Angelica biserrata
Angelica biserrata
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.

Natural products/compounds from Angelica biserrata
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
BCN8246
Angenomalin18199-64-9
Instructions

-
BCN5065
Falcarindiol225110-25-8
Instructions

-
BCN2652
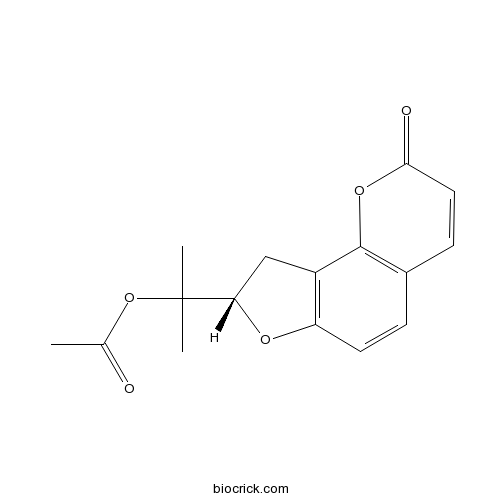
Columbianetin acetate23180-65-6
Instructions
-
BCN5205
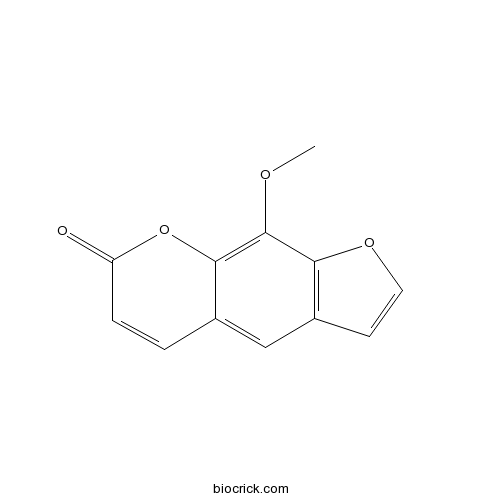
Xanthotoxin298-81-7
Instructions
-
BCN2331
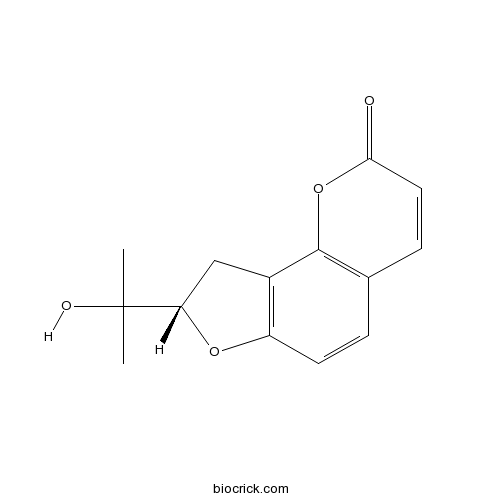
(+)-columbianetin3804-70-4
Instructions
-
BCN9028
Byakangelicin482-25-7
Instructions

