DaphnetinCAS# 486-35-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 486-35-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5280569 | Appearance | White-yellowish powder |
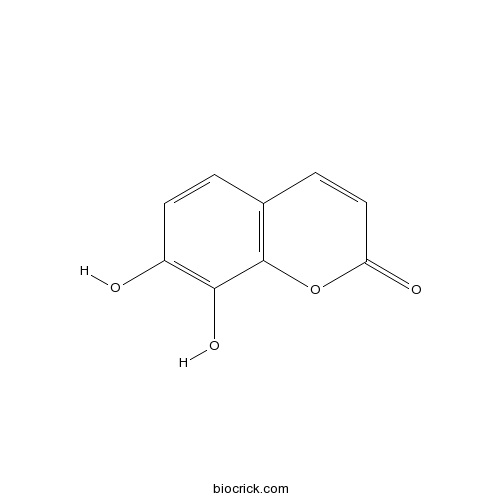
| Formula | C9H6O4 | M.Wt | 178.14 |
| Type of Compound | Coumarins | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Daphnetol; 7,8-Dihydroxycoumarin; Ruixiangsu | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : 50 mg/mL (280.68 mM; Need ultrasonic) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL (insoluble) | ||
| Chemical Name | 7,8-dihydroxychromen-2-one | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC(=C(C2=C1C=CC(=O)O2)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ATEFPOUAMCWAQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C9H6O4/c10-6-3-1-5-2-4-7(11)13-9(5)8(6)12/h1-4,10,12H | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Daphnetin is a dihydroxycoumarin that is being used in China for the treatment of coagulation disorders, is a protein kinase inhibitor, inhibits EGFR, PKA and PKC with IC50 of 7.67 μM, 9.33 μM and 25.01 μM, respectively, also known to exhibit antimalarial, anti-rheumatoid arthritis, anti-proliferative, anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant activities. it is also a chelator and an antioxidant. Daphnetin can enhance immunological functions of B lymphocytes, the expression of IL-12 in B lymphocytes can be up-regulated by daphnetin through natural immunity approach. |
| Targets | NF-kB | TNF-α | Bcl-2/Bax | Calcium Channel | IL Receptor | p38MAPK | ERK | P-gp | cAMP | PKA | PKC | EGFR |
| In vitro | Differential effects of esculetin and daphnetin on in vitro cell proliferation and in vivo estrogenicity.[Pubmed: 21741969]Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):35-41.Esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) and Daphnetin (7,8-dihydroxycoumarin) are secondary metabolites of plants used in folk medicine. These compounds have showed great antiproliferative activity in several tumor cell lines and have been proposed as potential anticancer agents. However, the estrogenic potential of these two compounds has to date not been reported.
Daphnetin: a novel antimalarial agent with in vitro and in vivo activity.[Pubmed: 1311154]Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Jan;46(1):15-20.Daphnetin is a dihydroxycoumarin that is being used in China for the treatment of coagulation disorders. It is also a chelator and an antioxidant. In vitro, Daphnetin causes a 50% inhibition (IC50) of 3H-hypoxanthine incorporation by Plasmodium falciparum at concentrations between 25 and 40 microM. Several related compounds, such as scopoletin, 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid show no inhibitory activity. The antimalarial activity of Daphnetin is inhibited by the addition of iron. Daphnetin does not appear to be an oxidant drug, since it does not spontaneously generate superoxide in vitro. However, it does alkylate bovine serum albumin when incubated in the presence of iron. In vivo, Daphnetin significantly prolongs survival of P. yoelli-infected mice. |
| In vivo | Anti-inflammatory and protective properties of daphnetin in endotoxin-induced lung injury.[Pubmed: 25419854]J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Dec 24;62(51):12315-25.Uncontrolled inflammatory responses cause tissue injury and severe immunopathology. Pharmacological interference of intracellular pro-inflammatory signaling may confer a therapeutic benefit under these conditions.
