Cinnamomum cassia
Cinnamomum cassia
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
Natural products/compounds from Cinnamomum cassia
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
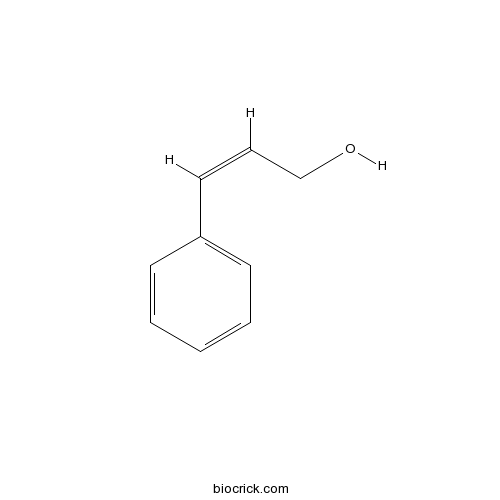
BCN4967
Cinnamyl alcohol104-54-1
Instructions
-
BCN2914
Isoliquiritin apioside120926-46-7
Instructions

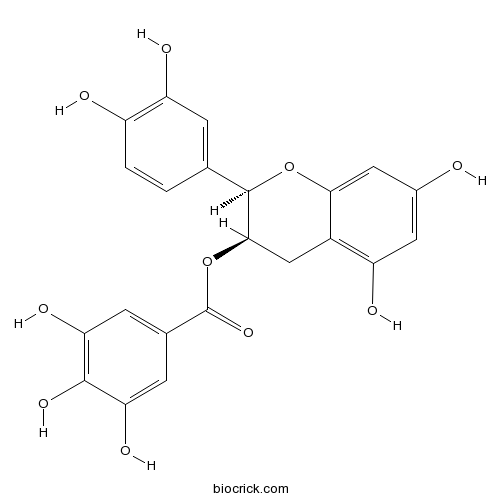
-
BCN6327
(-)-Epicatechin gallate1257-08-5
Instructions
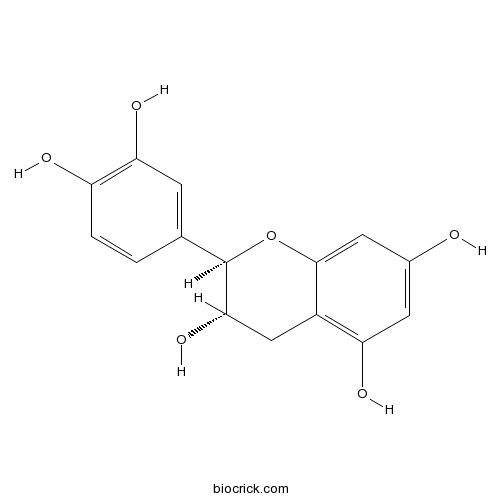
-
BCN1688
Catechin154-23-4
Instructions
-
BCN6314
Procyanidin B120315-25-7
Instructions

-
BCN6315
Procyanidin B229106-49-8
Instructions

-
BCN6805
Procyanidin A241743-41-3
Instructions

-
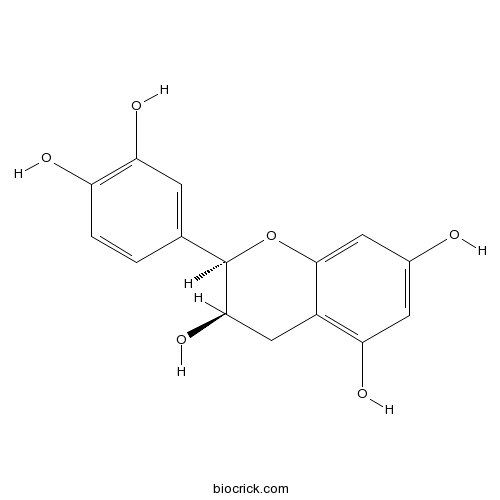
BCN5550
Taxifolin480-18-2
Instructions

-
BCN5597
Epicatechin490-46-0
Instructions
-
BCN3820
Stearic Acid57-11-4
Instructions

-
BCN5038
2-Methoxycinnamic acid6099-03-2
Instructions

-
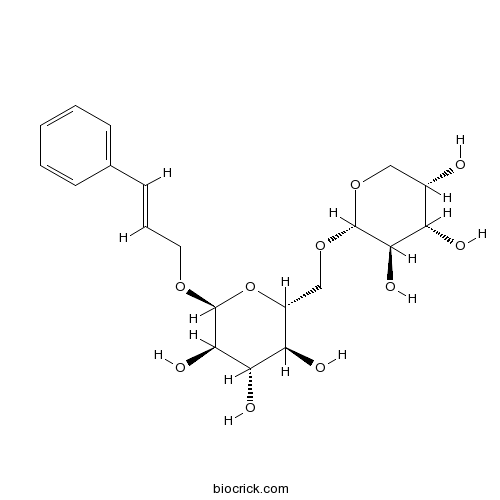
BCN5968
Rosavin84954-92-7
Instructions
-
BCN6309
Coumarin91-64-5
Instructions

-
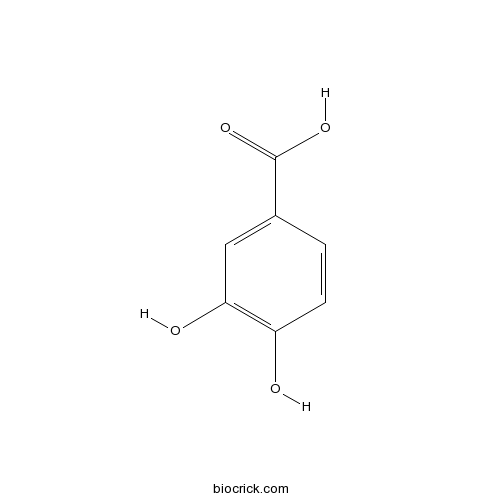
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
Tissue-specific chemical profiling and quantitative analysis of bioactive components of Cinnamomum cassia by combining laser-microdissection with UPLC-Q/TOF-MS.[Pubmed: 29931454]
Cinnamomi Cortex, the dried stem bark of Cinnamomum cassia Presl (Rougui in Chinese) has been widely used in traditional Chinese medicine, cooking and perfumery for thousands of years. Traditionally, the Cinnamomi Cortex of thick size is considered to be of good quality; however, there is no scientific data to support this point. Considering that essential oils are the main bioactive components, Cinnamomi Cortex of greater variety and amount essential oils is thought to be of better quality. In this study, laser microdissection coupled with ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole/time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q/TOF-MS) was applied to profile the essential oils in different tissues of Cinnamomi Cortex and to determine if there is a correlation between the essential oil content and the stem bark thickness.
Phenolic Constituents Isolated from the Twigs of Cinnamomum cassia and Their Potential Neuroprotective Effects.[Pubmed: 29883114]
None
Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Properties of Bioactive Metabolites Produced by Streptomyces cavourensis YBQ59 Isolated from Cinnamomum cassia Prels in Yen Bai Province of Vietnam.[Pubmed: 29869093]
None
Supercritical carbon dioxide extract of Cinnamomum cassia bark: toxicity and repellency against two stored-product beetle species.[Pubmed: 29804253]
None
Investigation of the Antifungal Activity and Mode of Action of Thymus vulgaris, Citrus limonum, Pelargonium graveolens, Cinnamomum cassia, Ocimum basilicum, and Eugenia caryophyllus Essential Oils.[Pubmed: 29738503]
None


