Apocynum venetum
Apocynum venetum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Apocynum venetum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
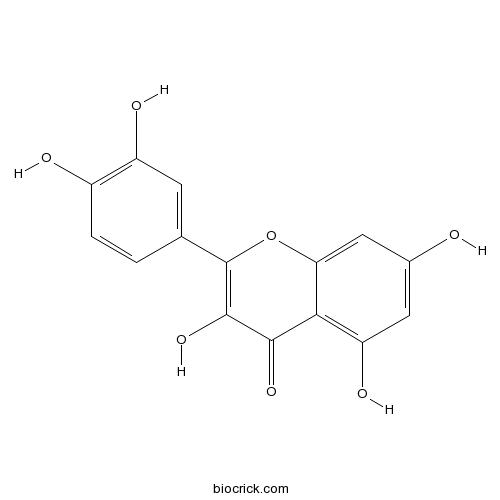
BCN6049
Quercetin117-39-5
Instructions
-
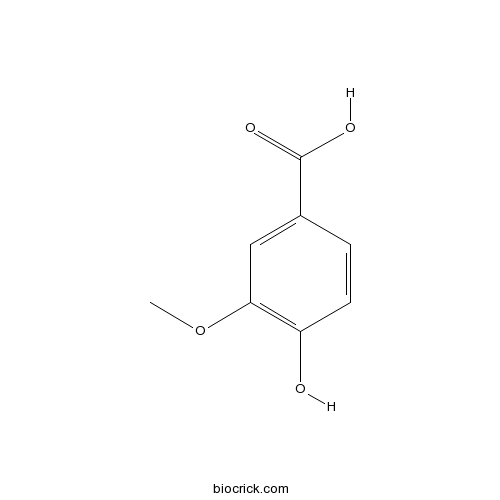
BCN6105
Vanillic acid121-34-6
Instructions
-
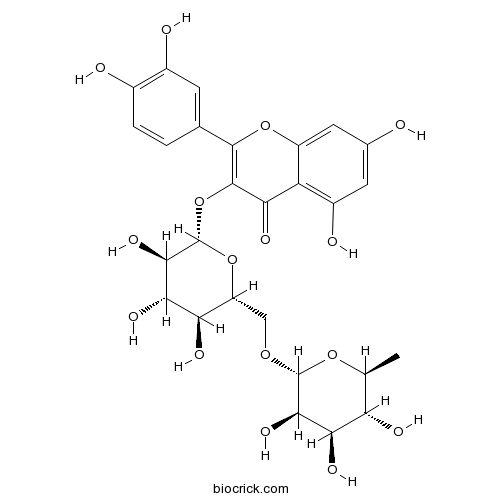
BCN1684
Rutin153-18-4
Instructions
-
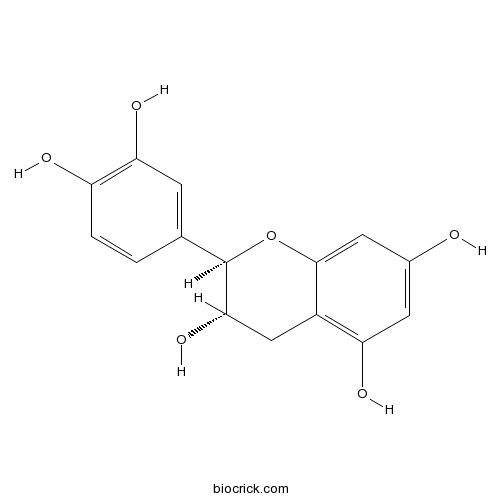
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
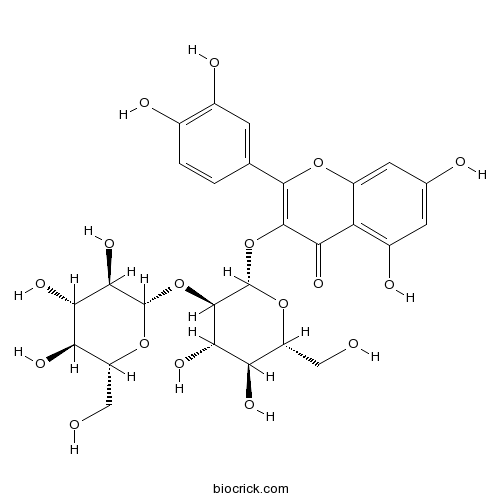
BCN2771
Quercetin-3-O-sophoroside18609-17-1
Instructions
-
BCN6315
Procyanidin B229106-49-8
Instructions

-
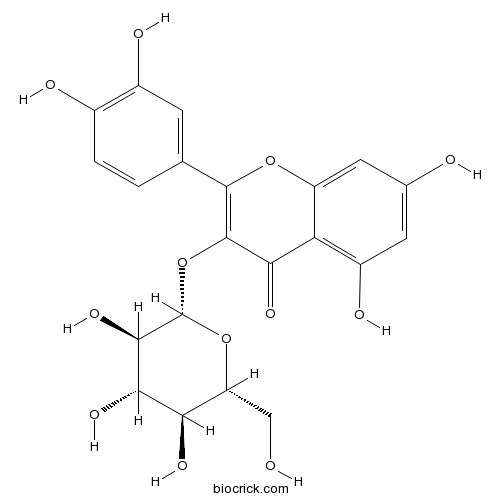
BCN5569
Isoquercitrin482-35-9
Instructions
-
BCN5570
Hyperoside482-36-0
Instructions

-
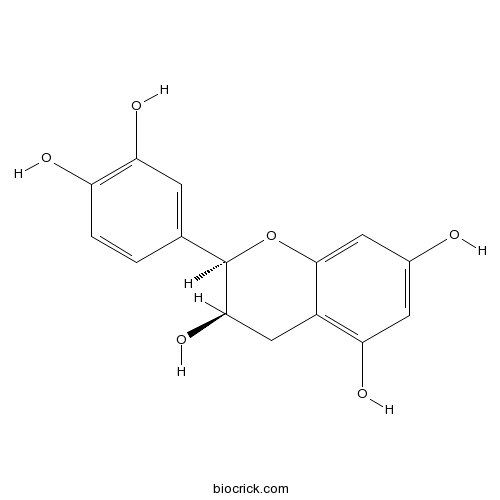
BCN5597
Epicatechin490-46-0
Instructions
-
BCN5608
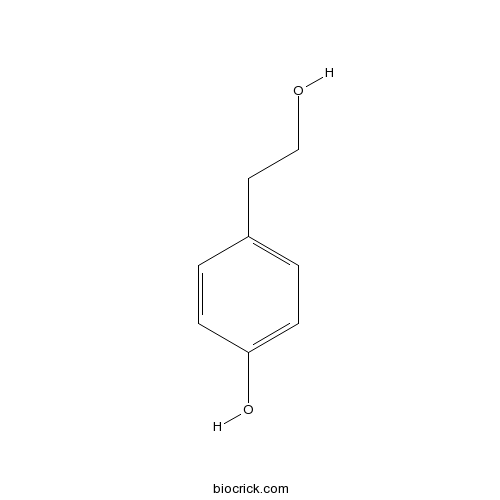
2-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)ethanol501-94-0
Instructions
-
BCN1015
