Euphorbia lathyris
Euphorbia lathyris
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
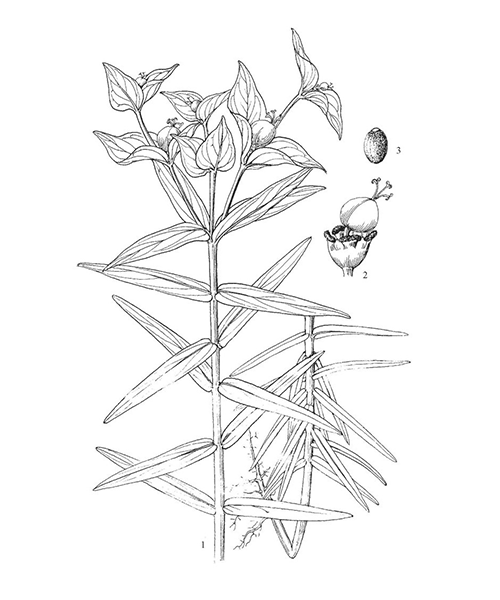
Natural products/compounds from Euphorbia lathyris
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
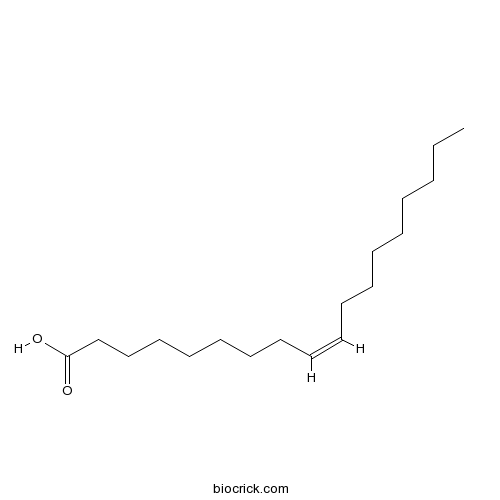
BCN7159
Oleic acid112-80-1
Instructions
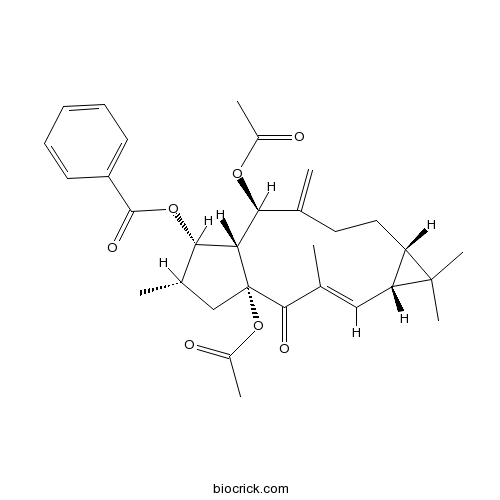
-
BCN3783
Euphorbia factor L2218916-51-9
Instructions
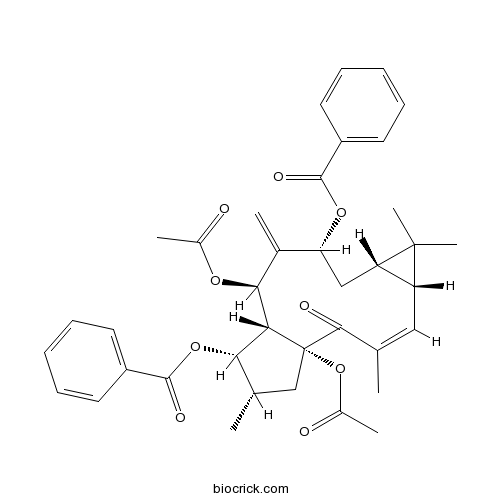
-
BCN1196
5,15-Diacetyl-3-benzoyllathyrol218916-52-0
Instructions
-
BCN3785
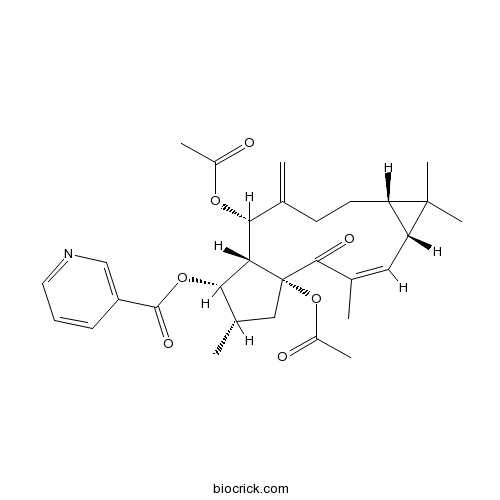
Euphorbia factor L8218916-53-1
Instructions
-
BCN2781
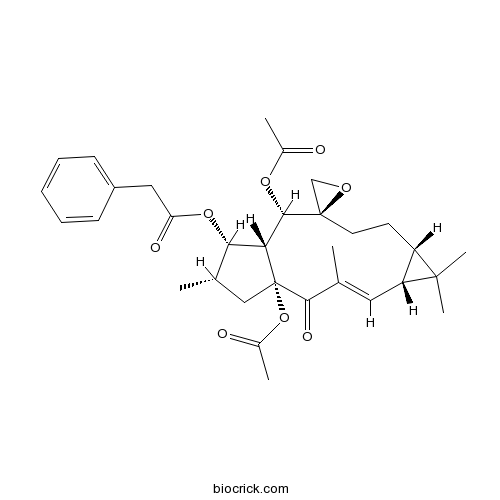
Euphorbiasteroid28649-59-4
Instructions
-
BCN2333
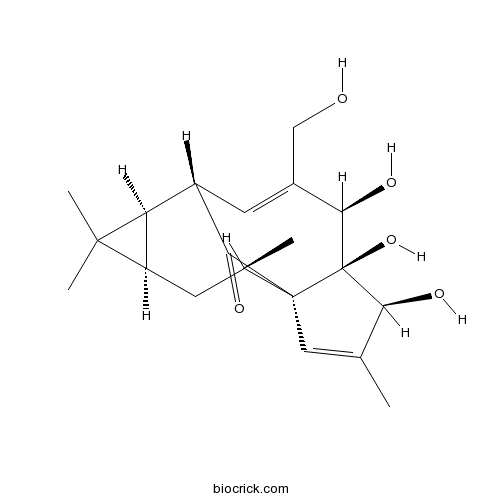
Ingenol30220-46-3
Instructions
-
BCN4963
Lathyrol34420-19-4
Instructions

-
BCN1051
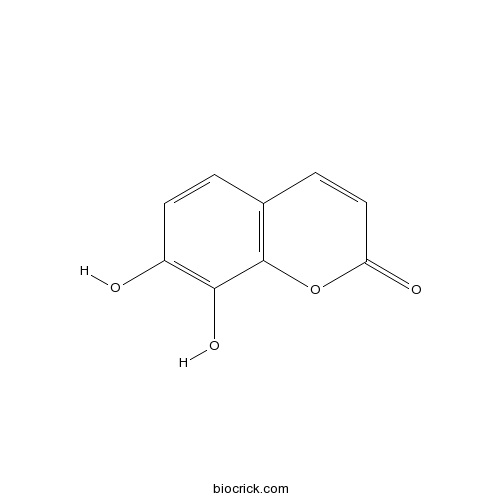
Daphnetin486-35-1
Instructions
-
BCN0415
Euphorbia factor L176376-43-7
Instructions

-
BCN3784
Euphorbia factor L7a93550-94-8
Instructions

-
BCN8649
Euphorbia factor L7b93550-95-9
Instructions
-
BCN4546
4-Hydroxybenzoic acid99-96-7
Instructions

Euphorbia factor L2 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury and inflammation in mice through the suppression of NF-κB activation.[Pubmed: 30055150]
Acute respiratory distress syndrome threatens public health with high morbidity and mortality due to ineffective intervention whereby lipopolysaccharide (LPS) induced acute lung injury (ALI) in mice provides a research model. The seeds of Euphorbia lathyris L. have a long history of