-
BCN5568
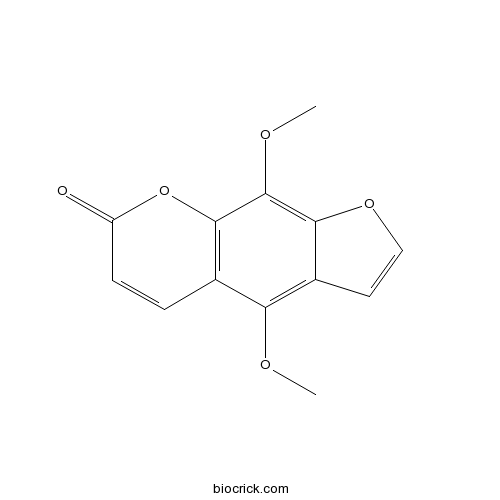
Isopimpinellin482-27-9
Instructions
-
BCN5897
Isoimperatorin482-45-1
Instructions
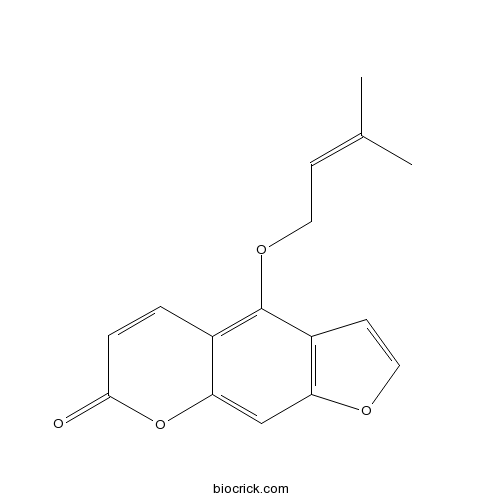
-
BCN5581
Osthol484-12-8
Instructions
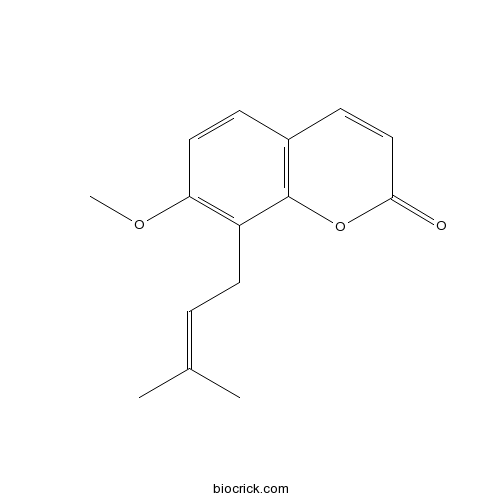
-
BCN5582
Bergapten484-20-8
Instructions
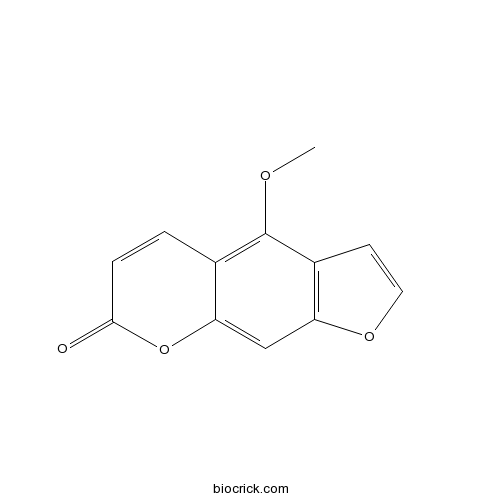
-
BCN3617
Ammijin495-30-7
Instructions
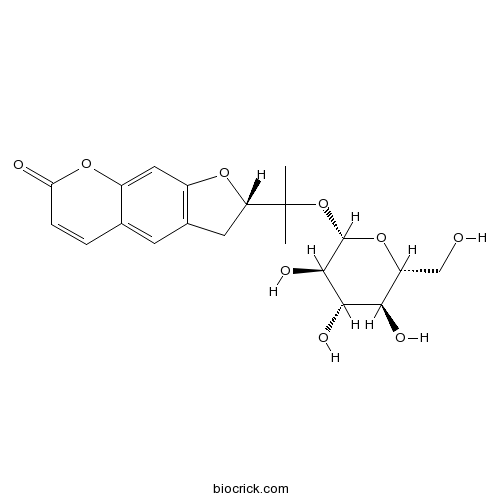
-
BCN2378
Nodakenin495-31-8
Instructions
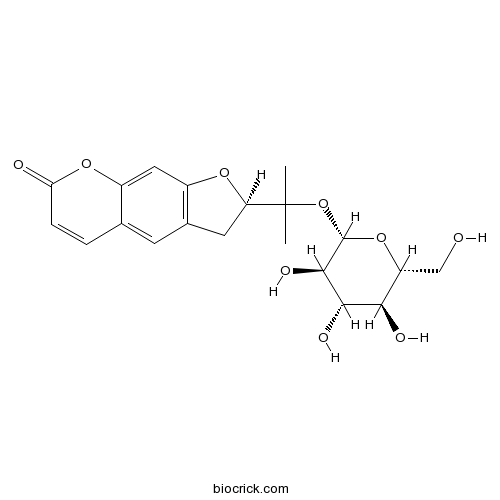
-
BCN5604
Nodakenetin495-32-9
Instructions
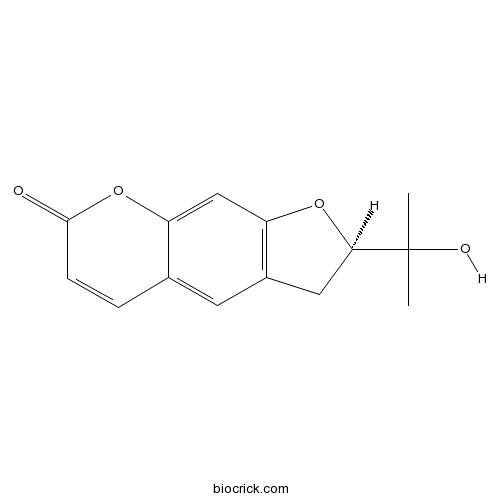
-
BCN1275
Columbianadin5058-13-9
Instructions
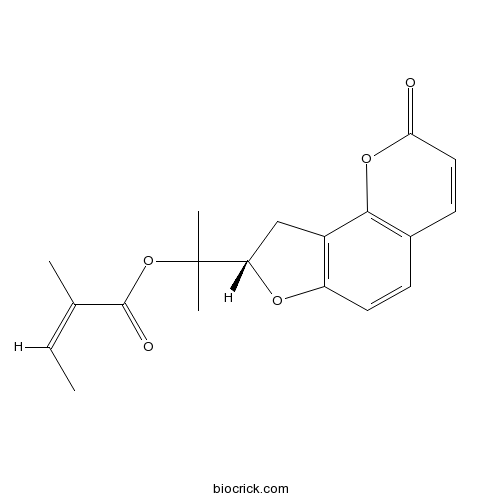
-
BCN4219
Psoralen66-97-7
Instructions