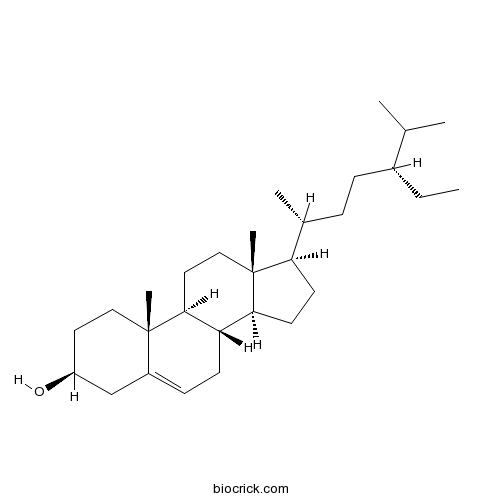
Beta-Sitosterol83-46-5
Instructions
-
BCN4519
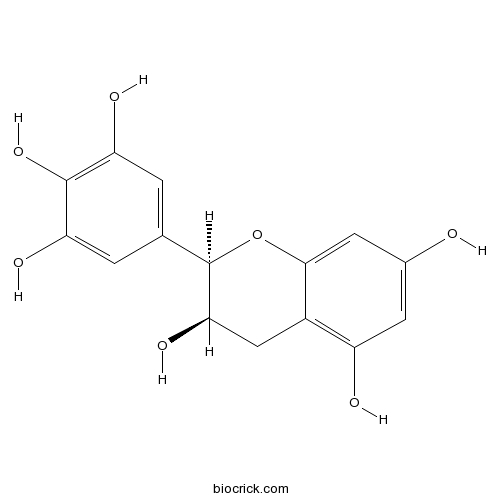
(-)-Epigallocatechin(EGC)970-74-1
Instructions
-
BCN4537
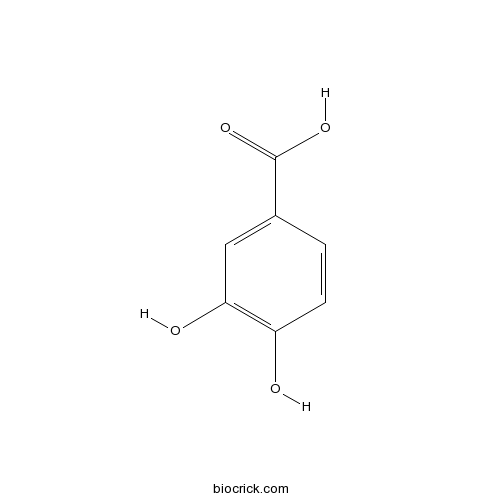
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Protective effect of the total flavonoids from Apocynum venetum L. on carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed: 29541948]
None
Apocynum venetum leaf extract reverses depressive-like behaviors in chronically stressed rats by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis.[Pubmed: 29454288]
Major depressive disorder (MDD) is a common but serious psychiatric disorder, but current treatments are inadequate for approximately half of the patients with MDD. Thus, better methods of treatment are urgently needed. This study aimed to investigate the antidepressant-like effects and potential mechanism of Apocynum venetum leaf extract (AVLE) in chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) rat model of depression.