Daphnetin, a natural coumarin derivative, has been used to treat inflammatory diseases including bronchitis. However, the protective effect of Daphnetin in inflammatory airway disorders has yet to be determined, and the molecular basis for its anti-inflammatory properties is unknown.
|
| Kinase Assay | Daphnetin induced differentiation of human renal carcinoma cells and its mediation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed: 15081877 ]Groove binding interaction between daphnetin and calf thymus DNA.[Pubmed: 25541356]Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Mar;74:185-94.The binding characteristics of Daphnetin with calf thymus DNA (ctDNA) were investigated by multispectroscopic and chemometric approaches coupled with DNA viscosity measurements, melting studies and molecular docking technique.
Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 May 1;67(9):1779-88.Daphnetin has been shown to be a potent in vitro anti-proliferative agent to the human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell line, A-498.
|
| Cell Research | Neuroprotective effects of daphnetin against NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity.[Pubmed: 25225718]Molecules. 2014 Sep 15;19(9):14542-55.The accumulation of glutamate can excessively activate the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and cause excitotoxicity. Daphnetin (Dap), a coumarin derivative, is a protein kinase inhibitor that exhibits antioxidant and neuroprotective properties. However, little is known about the neuroprotective effects of Dap on glutamate-induced excitotoxicity.
|
| Animal Research | Therapeutic effects of daphnetin on adjuvant-induced arthritic rats.[Pubmed: 18835428 ]J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):259-63.Daphnetin was regarded as the mark compound for quality control of Zushima-Pian, a traditional Chinese medicine tablet for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, no in vivo study on the therapeutic effects of Daphnetin for RA has been reported.
|
| Structure Identification | Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Jul 14;260(3):682-5.Daphnetin, one of coumarin derivatives, is a protein kinase inhibitor.[Pubmed: 10403826 ]Protein kinases play key roles in the control of cell proliferation, differentiation and metabolism.
|

Daphnetin Dilution Calculator

Daphnetin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.6136 mL | 28.0678 mL | 56.1356 mL | 112.2712 mL | 140.3391 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1227 mL | 5.6136 mL | 11.2271 mL | 22.4542 mL | 28.0678 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5614 mL | 2.8068 mL | 5.6136 mL | 11.2271 mL | 14.0339 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.1123 mL | 0.5614 mL | 1.1227 mL | 2.2454 mL | 2.8068 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0561 mL | 0.2807 mL | 0.5614 mL | 1.1227 mL | 1.4034 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Fraxinol
Catalog No.:BCN5584
CAS No.:486-28-2
- Isofraxidin
Catalog No.:BCN2327
CAS No.:486-21-5
- PMX 464
Catalog No.:BCC6348
CAS No.:485842-97-5
- Mirabijalone D
Catalog No.:BCN4071
CAS No.:485811-84-5
- Choline sulphate
Catalog No.:BCN1792
CAS No.:4858-96-2
- Proanthocyanidins
Catalog No.:BCN6313
CAS No.:4852-22-6
- 5,7,3'-Trihydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCC8269
CAS No.:104732-07-2
- Hydrangetin
Catalog No.:BCN7439
CAS No.:485-90-5
- Formononetin
Catalog No.:BCN1061
CAS No.:485-72-3
- Cinchonidine
Catalog No.:BCC5316
CAS No.:485-71-2
- (+)-Bicuculline
Catalog No.:BCN1238
CAS No.:485-49-4
- Cytisine
Catalog No.:BCN6270
CAS No.:485-35-8
- (S)-Coclaurine
Catalog No.:BCN5585
CAS No.:486-39-5
- (-)-Cotinine
Catalog No.:BCC7569
CAS No.:486-56-6
- Bergaptol
Catalog No.:BCN5588
CAS No.:486-60-2
- Ononin
Catalog No.:BCN5926
CAS No.:486-62-4
- Isoformononetin
Catalog No.:BCN8206
CAS No.:486-63-5
- Vasicinone
Catalog No.:BCN5589
CAS No.:486-64-6
- Daidzein
Catalog No.:BCN5590
CAS No.:486-66-8
- Harman
Catalog No.:BCN3998
CAS No.:486-84-0
- N-Methylcytisine
Catalog No.:BCN1266
CAS No.:486-86-2
- alpha-Isolupanine
Catalog No.:BCN7989
CAS No.:486-87-3
- Anagyrine
Catalog No.:BCN3049
CAS No.:486-89-5
- Thermopsine
Catalog No.:BCN2603
CAS No.:486-90-8
Neuroprotective effects of daphnetin against NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity.[Pubmed:25225718]
Molecules. 2014 Sep 15;19(9):14542-55.
