3F8GSK-3β inhibitor CAS# 159109-11-2 |
- Pyridostatin
Catalog No.:BCC1875
CAS No.:1085412-37-8
- 360A iodide
Catalog No.:BCC1308
CAS No.:737763-37-0
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 159109-11-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 23829003 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C15H14N2O4 | M.Wt | 286.28 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble to 25 mM in DMSO | ||
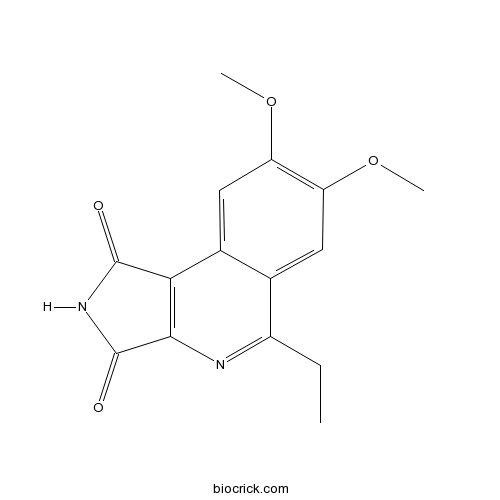
| Chemical Name | 5-ethyl-7,8-dimethoxypyrrolo[3,4-c]isoquinoline-1,3-dione | ||
| SMILES | CCC1=NC2=C(C3=CC(=C(C=C31)OC)OC)C(=O)NC2=O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ULVWJFBHQIXEPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C15H14N2O4/c1-4-9-7-5-10(20-2)11(21-3)6-8(7)12-13(16-9)15(19)17-14(12)18/h5-6H,4H2,1-3H3,(H,17,18,19) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent and selective GSK-3β inhibitor (IC50 values are 34 and 304 nM in the presence of 10 and 100 μM ATP respectively). |

3F8 Dilution Calculator

3F8 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4931 mL | 17.4654 mL | 34.9308 mL | 69.8617 mL | 87.3271 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6986 mL | 3.4931 mL | 6.9862 mL | 13.9723 mL | 17.4654 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3493 mL | 1.7465 mL | 3.4931 mL | 6.9862 mL | 8.7327 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0699 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 1.3972 mL | 1.7465 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0349 mL | 0.1747 mL | 0.3493 mL | 0.6986 mL | 0.8733 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 34 and 304 nM in the presence of 10 and 100 μM ATP, respectively.
3F8 is a potent and selective GSK-3β (Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3) inhibitor
GSK3 was identified as a serine/threonine protein kinase for the first time in the late 1970s and is highly conserved in all animals examined. GSK3 can regulate cell differentiation and apoptosis, and is an important component of the canonical Wnt pathway as well as the hedgehog pathway
In vitro: 3F8 specifically abolishes eye and forebrain formation in zebrafish embryos with the similar as a typical Wnt overexpression phenotype. Cell reporter assays, chemical informatics analysis and in vitro kinase experiments exhibited that 3F8 is a selective GSK3 inhibitor with more potent than SB216763 (a commonly used GSK3 inhibitor). Together, 3F8 and its derivatives could be useful as new agents and potential therapeutic candidates for GSK3 related diseases [1].
The interaction of 3F8 with its binding site were studied. To this end, first computational analysis conducted, and the results suggested that maleimide moiety of 3F8 might interact with the ATP binding site of GSK-3β, and the N-4 and C-5 positions were solvent-exposed, indicating the less key role of this region to the binding affinity. [2].
In vivo: The lowest ratio (CE/IC50 = 221) of 3F8 implied that 3F8 was more efficient in vivo, likely according to better absorption and/or stability [1]. By injection of a sub-lethal amount of morpholino antisense oligonucleotides, individual knockdown of gsk3a and gsk3b translations in zebrafish caused cardiac defect [1].
Clinical trial: Clinical study has been conducted.
References:
[1]. Zhong H, Zou H, Semenov MV, Moshinsky D, He X, Huang H, Li S, Quan J, Yang Z, Lin S. Characterization and development of novel small-molecules inhibiting GSK3 and activating Wnt signaling. Mol Biosyst. 2009 Nov;5(11):1356-60.
[2]. Zou H, Zhou L, Li Y, Cui Y, Zhong H, Pan Z, Yang Z, Quan J. Benzo[e]isoindole-1,3-diones as potential inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3). Synthesis, kinase inhibitory activity, zebrafish phenotype, and modeling of binding mode. J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 11;53(3):994-1003.
