ZD 7155 hydrochlorideCAS# 146709-78-6 |
- ML 141
Catalog No.:BCC8092
CAS No.:71203-35-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 146709-78-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 9826191 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C26H27ClN6O | M.Wt | 474.99 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 10 mM in water with gentle warming | ||
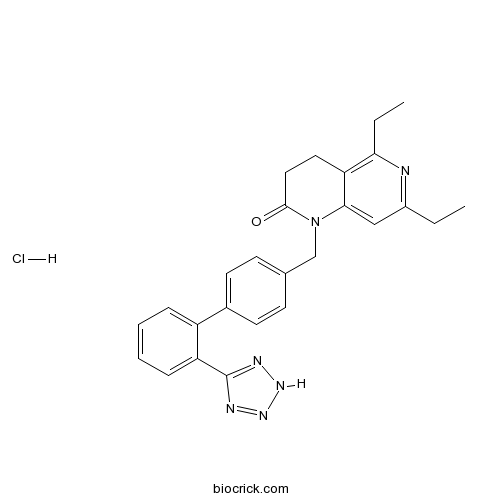
| Chemical Name | 5,7-diethyl-1-[[4-[2-(2H-tetrazol-5-yl)phenyl]phenyl]methyl]-3,4-dihydro-1,6-naphthyridin-2-one;hydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=NC(=C2CCC(=O)N(C2=C1)CC3=CC=C(C=C3)C4=CC=CC=C4C5=NNN=N5)CC.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | NAGGAAHTUXEGFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C26H26N6O.ClH/c1-3-19-15-24-22(23(4-2)27-19)13-14-25(33)32(24)16-17-9-11-18(12-10-17)20-7-5-6-8-21(20)26-28-30-31-29-26;/h5-12,15H,3-4,13-14,16H2,1-2H3,(H,28,29,30,31);1H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | A potent and selective competitive antagonist for the angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor. Displaces [125I]-angiotensin II binding with an IC50 value of 3.8 nM in guinea pig adrenal gland membranes. Orally active, and is more potent and longer-acting than the prototype AT1 antagonist, losartan. |

ZD 7155 hydrochloride Dilution Calculator

ZD 7155 hydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1053 mL | 10.5265 mL | 21.0531 mL | 42.1061 mL | 52.6327 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4211 mL | 2.1053 mL | 4.2106 mL | 8.4212 mL | 10.5265 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2105 mL | 1.0527 mL | 2.1053 mL | 4.2106 mL | 5.2633 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0421 mL | 0.2105 mL | 0.4211 mL | 0.8421 mL | 1.0527 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0211 mL | 0.1053 mL | 0.2105 mL | 0.4211 mL | 0.5263 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Daphnicyclidin I
Catalog No.:BCN7038
CAS No.:1467083-10-8
- Hybridaphniphylline B
Catalog No.:BCN7045
CAS No.:1467083-09-5
- Hybridaphniphylline A
Catalog No.:BCN7042
CAS No.:1467083-07-3
- SR 11237
Catalog No.:BCC7681
CAS No.:146670-40-8
- (RS)-MCPG
Catalog No.:BCC6610
CAS No.:146669-29-6
- SR 2640 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7180
CAS No.:146662-42-2
- H-Trp(Boc)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3115
CAS No.:146645-63-8
- Dantrolene, sodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6673
CAS No.:14663-23-1
- 2,6-Dimethoxybenzoic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1651
CAS No.:1466-76-8
- 2-Cyclopropyl-3-[(diphenylphosphinyl)methyl]-4-(4-fluorophenyl)quinoline
Catalog No.:BCC8572
CAS No.:146578-99-6
- Fmoc-Gly(allyl)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3156
CAS No.:146549-21-5
- Tyrphostin AG 1296
Catalog No.:BCC1195
CAS No.:146535-11-7
- Boc-D-Phe(4-CN)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3183
CAS No.:146727-62-0
- N-desmethyldauricine
Catalog No.:BCC8217
CAS No.:146763-55-5
- Y-29794 oxalate
Catalog No.:BCC5795
CAS No.:146794-84-5
- 2-Bromo-1-(3-thienyl)-1-ethanone
Catalog No.:BCN2657
CAS No.:1468-82-2
- 1,5-Dihydroxyxanthone
Catalog No.:BCN7423
CAS No.:14686-65-8
- Triptobenzene H
Catalog No.:BCN6784
CAS No.:146900-55-2
- 1,2-Diacetoxy-4,7,8-trihydroxy-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)dibenzofuran
Catalog No.:BCN7691
CAS No.:146905-24-0
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 9
Catalog No.:BCC6500
CAS No.:1469337-91-4
- K-Ras(G12C) inhibitor 12
Catalog No.:BCC5562
CAS No.:1469337-95-8
- Ziprasidone
Catalog No.:BCC2071
CAS No.:146939-27-7
- Codaphniphylline
Catalog No.:BCN1652
CAS No.:14694-15-6
- Fmoc-Asp(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3089
CAS No.:146982-24-3
Endogenous angiotensin II and the reflex response to stimulation of cardiopulmonary serotonin 5HT3 receptors.[Pubmed:9886768]
Br J Pharmacol. 1998 Dec;125(8):1761-7.