Apocynum leaf extract inhibits the progress of atherosclerosis in rats via the AMPK/mTOR pathway.[Pubmed: 29441896]
Apocynum leaf extract is an extract of the dried leaves of Apocynum venetum (a member of the Apocynaceae family) that has many effects on the cardiovascular system. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the protective effects of apocynum leaf extract on the atherosclerosis in rats induced by high-fat diet combined with vitamin D3 intraperitoneal injection. The atherosclerosis in rats were induced with a high-fat diet and an intraperitoneal injection of VD3 once daily for three contiguous days at a total injection dose of 70 U/kg. At the end of the 18th week, serum total cholesterol (TC) and triglyceride (TG) contents were measured. Hydroxyproline content in the aorta were measured by the alkali hydrolysis method. The hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and immunohistochemical staining were applied to evaluate the morphological changes and the collagen I and α-smooth muscle actin expression. The protein expression and the mRNA level of AMPK and mTOR were detected by western blot analysis and reverse transcript PCR. After treatment with apocynum leaf extract, the serum total cholesterol and triglyceride concentration of the atherosclerotic rats were significantly decreased, both the Collagen I expression and the hydroxyproline content in the aorta were significantly reduced, and the α-SMA, a smooth muscle-specific marker, expression were also lower than the untreated atherosclerotic rats. Western blot analyses showed that the apocynum can marked increase the p-AMPK but decrease the mTOR protein expression. The apocynum leaf extract also exhibited higher AMPK and lower mTOR mRNA expression of the aorta in the atherosclerotic rats. We believe that the apocynum leaf extract can effectively reduce blood lipid levels in rats with atherosclerosis, delay atherosclerotic progression by inhibiting excessive collagen synthesis and inhibiting smooth muscle cell over-proliferation. The underlying mechanism may be related to the AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway activity. Our results contribute towards validation of the traditional use of apocynum leaf extract in the treatment of atherosclerosis.
High lithium tolerance of Apocynum venetum seeds during germination.[Pubmed: 29344914]
None
[Projection of potential geographic distribution of Apocynum venetum under climate change in northern China].[Pubmed: 29027426]
Apocynum venetum belongs to apocynaceae and is a perennial medicinal plant, its stem is an important textile raw materials. The projection of potential geographic distribution of A. venetum has an important significance for the protection and sustainable utilization of the plant. This study was conducted to determine the potential geographic distribution of A. venetum and to project how climate change would affect its geographic distribution. The projection geographic distribution of A. venetum under current bioclimatic conditions in northern China was simulated using MaxEnt software based on species presence data at 44 locations and 19 bioclimatic parameters. The future distributions of A. venetum were also projected in 2050 and 2070 under the climate change scenarios of RCP2.6 and RCP8.5 described in 5th Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The result showed that min air temperature of the coldest month, annual mean air temperature, precipitation of the coldest quarter and mean air temperature of the wettest quarter dominated the geographic distribution of A. venetum. Under current climate, the suitable habitats of A. venetum is 11.94% in China, the suitable habitats are mainly located in the middle of Xinjiang, in the northern part of Gansu, in the southern part of Neimeng, in the northern part of Ningxia, in the middle and northern part of Shaanxi, in the southern part of Shanxi, in the middle and northern part of Henan, in the middle and southern part of Hebei, Shandong, Tianjin, in the southern part of Liaoning and part of Beijing. From 2050 to 2070, the model outputs indicated that the suitable habitats of A. venetum would decrease under the climate change scenarios of RCP2.6 and RCP8.5.
Chemopreventive Potential of Ethanolic Extracts of Luobuma Leaves (Apocynum venetum L.) in Androgen Insensitive Prostate Cancer.[Pubmed: 28846663]
None