- F1839-I
Catalog No.:BCN6450
CAS No.:159096-49-8
- 6-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8769
CAS No.:15903-94-3
- Wedelobatin B
Catalog No.:BCN6730
CAS No.:1589488-35-6
- Wedelobatin A
Catalog No.:BCN6731
CAS No.:1589488-34-5
- Secoisolarisiresinol Diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCC9140
CAS No.:158932-33-3
- Boc-D-Tryptophanol
Catalog No.:BCC2698
CAS No.:158932-00-4
- APC 366
Catalog No.:BCC7392
CAS No.:158921-85-8
- GR 231118
Catalog No.:BCC7085
CAS No.:158859-98-4
- BET-BAY 002
Catalog No.:BCC5510
CAS No.:1588521-78-1
- ent-17-Hydroxykaura-9(11),15-dien-19-oic acid
Catalog No.:BCN6788
CAS No.:1588516-88-4
- 3Alaph-Tigloyloxypterokaurene L3
Catalog No.:BCN6787
CAS No.:1588516-87-3
- Boc-ß-HoAla-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3224
CAS No.:158851-30-0
- CARIPORIDE
Catalog No.:BCC6432
CAS No.:159138-80-4
- L-755,507
Catalog No.:BCC7282
CAS No.:159182-43-1
- MM 77 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6854
CAS No.:159187-70-9
- L-NIO dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6689
CAS No.:159190-44-0
- Isokaempferide
Catalog No.:BCN3790
CAS No.:1592-70-7
- PNU 22394 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7285
CAS No.:15923-42-9
- MPDC
Catalog No.:BCC6873
CAS No.:159262-32-5
- Everolimus (RAD001)
Catalog No.:BCC3594
CAS No.:159351-69-6
- N-Acetyl-O-phosphono-Tyr-Glu-Glu-Ile-Glu
Catalog No.:BCC5853
CAS No.:159439-02-8
- Enfuvirtide
Catalog No.:BCC5641
CAS No.:159519-65-0
- Fluconazole mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4236
CAS No.:159532-41-9
- GR 55562 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6913
CAS No.:159533-25-2
Key role for myeloid cells: phase II results of anti-G(D2) antibody 3F8 plus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor for chemoresistant osteomedullary neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:24644014]
Int J Cancer. 2014 Nov 1;135(9):2199-205.
Anti-G(D2) murine antibody 3F8 plus subcutaneously (sc) administered granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) was used against primary refractory neuroblastoma in metastatic osteomedullary sites. Large study size and long follow-up allowed assessment of prognostic factors in a multivariate analysis not reported with other anti-G(D2) antibodies. In a phase II trial, 79 patients without prior progressive disease were treated for persistent osteomedullary neuroblastoma documented by histology and/or metaiodobenzyl-guanidine (MIBG) scan. In the absence of human antimouse antibody, 3F8 + scGM-CSF cycles were repeated up to 24 months. Minimal residual disease (MRD) in bone marrow was measured by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction pre-enrollment and post-cycle #2, before initiation of 13-cis-retinoic acid. Study endpoints were: (i) progression-free survival (PFS) compared with the predecessor trial of 3F8 plus intravenously administered (iv) GM-CSF (26 patients) and (ii) impact of MRD on PFS. Using all 105 patients from the two consecutive 3F8 + GM-CSF trials, prognostic factors were analyzed by multivariate Cox regression model. Complete response rates to 3F8 + scGM-CSF were 87% by histology and 38% by MIBG. Five-year PFS was 24 +/- 6%, which was significantly superior to 11 +/- 7% with 3F8 + ivGM-CSF (p = 0.002). In the multivariate analysis, significantly better PFS was associated with R/R or H/R FCGR2A polymorphism, sc route of GM-CSF and early MRD response. MYCN amplification was not prognostic. Complement consumption was similar with either route of GM-CSF. Toxicities were manageable, allowing outpatient treatment. 3F8 + scGM-CSF is highly active against chemoresistant osteomedullary neuroblastoma. MRD response may be an indicator of tumor sensitivity to anti-G(D2) immunotherapy. Correlative studies highlight the antineoplastic potency of myeloid effectors.
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome in neuroblastoma patients receiving anti-GD2 3F8 monoclonal antibody.[Pubmed:23633099]
Cancer. 2013 Aug 1;119(15):2789-95.
BACKGROUND: Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) comprises clinical and radiologic findings with rapid onset and potentially dire consequences. Patients experience hypertension, seizures, headache, visual disturbance, and/or altered mentation. Magnetic resonance imaging reveals edematous changes in the brain (especially in the parietal and occipital lobes). In this report, the authors describe PRES associated with antidisialoganglioside (anti-GD2 ) monoclonal antibody (MoAb) immunotherapy, which is now standard for high-risk neuroblastoma but has not previously been implicated in PRES. METHODS: Successive clinical trials using the anti-GD2 MoAb 3F8 (a murine immunoglobulin 3 MoAb specific for GD2) for patients with neuroblastoma involved multiple cycles of standard-dose 3F8 (SD-3F8) (20 mg/m2 daily for 5 days per cycle) or 2 cycles of high-dose 3F8 (HD-3F8) (80 mg/m2 daily for 5 days per cycle) followed by cycles of SD-3F8. RESULTS: PRES was diagnosed in 5 of 215 patients (2.3%), including 3 of 160 (1.9%) who received SD-3F8 and 2 of 55 (3.6%) who received HD-3F8 (P = .6). All 5 patients had a rapid return to clinical-radiologic baseline. PRES occurred in 3 of 26 patients (11.5%) whose prior treatment included external-beam radiotherapy to the brain (2 of 6 patients status-post total body irradiation and 1 of 20 patients status-post craniospinal irradiation) compared with 2 of 189 patients (1.1%) who had not received prior brain irradiation (P = .01). Hypertension, which is strongly linked to PRES, reached grade 3 toxicity in 12 of 215 patients (5.6%), including the 5 patients with PRES and 7 patients without PRES. CONCLUSIONS: Patients who receive anti-GD2 MoAb immunotherapy should be closely monitored for, and undergo urgent treatment or evaluation of, symptoms that may herald PRES (eg, hypertension or headaches). Prior brain irradiation may be a predisposing factor for PRES with this immunotherapy.
