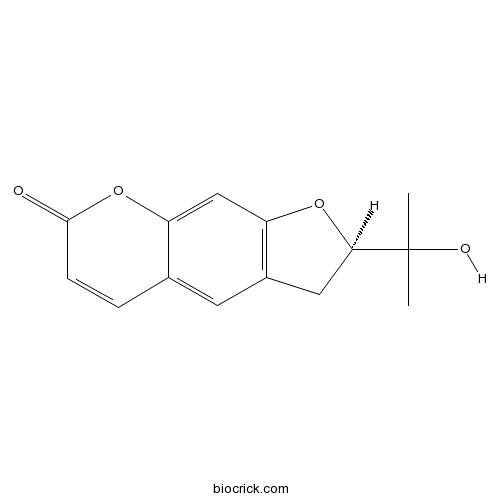
NodakenetinCAS# 495-32-9 |
- (±)-Marmesin
Catalog No.:BCN3618
CAS No.:13710-70-8
- S-(+)-Marmesin
Catalog No.:BCN8288
CAS No.:13849-08-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 495-32-9 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 26305 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H14O4 | M.Wt | 246.3 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2R)-2-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)-2,3-dihydrofuro[3,2-g]chromen-7-one | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)(C1CC2=C(O1)C=C3C(=C2)C=CC(=O)O3)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FWYSBEAFFPBAQU-GFCCVEGCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14O4/c1-14(2,16)12-6-9-5-8-3-4-13(15)18-10(8)7-11(9)17-12/h3-5,7,12,16H,6H2,1-2H3/t12-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Nodakenetin has antioxidant activity, it displays the least irritant and least persistent reactions on mouse ears, and exhibits the least cytotoxic capacity against brine shrimp larvae. Nodakenetin angelate is used as an antiarthritic and nerve tonic. |
| Targets | NO |
| In vitro | In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Angelica decursiva.[Pubmed: 22297757 ]Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Jan;35(1):179-92.Mounting evidences continue to support the involvement of oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of many diseases. Plant constituents having antioxidant activities together with anti-inflammatory activities may provide better opportunities to develop anti-inflammatory agents.
|
| In vivo | Irritant and cytotoxic coumarins from Angelica glauca Edgew roots.[Pubmed: 18058380 ]J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2008 Jan-Feb;10(1-2):49-58.Irritant and cytotoxic potentiality of six coumarins, isolated for the first time from the roots of Angelica glauca identified as 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin, 6-methoxy-7,8-methylenedioxycoumarin, bergapten, decursinol angelate, decursin, and Nodakenetin, were investigated. |
| Structure Identification | Biomed Chromatogr. 2010 Feb;24(2):216-21.A new metabolite of nodakenetin by rat liver microsomes and its quantification by RP-HPLC method.[Pubmed: 19572262]The biotransformation of Nodakenetin (NANI) by rat liver microsomes in vitro was investigated. J. Raman Spectrosc., 2005, 36(1):63-72.Near-infrared Fourier transform Raman, surface-enhanced Raman scattering and Fourier transform infrared spectra and ab initio calculations of the natural product nodakenetin angelate.[Reference: WebLink]
|

Nodakenetin Dilution Calculator

Nodakenetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0601 mL | 20.3004 mL | 40.6009 mL | 81.2018 mL | 101.5022 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.812 mL | 4.0601 mL | 8.1202 mL | 16.2404 mL | 20.3004 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.406 mL | 2.03 mL | 4.0601 mL | 8.1202 mL | 10.1502 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0812 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.812 mL | 1.624 mL | 2.03 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0406 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.406 mL | 0.812 mL | 1.015 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Nodakenin
Catalog No.:BCN2378
CAS No.:495-31-8
- Ammijin
Catalog No.:BCN3617
CAS No.:495-30-7
- Auraptene
Catalog No.:BCN5603
CAS No.:495-02-3
- Ginsenoside Rk1
Catalog No.:BCN3552
CAS No.:494753-69-4
- TC-G 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6316
CAS No.:494191-73-0
- Nornicotine
Catalog No.:BCN8176
CAS No.:494-97-3
- Isoammodendrine
Catalog No.:BCN2146
CAS No.:494-15-5
- Nifuratel
Catalog No.:BCC1800
CAS No.:4936-47-4
- Methyl L-pyroglutamate
Catalog No.:BCN7060
CAS No.:4931-66-2
- Savinin
Catalog No.:BCN5602
CAS No.:493-95-8
- α-D-Glucose
Catalog No.:BCC9197
CAS No.:492-62-6
- Kynurenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN2228
CAS No.:492-27-3
- Desoxypeganine
Catalog No.:BCN8032
CAS No.:495-59-0
- Tropine isobutyrate
Catalog No.:BCN1923
CAS No.:495-80-7
- Valtropine
Catalog No.:BCN1926
CAS No.:495-82-9
- Tigloyltropeine
Catalog No.:BCN1944
CAS No.:495-83-0
- (+)-Methysticin
Catalog No.:BCN8429
CAS No.:495-85-2
- Org 25543 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6288
CAS No.:495076-64-7
- 11alpha,12alpha-Oxidotaraxerol palmitate
Catalog No.:BCN7129
CAS No.:495389-95-2
- Estradiol heptanoate
Catalog No.:BCC8961
CAS No.:4956-37-0
- Fenofibrate
Catalog No.:BCC4781
CAS No.:49562-28-9
- Benzofuran-2-carboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8851
CAS No.:496-41-3
- Pyromeconic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7177
CAS No.:496-63-9
- Helicianeoide A
Catalog No.:BCN2486
CAS No.:496066-82-1
A new metabolite of nodakenetin by rat liver microsomes and its quantification by RP-HPLC method.[Pubmed:19572262]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2010 Feb;24(2):216-21.
