Aconitum carmichaelii
Aconitum carmichaelii
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Aconitum carmichaelii
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
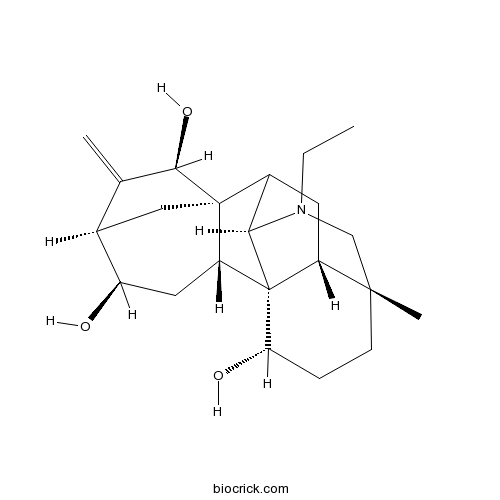
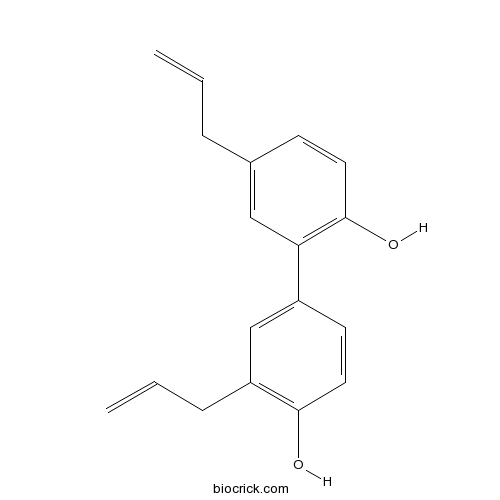
BCN2800
12-Epinapelline110064-71-6
Instructions
-
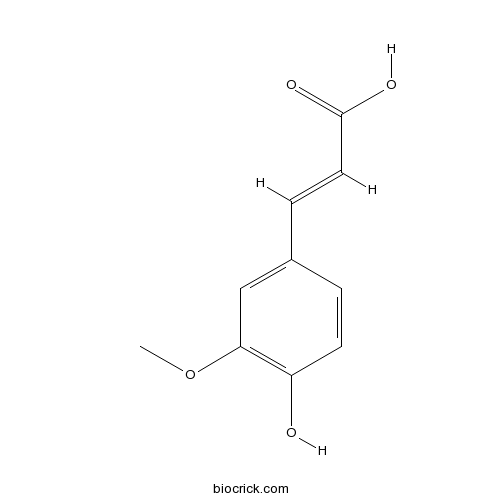
BCN5948
Ferulic acid1135-24-6
Instructions
-
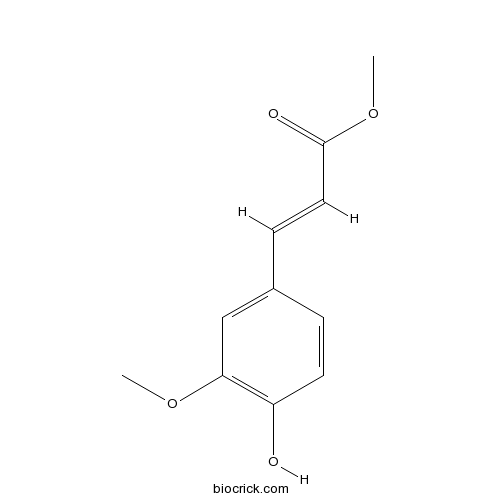
BCN9073
Ferulic Acid Methyl Ester2309-07-1
Instructions
-
BCN5406
Denudatine26166-37-0
Instructions

-
BCN5987
Mesaconitine2752-64-9
Instructions

-
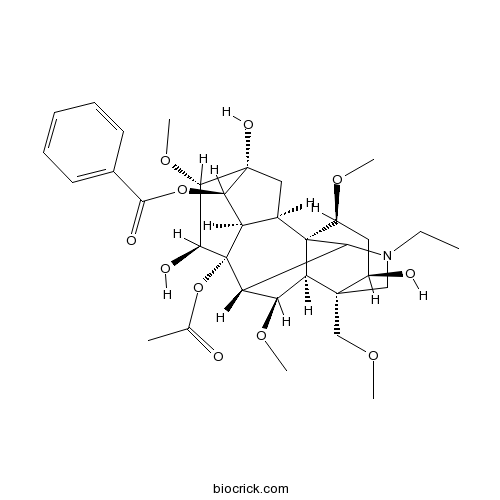
BCN1014
Aconitine302-27-2
Instructions
-
BCN2797
3-Deoxyaconitine3175-95-9
Instructions

-
BCN1001
Honokiol35354-74-6
Instructions
-
BCC8331
Karakoline39089-30-0
Instructions

-
BCN6259
Indaconitine4491-19-4
Instructions

-
BCN5400
Benzoylaconine466-24-0
Instructions

-
BCN2375
Bullatine B466-26-2
Instructions

-
BCN2394
Aconine509-20-6
Instructions

-
BCN2536
Napellonine509-24-0
Instructions

-
BCC8317
DL-Demethylcoclaurine5843-65-2
Instructions

-
BCN2821
Benzoylhypacoitine63238-66-4
Instructions

-
BCN5398
Benzoylmesaconine63238-67-5
Instructions

-
BCN4211
Uracil66-22-8
Instructions

-
BCN5404
Deltaline6836-11-9
Instructions

-
BCN5988
Hypaconitine6900-87-4
Instructions

-
BCN2516
Crassicauline A79592-91-9
Instructions

-
BCN2822
Fuziline80665-72-1
Instructions

The influences of thermal processing on phytochemicals and possible routes to the discovery of new phytochemical conjugates.[Pubmed: 29787299]
In our diets, many of the consumed foods are subjected to various forms of heating and thermal processing. Besides enhancing the taste, texture, and aroma of the foods, heating helps to sterilize and facilitate food storage. On the other hand, heating and thermal processing are frequently reported during the preparation of various traditional herbal medicines. In this review, we intend to highlight works by various research groups which reported on changes in phytochemicals and bioactivities, following thermal processing of selected plant-derived foods and herbal medicines. Relevant cases from plant-derived foods (garlic, coffee, cocoa, barley) and traditional herbal medicines (Panax ginseng, Polygonum multiforum, Aconitum carmichaelii Debeaux, Angelica sinensis Radix) will be presented in this review. Additionally, related works using pure phytochemical compounds will also be highlighted. In some of these cases, the amazing formation of new compounds were being reported. Maillard reaction could be concluded as the predominant pathway leading to the formation of new conjugates, along with other possibilities being suggested (degradation, transglycosylation, deglycosylation and dehydration). With collective efforts from all researchers, it is hoped that more details will be revealed and lead to the possible discovery of new, heat-mediated phytochemical conjugates.
Four New Diterpenoid Alkaloids from the Roots of Aconitum carmichaelii.[Pubmed: 29785743]
None
Qualitative and quantitative analysis of lipo-alkaloids and fatty acids in Aconitum carmichaelii using LC-MS and GC-MS.[Pubmed: 29603449]
None
New dianthramide and cinnamic ester glucosides from the roots of Aconitum carmichaelii.[Pubmed: 29597834]
None