1. Angiotensin (Ang) II modulates cardiovascular baroreflexes; whether or not the peptide influences chemosensitive cardiovascular reflexes is not known. We tested the hypothesis that Ang II modulates the reflex control of sympathetic nerve activity exerted by 5-hydroxytryptamine 3 (5HT3) cardiopulmonary receptors. 2. The 5HT3 receptor agonist phenylbiguanide (PBG), infused intravenously for 15 min, elicited a sustained reflex decrease of renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) but only transient (<3 min) changes of arterial blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) in methohexital-anaesthesized rats. 3. Infusion of Ang II at a dose that did not affect baseline BP, HR and RSNA enhanced the PBG-evoked reflex decrease of RSNA (-54+/-5% in Ang II treated versus -33+/-6% in control rats after 15 min PBG, P<0.05, n = 6 each) in methohexital-anaesthetized rats. 4. The angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor lisinopril blunted the reflex responses to PBG in anaesthetized as well as conscious animals. The effect of the ACE inhibitor was abolished by concomitant infusion of Ang II. 5. The reflex response to stimulation of cardiopulmonary 5HT3 afferents was also impaired by the Ang II type 1 receptor (AT1) blocker ZD7155 but not by the type 2 (AT2) blocker PD 123319. 6. Infusion of a volume load to stimulate cardiopulmonary baroreceptors induced a gradual decrease of RSNA which was impaired by exogenous Ang II (RSNA -26+/-6% in Ang II treated versus -47+/-6% in control rats after volume load, P<0.05, n = 6 each) but unaffected by ACE inhibition. 7. The reflex control of RSNA by cardiopulmonary 5HT3 receptors is enhanced by Ang II via AT1 receptors. Thus, Ang II facilitates a chemosensitive cardiovascular reflex, in contrast to its inhibitory influences on mechanosensitive reflexes.
Comparative cardiovascular effects of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonists ZD 7155 and losartan in the rat.[Pubmed:8887734]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 1996 Aug;48(8):829-33.
Binding experiments show that ZD 7155 is a potent angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist. In this study this novel substance was studied in normotensive and hypertensive rats. The relative potency and duration of the antihypertensive effects of ZD 7155 were compared with those of the reference substance, losartan. The inhibitory effects of both compounds on angiotensin II-induced pressor actions were studied in the conscious normotensive Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat and in the conscious, spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR). Arterial blood pressure and heart rate (HR) were obtained by direct intraarterial recording. Angiotensin II infusion was administered intravenously in the dose range 53.3 ng-12.8 micrograms kg-1 min-1 to the conscious rats. ZD 7155 was administered in a bolus dose of 1.082 mumol kg-1 (0.51 mg kg-1) and losartan in bolus doses of 2.165 and 6.495 mumol kg-1 (1.0 and 3.0 mg kg-1). In conscious SD rats, ZD 7155 and losartan behaved as competitive antagonists and the pressor response curve to angiotensin II was shifted to the right. Experiments in conscious SD rats also showed that ZD 7155 was approximately ten times as potent as losartan in suppressing the angiotensin II-induced pressor response (240 ng kg-1; 10 min infusion). In addition, experiments with conscious rats demonstrated that ZD 7155 could suppress the angiotensin II-induced pressor response for approximately 24 h when ZD 7155 was administered intravenously in a 1.082 mumol kg-1 bolus dose and angiotensin II was given at 240 ng kg-1 (in a 10-min infusion). Experiments in conscious SHRs using ZD 7155 (1.082 mumol kg-1) and losartan (6.495 mumol kg-1) as intravenous boluses indicated that both ZD 7155 and the reference compound losartan exhibited a significant antihypertensive effect. These results demonstrate that ZD 7155 is a potent angiotensin II-type 1 antagonist which is approximately ten times as potent as losartan in suppressing the angiotensin II-induced pressor response. Furthermore, ZD 7155 may suppress the angiotensin II-induced pressor response for 24 h and in the SHR ZD 7155 induces a pronounced and persistent antihypertensive effect.