The biotransformation of Nodakenetin (NANI) by rat liver microsomes in vitro was investigated. Two major polar metabolites were produced by liver microsomes from phenobarbital-pretreated rats and detected by reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) analysis. The chemical structures of two metabolites were firmly identified as 3'(R)-hydroxy-Nodakenetin-3'-ol and 3'(S)-hydroxy-Nodakenetin-3'-ol, respectively, on the basis of their (1)H-NMR, MS and optical rotation analysis. The latter was a new compound. A sensitive, selective and simple RP-HPLC method has been developed for the simultaneous determination of NANI and its two major metabolites in rat liver microsomes. Chromatographic conditions comprise a C(18) column, a mobile phase with MeOH-H(2)O (40 : 60, v/v), a total run time of 40 min, and ultraviolet absorbance detection at 330 nm. In the rat heat-inactivated liver microsomal supernatant, the lower limits of detection and quantification of metabolite I, metabolite II and NANI were 5.0, 2.0, 10.0 ng/mL and 20.0, 5.0, 50.0 ng/mL, respectively, and their calibration curves were linear over the concentration range 50-400, 20-120 and 150-24000 ng/mL, respectively. The results provided a firm basis for further evaluating the pharmacokinetics and clinical efficacy of NANI.
Irritant and cytotoxic coumarins from Angelica glauca Edgew roots.[Pubmed:18058380]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2008 Jan-Feb;10(1-2):49-58.
Irritant and cytotoxic potentiality of six coumarins, isolated for the first time from the roots of Angelica glauca identified as 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin, 6-methoxy-7,8-methylenedioxycoumarin, bergapten, decursinol angelate, decursin, and Nodakenetin, were investigated. The irritant potential was explored by open mouse ear assay, evaluating their ID(50) after acute and by IU (Irritant units) after chronic effects, while the cytotoxic capability was explored by their LC(50), using brine shrimp (Artemia salina) larvae (nauplii). All the coumarins exhibited well-defined irritancy on mouse's ears, compared with the positive controlled euphorbium reaction and cytotoxic response against brine shrimp larvae, compared with the positive control colchicine. Decursinol angelate and decursin were the most potent and persistent irritant compounds with least ID(50), whose reactions lasted for 48 h. 6-Methoxy-7,8-methylenedioxycoumarin and bergaten revealed an intermediate irritant reactions, while 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin and Nodakenetin displayed the least irritant and least persistent reactions on mouse ears. Both decursin and decursinol angelate also appeared to be the stronger cytotoxic agents than other coumarins. 5,6,7-trimethoxycoumarin displayed an intermediate cytotoxic behaviour, while other three coumarins, i.e., 6-methoxy-7,8-methylenedioxycoumarin, bergapten, and Nodakenetin, exhibited the least cytotoxic capacity against brine shrimp larvae.
In vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Angelica decursiva.[Pubmed:22297757]
Arch Pharm Res. 2012 Jan;35(1):179-92.
Mounting evidences continue to support the involvement of oxidative/nitrosative stress and inflammation in the pathogenesis of many diseases. Plant constituents having antioxidant activities together with anti-inflammatory activities may provide better opportunities to develop anti-inflammatory agents. In view of this, we evaluated the antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of methanolic extract of whole plants of Angelica decursiva, and its solvent soluble fractions via in vitro activities against lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide (NO) production in RAW 264.7 cells, as well as in vitro scavenging activities against 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl, 2,2'-azino-bis-3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid, NO, and peroxynitrite. Among the tested fractions, the ethyl acetate fraction was found as the most active antioxidant fraction together with significant anti-inflammatory effect. From the active ethyl acetate fraction, four coumarin derivatives consisting of nodakenin, Nodakenetin, umbelliferone, and umbelliferone-6-carboxylic acid, along with a phenolic compound, vanillic acid, were isolated. Among them, umbelliferone 6-carboxylic acid and vanillic acid were isolated for the first time from this plant. In all antioxidant assays, vanillic acid showed the highest antioxidant potential followed by umbelliferone 6-carboxylic acid among the isolated compounds. In the anti-inflammatory assay, umbelliferone 6-carboxylic acid exhibited the highest inhibitory activity against lipopolysaccharide-induced NO production in RAW 264.7 cells with an IC(50) value of 72.98 mug/mL. Therefore, the present study reveals the potential antioxidant and antiinflammatory activities of whole plants of A. decursiva and its constituents, mainly umbelliferone 6-carboxylic acid, which could be used in the development of therapeutic and preventive agents for oxidative stress-related inflammatory diseases.