-
BCN8037
Angelol B83156-04-1
Instructions

-
BCN6309
Coumarin91-64-5
Instructions

-
BCN4470
Scopoletin92-61-5
Instructions

-
BCN4477
Umbelliferone93-35-6
Instructions

Analgesic effect of coumarins from Radix angelicae pubescentis is mediated by inflammatory factors and TRPV1 in a spared nerve injury model of neuropathic pain.[Pubmed: 27915078]
Coumarins from Radix angelicae pubescentis (CRAP) are a major active component that are isolated from dried roots of Angelica biserrata Yuan et Shan, which has been used clinically to cure headaches for a long period of time, and it is an effective treatment for pain. The aim of the present study was to investigate the analgesic effect of CRAP on a spared nerve injury (SNI) model of neuropathy.
Rapid Authentication of the Herbal Medicine Plant Species Aralia continentalis Kitag. and Angelica biserrata C.Q. Yuan and R.H. Shan Using ITS2 Sequences and Multiplex-SCAR Markers.[Pubmed: 26938512]
Accurate identification of the plant species that are present in herbal medicines is important for quality control. Although the dried roots of Aralia continentalis (Araliae Continentalis Radix) and Angelica biserrata (Angelicae Pubescentis Radix) are used in the same traditional medicine, namely Dok-Hwal in Korean and Du-Huo in Chinese, the medicines are described differently in the national pharmacopeia. Further confusion arises from the distribution of dried Levisticum officinale and Heracleum moellendorffii roots as the same medicine. Medicinal ingredients from all four plants are morphologically similar, and discrimination is difficult using conventional methods. Molecular identification methods offer rapidity and accuracy. The internal transcribed spacer 2 (ITS2) region of the nuclear ribosomal RNA gene (rDNA) was sequenced in all four plant species, and the sequences were used to design species-specific primers. Primers for each species were then combined to allow sample analysis in a single PCR reaction. Commercial herbal medicine samples were obtained from Korea and China and analyzed using the multiplex assay. The assay successfully identified authentic medicines and also identified inauthentic or adulterated samples. The multiplex assay will be a useful tool for identification of authentic Araliae Continentalis Radix and/or Angelicae Pubescentis Radix preparations in Korea and China.


