Solanum lyratum
Solanum lyratum
1. The products in our compound library are selected from thousands of unique natural products; 2. It has the characteristics of diverse structure, diverse sources and wide coverage of activities; 3. Provide information on the activity of products from major journals, patents and research reports around the world, providing theoretical direction and research basis for further research and screening; 4. Free combination according to the type, source, target and disease of natural product; 5. The compound powder is placed in a covered tube and then discharged into a 10 x 10 cryostat; 6. Transport in ice pack or dry ice pack. Please store it at -20 °C as soon as possible after receiving the product, and use it as soon as possible after opening.
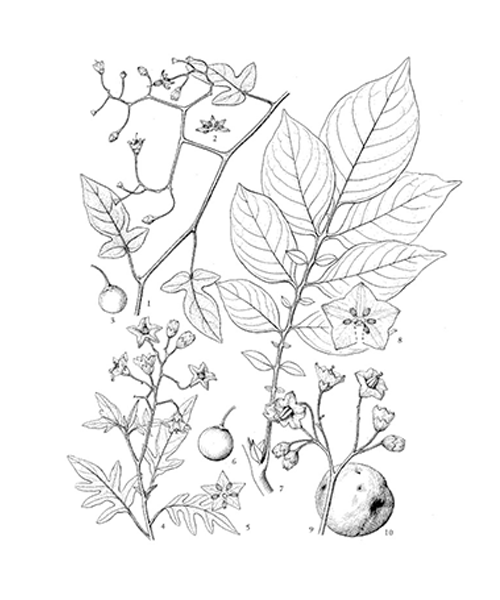
Natural products/compounds from Solanum lyratum
- Cat.No. Product Name CAS Number COA
-
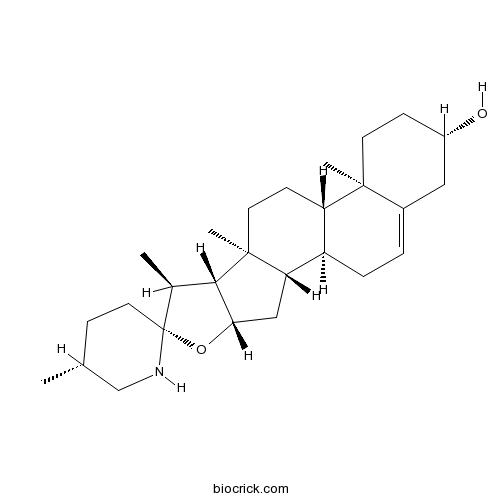
BCN2346
Solasodine126-17-0
Instructions
-
BCN8170
Physcion 1-glucoside23451-01-6
Instructions

-
BCN1061
Formononetin485-72-3
Instructions

-
BCN5926
Ononin486-62-4
Instructions

-
BCN5590
Daidzein486-66-8
Instructions

-
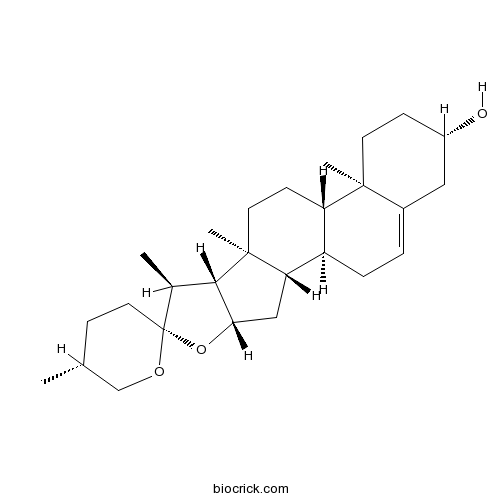
BCN6272
Diosgenin512-04-9
Instructions
-
BCN2396
Genistin529-59-9
Instructions