The accumulation of glutamate can excessively activate the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and cause excitotoxicity. Daphnetin (Dap), a coumarin derivative, is a protein kinase inhibitor that exhibits antioxidant and neuroprotective properties. However, little is known about the neuroprotective effects of Dap on glutamate-induced excitotoxicity. We evaluated the neuroprotective activities in the primary cultured cortical neurons against NMDA-induced excitotoxicity. Pretreatment with Dap significantly prevented NMDA-induced neuronal cell loss. Dap significantly inhibited the neuronal apoptosis by regulating balance of Bcl-2 and Bax expression. Furthermore, pretreatment of Dap reversed the up-regulation of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors and inhibited the intracellular Ca2+ overload induced by NMDA exposure. In addition, Dap prevented cerebral ischemic injury in mice induced via a 2 h middle cerebral artery occlusion and a 24 h reperfusion in vivo. The findings suggest that Dap prevents the excitotoxicity through inhibiting the NR2B-containing NMDA receptors and the subsequent calcium overload in cultured cortical neurons.
Daphnetin: a novel antimalarial agent with in vitro and in vivo activity.[Pubmed:1311154]
Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1992 Jan;46(1):15-20.
Daphnetin is a dihydroxycoumarin that is being used in China for the treatment of coagulation disorders. It is also a chelator and an antioxidant. In vitro, Daphnetin causes a 50% inhibition (IC50) of 3H-hypoxanthine incorporation by Plasmodium falciparum at concentrations between 25 and 40 microM. Several related compounds, such as scopoletin, 2, 3-dihydroxybenzoic acid and 3, 4-dihydroxybenzoic acid show no inhibitory activity. The antimalarial activity of Daphnetin is inhibited by the addition of iron. Daphnetin does not appear to be an oxidant drug, since it does not spontaneously generate superoxide in vitro. However, it does alkylate bovine serum albumin when incubated in the presence of iron. In vivo, Daphnetin significantly prolongs survival of P. yoelli-infected mice.
Differential effects of esculetin and daphnetin on in vitro cell proliferation and in vivo estrogenicity.[Pubmed:21741969]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2011 Oct 1;668(1-2):35-41.
Esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) and Daphnetin (7,8-dihydroxycoumarin) are secondary metabolites of plants used in folk medicine. These compounds have showed great antiproliferative activity in several tumor cell lines and have been proposed as potential anticancer agents. However, the estrogenic potential of these two compounds has to date not been reported. The present study compared esculetin and Daphnetin on the inhibition of cell proliferation and cell cycle progression of the MCF-7 estrogen-responsive human carcinoma cell line. In vivo and in vitro estrogenic activity for both compounds was also evaluated. Esculetin inhibited cell proliferation after 72 h exposure (IC50=193 +/- 6.6 muM), while Daphnetin evidenced inhibiting effects starting at 24-h exposure (72 h, IC50=73 +/- 4.1 muM). Both effects showed changes in cyclin D1 gene expression. In non-estrogenic conditions (E-screening assay), esculetin produced biphasic response on proliferation of the MCF-7 cells; at 10(-8)-10(-6)M, concentrations induced proliferative effects as EC50=4.07 x 10(-9)M (E(2)=2.91 x 10(-12)M); at higher concentrations (10(-5)-10(-4)M), cell proliferation was inhibited. Relative proliferative effect at E(2) was 52% (E(2)=100), relative proliferative potency was 0.072 (E(2)=100). Additionally, esculetin tested in vivo showed estrogenic effects at 50-100mg/kg doses; relative uterotrophic effect at E(2) was 37%, with relative uterotrophic potency registered at 0.003. In contrast, Daphnetin did not induce estrogenic effects in vitro or with in vivo models. The low estrogenic activity of esculetin could prove useful in postmenopausal therapy but not as a safe antitumor agent in estrogen-dependent tumors. Daphnetin-based antiproliferative selectivity with MCF-7 cells showed that Daphnetin is a promising antitumoral agent also acting on estrogen dependent tumors.