usage in Traditional Chinese Medicine. Euphorbia factors L1-L11, extracted from this herb, have been reported to have anti-inflammation and anti-cancer effects. Here, we report the preventive and therapeutic potential of Euphorbia factor L2 (EFL2) on LPS-induced ALI in mice, where EFL2 attenuated pathological alterations in the lung and improved survival. Significant suppression of the recruitment and transmigration of inflammatory cells, specifically neutrophils, by 40 mg/kg of EFL2 was observed. EFL2 exerted potent anti-inflammatory effects by decreasing the levels of interleukin-1β (IL-1 β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF- α), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and myeloperoxidase (MPO) in the lung and bronchioalveolar lavage fluid. Consistent with the findings in vivo, EFL2 also showed robust inhibitory effects on the production of IL-1 β, IL-6, TNF- α and IL-8 released from LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 cells in vitro. Interestingly, this effect appeared to be mediated by EFL2's inhibition of NF-κB signaling activation, but not the MAPK pathway. Not only phosphorylation of IKK α/β and IκBα was down-regulated, p65 translocation and its DNA-binding activity were also significantly suppressed by EFL2. Moreover, overexpression of p65 reversed the inhibitory effect of EFL2 in LPS-induced NF-κB activation and cytokines production. The observed anti-inflammatory bioactivity of EFL2 indicates its potential as a drug development candidate, particularly for LPS-mediated disorders of inflammation.