-
BCN5891
Daidzin552-66-9
Instructions

-
BCN2502
Isovanillin621-59-0
Instructions

-
BCN4604
N-Feruloyloctopamine66648-44-0
Instructions

-
BCN4327
Ursolic acid77-52-1
Instructions

-
BCN5327
Tigogenin77-60-1
Instructions

-
BCN4450
Neochlorogenic acid906-33-2
Instructions

-
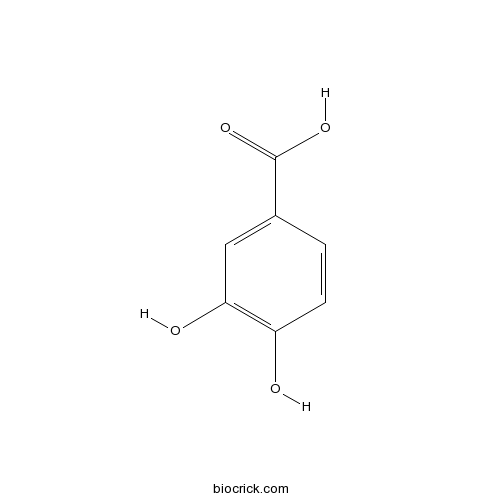
BCN4537
3,4-Dihydroxybenzoic acid99-50-3
Instructions
New steroidal alkaloid and furostanol glycosides isolated from Solanum lyratum with cytotoxicity.[Pubmed: 30080648]
Two previously undescribed steroidal compounds, 16, 23-epoxy-22, 26-epimino-cholest-22(N), 23, 25(26)-trien-3β-ol-3-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-D-galactopyranoside (1) and 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-5α-furost-20(22)-en-3β, 26-diol (2), together with 7 known ones including 26-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(25R)-5, 20(22)-dien-furost-3β, 26-diol (3), (25R)-5-en-spirost-3β-ol-O-β-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→4)-[α-L-rhmanopyranosyl-(1→2)]-β-D-galactopyranoside (4), funkioside D (5), aspidistrin (6), tigogenin-3-O-β-D-lucotrioside (7), desglucolanatigonin II (8), and degalactotigonin (9), were isolated from Solanum lyratum Thunb. Their cytotoxic activities were tested in two cancer cell lines by MTT method. One of the steroidal glycosides (6) showed significant cytotoxic activity against gastric cancer SGC7901 and liver cancer BEL-7402 cells.
Chloroform Extract of Solanum lyratum Induced G0/G1 Arrest via p21/p16 and Induced Apoptosis via Reactive Oxygen Species, Caspases and Mitochondrial Pathways in Human Oral Cancer Cell Lines.[Pubmed: 26477797]
Solanum lyratum (SLEC) Thunberg (Solanaceae) has been used as a traditional herbal medicine in China for centuries. Numerous studies have shown that SLEC Thunberg (Solanaceae) extract inhibited cancer cell growth in vitro. Herein, we investigated cell death-induced by EcoAc, water, chloroform, butanol extract of SLEC in human oral cancer cell lines (HSC-3, SAS, and CAL-27) in vitro. Different SLEC extract induced cytotoxic effects in human oral cancer cells were examined by contrast phase microscopy. We selected the chloroform extract of SLEC to examine the cytotoxic effects by using DAPI staining, comet assays, flow cytometric assay, Western blotting and examination of confocal laser microscopy. SLEC decreased the percentage of viable cells, induced G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis. These effects were concentration- and time-dependent manners. SLEC increased protein levels of p21, p16, CDK2, and cyclin D1 in HSC-3, SAS, and CAL-27 cells. Also, SLEC increased CDK6 in HSC-3 and CAL-27 cells, but inhibited CDK6 in SAS cells. Cyclin E in HSC-3 and SAS cells was increased by SLEC, but it was inhibited in CAL-27 cells. SLEC suppressed the anti-apoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-xl, but increased the pro-apoptotic proteins Bax and Bad in HSC-3, SAS, and CAL-27 cells. SLEC promoted the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and Ca²⁺, decreased the mitochondrial membrane potential (Δψm) and stimulated NO production in HSC-3, SAS, and CAL-27 cells. Specific caspase inhibitors (caspase-8 inhibitor: Z-IETD-FMK; caspase-9 inhibitor: Z-LEHD-FMK and caspase-3 inhibitor: Z-DEVD-FMK) for caspase-8, -9, and -3 blocked SLE-activated caspase-8, -9, and -3 activities which were associated with an increase in the percentage of viable cells. Taken together, SLE induced G0/G1 arrest and apoptosis via extrinsic- and intrinsic-dependent pathways in HSC-3, SAS, and CAL-27 cells.
