry-based methods. A wound healing assay and digital holographic microscopy were used to investigate effects on cell movement. A reporter assay was used to study effects on signal transduction pathways and Western blot for protein expression. RESULTS: The dose response data showed that 8-methoxycirsilineol was non-toxic at concentrations below 100 muM, that the IC(50) of Xanthomicrol was between 50 and 100 muM, while sideritoflavone was highly toxic with a single digit muM IC(50) in all cell lines. Treatment of the JIMT-1 cells with 2 muM sideritoflavone did not selectively effect the CSC sub-population. Instead, sideritoflavone treatment inhibited the proliferation of both the non-CSC and the CSC sub-populations to the same extent. The inhibition of cell proliferation resulted in an accumulation of cells in the G(2) phase of the cell cycle and the treated cells showed an increased level of gamma-H2A histone family member X indicating DNA double strand breaks. Analysis of the effect of sideritoflavone treatment on signal transduction pathways showed activation of the Wnt, Myc/Max, and transforming growth factor-beta pathways. The level of p65/nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated Beta cells was increased in sideritoflavone-treated cells. Cell movement was decreased by sideritoflavone treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Altogether our data show that the methoxyflavone sideritoflavone has favourable anti-cancer effects that may be exploited for development to be used in combination with CSC specific compounds.
Phenols from Origanum dictamnus L. and Thymus vulgaris L. and their activity against Malassezia globosa carbonic anhydrase.[Pubmed:33533668]
Nat Prod Res. 2022 Mar;36(6):1558-1564.
Malassezia spp. are lipophilic fungi that are part of the normal flora of the human skin and are the etiological agents of dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. beta-Carbonic Anhydrases (CAs; EC 4.2.1.1) expressed from the pathogenic fungi are an alternative/complementary drug target. Previous work by our groups demonstrated that flavonoids and depsides can effectively inhibit Malassezia globosa beta-CA (MgCA). In continuation of this study herein we report the inhibitory activity of a variety of phenols from Origanum dictamnus L. and Thymus vulgaris L. against beta-MgCA, among them I4-II7-di-carvacrol, a new natural product. Structure elucidation of the compounds was performed by 1 D, 2 D NMR and spectrometric analyses. Xanthomicrol and rosmarinic acid were active in the (sub)micromolar range (K(IS) 0.6 and 2.2 muM, respectively vs 40.0 muM of the standard inhibitor acetazolamide). Finally, the compounds were not cytotoxic, but showed in vitro no activity against Malassezia furfur.
Xanthomicrol Exerts Antiangiogenic and Antitumor Effects in a Mouse Melanoma (B16F10) Allograft Model.[Pubmed:33424993]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2020 Dec 22;2020:8543872.
Xanthomicrol, a trimethoxylated hydroxyflavone, is the main active component of Dracocephalum kotschyi Boiss leaf extract. Preliminary in vitro studies identified this compound as a potential antiangiogenic and anticancer agent. This study aimed to evaluate in vivo anticancer effect of Xanthomicrol and investigate its molecular mechanism of action in a mouse melanoma (B16F10) model. Effect of Xanthomicrol on B16F10 melanoma cell viability was determined using the MTT assay. For in vivo experiments, C57BL/6 mice were inoculated subcutaneously with B16F10 cells. After five days, once daily administration of Xanthomicrol, thalidomide, or vehicle was commenced and continued for 21 consecutive days. On the 26th day, blood samples and tumor biopsies were taken for subsequent molecular analysis. Xanthomicrol showed inhibitory effect on viability of B16F10 melanoma cells (IC50 value: 3.433 mug/ml). Initial tumor growth, tumor volume and weight, and angiogenesis were significantly decreased in Xanthomicrol-treated animals compared with those in vehicle group. Protein expression of phosphorylated Akt, mRNA expressions of HIF-1alpha and VEGF in tumor tissues, and serum VEGF were significantly decreased in Xanthomicrol-treated animals compared with vehicle-treated animals. Thus, Xanthomicrol inhibited cancer cell growth both in vitro and in vivo. This effect, at least in part, was exerted by interfering with PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and inhibiting VEGF secretion by tumor cells. Further studies are required to elucidate the exact molecular mechanisms of antitumor activity of Xanthomicrol.