Expression of AQP2, AQP4 and AQP 8 in mouse intestine induced by unprocessed and processed Euphorbia lathyris.[Pubmed: 30033405]
The present research was designed to study expression of AQP2, AQP4 and AQP8 in mouse intestines induced by unprocessed and processed Euphorbia lathyris. KM mice were given by different dose lavage of unprocessed and processed Euphorbia lathyris, Euphorbia factor L1, Euphorbia factor L2, Euphorbia factor L3. Samples of mouse intestine were collected for protein levels of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 which were assessed by immunohistochemical staining and mRNA expression of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 which were quantified by Real Time-PCR. Comparing to the normal control group, the protein levels of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 were significantly decreased (P<0.05)by Semen Euphorbiae group and Semen Euphorbiae Pulveratum group (unprocessed and processed Euphorbia lathyris) induced. Protein expression of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 in the Euphorbia factor L1, Euphorbia factor L2 and Euphorbia factor L3 group were not significantly lower than normal control group. There had no differences on the levels of AQP2 and AQP 8 mRNA expressions between the high-dose group of semen Euphorbiae group, semen Euphorbiae Pulveratum group and positive control group, while significantly lower than normal control group (P<0.05). Expression of AQP4 mRNA in the Semen Euphorbiae group and Semen Euphorbiae Pulveratum group has not significantly decreased. But levels of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 mRNA in the Euphorbia factor L1 group had no significant differences in normal control group and positive control group. These findings suggest that semen Euphorbiae could regulate expression of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 protein and mRNA, which may be the possible one reason of semen Euphorbiae induces diarrhea. The semen Euphorbiae group has more significant effects on the levels of AQP2, AQP 4 and AQP 8 protein and mRNA than semen Euphorbiae Pulveratum group, which may be one of the mechanisms of processing attenuation.
LOL2 and LOL5 loci control latex production by laticifer cells in Euphorbia lathyris.[Pubmed: 29878406]
Laticifers are specialized plant cells capable of indefinite elongation that ramify extensively and are responsible for latex biosynthesis and accumulation. However, the mechanisms underlying laticifer cell differentiation, growth and production of latex remain largely unknown. In a search for mutants showing enhanced accumulation of latex we identified two LOT OF LATEX (LOL) loci in Euphorbia lathyris. lol2 and lol5 mutants show enhanced production of latex contained within laticifer cells. The recessive lol2 mutant carries increased biosynthesis of the plant hormone jasmonoyl-isoleucine (JA-Ile) and therefore establishes a genetic link between jasmonic acid (JA) signaling and latex production in laticifers. Instead, heightened production of latex in lol5 plants obeys to enhanced proliferation of laticifer cells. Phylogenetic analysis of laticifer-expressed genes in E. lathyris and in two other latex-bearing species, Euphorbia corallioides and Euphorbia palustris, allowed the identification of canonical JA responsive elements present in the gene promoter regions of laticifer marker genes. Moreover, we identified that the hormone JA functions not as a morphogen for laticifer differentiation but as a trigger for the fill out of laticifers with latex and the associated triterpenoids. The identification of LOL loci represents a further step towards the understanding of mechanisms controlling latex production in laticifer cells.