Daphnetin, one of coumarin derivatives, is a protein kinase inhibitor.[Pubmed:10403826]
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1999 Jul 14;260(3):682-5.
Protein kinases play key roles in the control of cell proliferation, differentiation and metabolism. In this work, we studied the effect of coumarin and its derivatives, including Daphnetin, esculin, 2-OH-coumarin, 4-OH-coumarin and 7-OH-coumarin, on the activity of protein kinases. It was found that, in these compounds, only Daphnetin was a protein kinase inhibitor. This compound inhibited tyrosine-specific protein kinase, EGF receptor (IC(50) = 7.67 microM), and serine/threonine-specific protein kinases, including cAMP-dependent protein kinase (PKA) (IC(50) = 9.33 microM) and protein kinase C (PKC) (IC(50) = 25.01 microM) in vitro. The inhibition of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase by Daphnetin was competitive to ATP and non-competitive to the peptide substrate. The inhibition of EGF-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of EGF receptor by Daphnetin was not observed in human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. The structural comparison of Daphnetin with coumarin and other coumarin derivatives suggests that the hydroxylation at C8 may be required for Daphnetin acting as a protein kinase inhibitor.
Anti-inflammatory and protective properties of daphnetin in endotoxin-induced lung injury.[Pubmed:25419854]
J Agric Food Chem. 2014 Dec 24;62(51):12315-25.
Uncontrolled inflammatory responses cause tissue injury and severe immunopathology. Pharmacological interference of intracellular pro-inflammatory signaling may confer a therapeutic benefit under these conditions. Daphnetin, a natural coumarin derivative, has been used to treat inflammatory diseases including bronchitis. However, the protective effect of Daphnetin in inflammatory airway disorders has yet to be determined, and the molecular basis for its anti-inflammatory properties is unknown. This paper shows that Daphnetin treatment conferred substantial protection from endotoxin-induced acute lung injury (ALI), in parallel with reductions in the production of inflammatory mediators, symptoms of airway response, and infiltration of inflammatory cells. Further studies indicate that activation of macrophage and human alveolar epithelial cells in response to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) was remarkably suppressed by Daphnetin, which was related to the down-regulation of NF-kappaB-dependent signaling events. Importantly, this study demonstrates that TNF-alpha-induced protein 3 (TNFAIP3), also known as A20, was significantly induced by Daphnetin, which appeared to be largely responsible for the down-regulation of NF-kappaB activity through modulation of nondegradative TRAF6 ubiquitination. Accordingly, the deletion of TNFAIP3 in primary macrophages reversed Daphnetin-elicited inhibition of immune response, and the beneficial effect of Daphnetin in the pathogenesis of ALI was, partially at least, abrogated by TNFAIP3 knockdown. These findings demonstrate the anti-inflammatory and protective functions of Daphnetin in endotoxin-induced lung inflammation and injury and also reveal the key mechanism underlying its action in vitro as well as in vivo.
Daphnetin induced differentiation of human renal carcinoma cells and its mediation by p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase.[Pubmed:15081877]
Biochem Pharmacol. 2004 May 1;67(9):1779-88.