[Sesquiterpenoids from Solanum lyratum].[Pubmed: 24946547]
Ten compounds were isolated and purified by column chromatography over silica gel, preparative TLC, and Sephadex LH-20 from the whole plant of Solanum lyratum. The structures were elucidated on the basis of physico-chemical properties and spectral data as 1beta-hydroxy-1 ,2-dihydro-alpha-santonin (1) , boscialin (2) , blumenol C (3), 3beta-hydroxy-5alpha, 6alpha-epoxy-7-megastigmen-9-one(4), dehydrovomifoliol(5) , blumenol A(6), (1'S,2R,5S, 10R) -2-(1', 2'-dihydroxy-l1'-methylethyl) -6,10-dimethylspiro[4,5] dec-6-en-8-one(7) , (1'R,2R,5S,10R)-2-( 1',2'-dihydroxy-l '-methylethyl) -6,1 l0-dimethylspiro[4,5]dec-6-en-8-one( 8) , 2-(1',2'-dihydroxy-1 '-methylethyl) -6,1 0-dimethyl-9-hydroxyspiro [4,5] dec-6-en-8-one (9) , and grasshopper ketone (10). Compounds 1-10 were isolated from this plant for the first time.
New eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoid from Solanum lyratum with cytotoxic activity.[Pubmed: 24654878]
In our continuing effort to discover more new cytotoxic sesquiterpenoids from Solanum lyratum, one new eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoid (1, 3-keto-eudesm-9β,11-diol, named lyratol G), together with one known eudesmane-type sesquiterpenoid (2, 1β-hydroxy-1,2-dihydro-α-santonin), was obtained. The structure of the new sesquiterpenoid was elucidated on the basis of integrated spectroscopic techniques, mainly HR-FAB-MS, 1D and 2D NMR ((1)H-(1)H COSY, HMQC, HMBC and ROESY). In vitro, two sesquiterpenoids were found to exhibit significant cytotoxicity against three cancer cell lines (P-388, HONE-1 and HT-29), and gave IC50 values in the range of 3.1-6.9 μM.
A study on the inhibitory effect of Solanum lyratum Thunb extract on Lewis lung carcinoma lines.[Pubmed: 24311865]
The objective of this paper was to observe the effects of Solanum lyratum Thunb extract on tumour inhibition, immune function and survival time of tumour-bearing mice. Lung carcinoma-bearing mouse model was established, the tumour-bearing mice were divided into model group, CTX group, Solanum lyratum Thunb extract high-dose group and low-dose group. By the examination of tumour inhibition rate of Solanum lyratum Thunb extract in Lewis lung carcinoma-bearing mice and determination of the number of NK cells and T cell subsets, the survival rate of tumour-bearing mice was observed. Solanum lyratum Thunb extract had some anti-tumour effect in Lewis tumour-bearing mice. The tumour inhibition rate of high-dose group reached 46.28%, and the tumour inhibition rate of low-dose group was 31.42%. Solanum lyratum Thunb extract can improve the NK cell activity of Lewis tumour-bearing mice, increase the number of CD4 cells in the tumour-bearing mice, and significantly increase the survival rate of tumour-bearing mice. The study concluded that Solanum lyratum Thunb extract has some anti-tumour effect and can improve immune function and survival rate of tumour-bearing mice.
A study on anti-tumour effect of Solanum lyratum Thunb. extract in S₁₈₀ tumour-bearing mice.[Pubmed: 24311848]
The objective of the study was to investigate the anti-tumour effect of ethanol extract of Solanum lyratum Thunb. in S₁₈₀ tumour-bearing mice, and to preliminarily explore its mechanism of action.
[Solanum lyratum Thunberg alkaloid induces human lung adenoearcinoma A549 cells apoptosis by inhibiting NF-kappaB signaling pathway].[Pubmed: 24218975]
To investigate the effects of solanum lyratum Thunberg alkaloid (STA) on induction of apoptosis and the expression of NF-kappaB signaling pathway related genes in A549 cells.