Jageum-Jung improves 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis-like skin lesions in mice and suppresses pro-inflammatory chemokine production by inhibiting TNF-α/IFN-γ-induced STAT-1 and NFκB signaling in HaCaT cells.[Pubmed: 29660465]
Jageum-Jung (JGJ) is an oriental herbal formula comprising five herbs (Melaphis chinensis Bell, Cremastra variabilis Nakai, Knoxia valerianoides Thorel, Euphorbia lathyris L., and Moschus moschiferus L.). It has been used for detoxification and treating cancer and inflammatory diseases in China, Japan, and Korea. However, the mechanism of action of JGJ on keratinocyte inflammatory response is poorly understood.
Cytotoxic Lathyrane-Type Diterpenes from Seeds of Euphorbia lathyris.[Pubmed: 29593174]
None
Mechanism of action of cytotoxic compounds from the seeds of Euphorbia lathyris.[Pubmed: 29519320]
The seeds of Euphorbia lathyris are used in traditional Chinese medicines for the treatment of various medical conditions. E. lathyris contains many natural diterpenes with a lathyrane skeleton.
High-titer production of lathyrane diterpenoids from sugar by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae.[Pubmed: 29247866]
Euphorbiaceae are an important source of medically important diterpenoids, such as the anticancer drug ingenol-3-angelate and the antiretroviral drug prostratin. However, extraction from the genetically intractable natural producers is often limited by the small quantities produced, while the organic synthesis of terpene-derived drugs is challenging and similarly low-yielding. While transplanting the biosynthetic pathway into a heterologous host has proven successful for some drugs, it has been largely unsuccessful for diterpenoids due to their elaborate biosynthetic pathways and lack of genetic resources and tools for gene discovery. We engineered casbene precursor production in S. cerevisiae, verified the ability of six Euphorbia lathyris and Jatropha curcas cytochrome P450s to oxidize casbene, and optimized the expression of these P450s and an alcohol dehydrogenase to generate jolkinol C, achieving ~800mg/L of jolkinol C and over 1g/L total oxidized casbanes in millititer plates, the highest titer of oxidized diterpenes in yeast reported to date. This strain enables the semisynthesis of biologically active jolkinol C derivatives and will be an important tool in the elucidation of the biosynthetic pathways for ingenanes, tiglianes, and lathyranes. These findings demonstrate the ability of S. cerevisiae to produce oxidized drug precursors in quantities that are sufficient for drug development and pathway discovery.
Phytochemicals of Euphorbia lathyris L. and Their Antioxidant Activities.[Pubmed: 28820480]
None
Euphorbia factor L1 inhibits osteoclastogenesis by regulating cellular redox status and induces Fas-mediated apoptosis in osteoclast.[Pubmed: 28774817]
Excessive bone resorption caused by increased osteoclast number or activity leads to a variety of bone diseases including osteoporosis, rheumatoid arthritis and periodontitis. Thus, the therapeutic strategy for these diseases has been focused primarily on the inhibition of osteoclast formation and function. This study shows that euphorbia factor L1 (EFL1), a diterpenoid isolated from Euphorbia lathyris, inhibited osteoclastogenesis and induced osteoclast apoptosis. EFL1 suppressed osteoclast formation and bone resorption at both initial and terminal differentiation stages. EFL1 inhibited receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL)-induced NFATc1 induction with attenuated NF-κB activation and c-Fos expression. EFL1 decreased the level of reactive oxygen species by scavenging them or activating Nrf2, and inhibited PGC-1β that regulates mitochondria biogenesis. In addition, EFL1 induced apoptosis in differentiated osteoclasts by increasing Fas ligand expression followed by caspase activation. Moreover, EFL1 inhibited inflammation-induced bone erosion and ovariectomy-induced bone loss in mice. These findings suggest that EFL1 inhibits osteoclast differentiation by regulating cellular redox status and induces Fas-mediated apoptosis in osteoclast, and may provide therapeutic potential for preventing or treating bone-related diseases caused by excessive osteoclast.