Daphnetin has been shown to be a potent in vitro anti-proliferative agent to the human renal cell carcinoma (RCC) cell line, A-498. In the present study, we investigated its effects on mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling along with cell cycle events and cellular differentiation. Daphnetin-activated p38, however, higher concentrations were required to inhibit ERK1/ERK2. In addition, it did not activate SAPK or induce apoptosis, but instead inhibited S phase cell cycle transition of A-498 cells at low concentrations and time of exposure. In addition, a late G(1), early S phase inhibition was observed at higher concentrations and time of exposure, indicating that the mechanism of Daphnetin-induced differentiation was concentration dependent. Increased expression of the epithelial differentiation markers cytokeratins 8 and 18, correlated with increasing concentrations of Daphnetin, while pre-treatment with a specific p38-inhibitor, served to limit this effect. There was no evidence that P-glycoprotein (P-gp) mediated multi-drug resistance (MDR) played a role in the anti-proliferative activity of Daphnetin. Consequently, we concluded that p38 MAP kinase is intrinsically involved in mediating the effect of Daphnetin in A-498 cells, suggesting that this drug may act by promotion of cellular maturation, and consequently may represent a novel low toxic approach for the treatment of poorly differentiated RCCs.
Therapeutic effects of daphnetin on adjuvant-induced arthritic rats.[Pubmed:18835428]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Nov 20;120(2):259-63.
AIM OF THIS STUDY: Daphnetin was regarded as the mark compound for quality control of Zushima-Pian, a traditional Chinese medicine tablet for treating rheumatoid arthritis (RA). However, no in vivo study on the therapeutic effects of Daphnetin for RA has been reported. MATERIALS AND METHODS: The adjuvant arthritic (AA) rat model was developed to evaluate the anti-arthritic effects of Daphnetin. After immunized with Freund's complete adjuvant (FCA), the rats were treated with Daphnetin (2.25 and 4.5mg/kg) for three weeks. We determined the change of secondary paw swelling and the arthritis scores of these tested rats. The severity of arthritis in the knee joints was evaluated by histological assessment of cartilage destruction. The levels of IL-1, TNF-alpha and MIF in the serum were measured by ELISA. RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS: Our results showed that Daphnetin significantly reduced paw swelling and decreased the arthritis scores. The pathological examination demonstrated that articular cartilage degeneration with synovial hyperplasia and inflammatory cells infiltration in AA rats were suppressed by Daphnetin. There was significant reduction in production of interleukin-1 (IL-1), tumor necrosis factor (TNF-alpha) and macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) in serum of AA rats treated with Daphnetin except the low dose group (2.25mg/kg) on TNF-alpha. In conclusion, we demonstrates that Daphnetin is highly effective on preventing and suppressing the development and progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis and provides direct evidences that Daphnetin is one of the active principle of Zushima-Pian for treating rheumatoid arthritis.
Groove binding interaction between daphnetin and calf thymus DNA.[Pubmed:25541356]
Int J Biol Macromol. 2015 Mar;74:185-94.
The binding characteristics of Daphnetin with calf thymus DNA (ctDNA) were investigated by multispectroscopic and chemometric approaches coupled with DNA viscosity measurements, melting studies and molecular docking technique. The expanded UV-vis spectral data matrix was processed by multivariate curve resolution-alternating least-squares method to obtain the concentration profiles of the components (Daphnetin, ctDNA and Daphnetin-ctDNA complex) to quantitatively monitor the Daphnetin-ctDNA interaction. The groove mode of Daphnetin binding to ctDNA was concluded by little change in melting temperature, viscosity of ctDNA and iodide quenching effect as well as increase in single-stranded DNA quenching effect. Moreover, the quantitative data for the competitive binding between Daphnetin and Hoechst 33258 for ctDNA obtained by resolving the three-way synchronous fluorescence spectra data using parallel factor analysis modeling further supported the groove binding. The molecular docking visualized the results of the Fourier transform infrared analysis that the adenine and thymine bases in the minor groove of ctDNA were the main binding sites for Daphnetin, and the circular dichroism spectra showed that the groove binding of Daphnetin to ctDNA led to the conformational change in ctDNA from B-form to A-form. This study revealed the interaction mechanism of Daphnetin with ctDNA.