Anti-GD2 antibody 3F8 and barley-derived (1 --> 3),(1 --> 4)-beta-D-glucan: A Phase I study in patients with chemoresistant neuroblastoma.[Pubmed:23802080]
Oncoimmunology. 2013 Mar 1;2(3):e23402.
beta-glucans are complex, naturally-occurring polysaccharides that prime leukocyte dectin and complement receptor 3. Based on our preclinical findings, indicating that oral barley-derived (1 --> 3),(1 --> 4)-beta-D-glucan (BG) synergizes with the murine anti-GD2 antibody 3F8 against neuroblastoma, we conducted a Phase I clinical study to evaluate the safety of this combinatorial regimen in patients affected by chemoresistant neuroblastoma. In this setting, four cohorts of six heavily pre-treated patients bearing recurrent or refractory advanced-stage neuroblastoma were treated with 3F8 plus BG. Each cycle consisted of intravenous 3F8 at a fixed dose of 10 mg/m(2)/day plus concurrent oral BG, dose-escalated from 10 to 80 mg/Kg/day, for 10 d. Patients who did not develop human anti-mouse antibodies could be treated for up to 4 cycles. Twenty-four patients completed 50 cycles of therapy. All patients completed at least one cycle and were evaluable for the assessment of toxicity and responses. The maximum tolerated dose of BG was not reached, but two patients developed dose-limiting toxicities. These individuals developed grade 4 thrombocytopenia after one cycle of BG at doses of 20 mg/Kg/day and 40 mg/Kg/day, respectively. Platelet counts recovered following the administration of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura therapy. There were no other toxicities of grade > 2. Eleven and 13 patients manifested stable and progressive disease, respectively. Thirteen out of 22 patients with pre-treatment positive (123)I-MIBG scans demonstrated clinical improvement on semiquantitative scoring. Responses did not correlate with BG dose or with in vitro cytotoxicity. In summary, 3F8 plus BG is well tolerated and shows antineoplastic activity in recurrent or refractory advanced-stage neuroblastoma patients. Further clinical investigation of this novel combinatorial immunotherapeutic regimen is warranted.
Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of GD2 ganglioside-specific monoclonal antibody 3F8 in human melanoma cells.[Pubmed:26405581]
Oncoimmunology. 2015 Apr 2;4(8):e1023975.
The beneficial clinical effects of immunotherapy with GD2-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) in melanoma and neuroblastoma patients have stimulated interest in characterizing the mechanisms underlying their antitumor effects. Previous studies have shown that GD2-specific mAbs mediate complement- and cell-dependent cytotoxicity and induce caspase-dependent apoptosis of tumor cells. In this study, we showed that GD2-specific mAb 3F8, which is undergoing clinical evaluation, inhibited the in vitro growth and induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. This effect was dose- and time-dependent, mediated by the interaction of mAb 3F8 combining site with GD2 ganglioside, associated with GD2 expression level on the cell surface, mAb internalization and increase of GD2 containing endosomes triggered by mAb 3F8. The induction of apoptosis by mAb 3F8 was mediated by caspase 3-, 7-, and 8-dependent pathways, downregulation of the anti-apoptotic molecules survivin and cytochrome c, and caspase 9 independent-AIF release from mitochondria. In addition, analyses of signaling pathway components demonstrated that mAb 3F8 strongly inhibited AKT and FAK activation and increased cleaved PARP expression. These results indicated that multiple mechanisms played a role in the antitumor activity of mAb 3F8 in melanoma cells. This information should provide a mechanistic basis for the optimization of the rational design of immunotherapeutic strategies in the mAb-based treatment of GD2 positive tumors.
Benzo[e]isoindole-1,3-diones as potential inhibitors of glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK-3). Synthesis, kinase inhibitory activity, zebrafish phenotype, and modeling of binding mode.[Pubmed:20030405]
J Med Chem. 2010 Feb 11;53(3):994-1003.
Benzo[e]isoindole-1,3-dione derivatives were synthesized, and the effects on GSK-3beta activity and zebrafish embryo growth were evaluated. A series of derivatives show obvious inhibitory activity against GSK-3beta. The most potent inhibitor, 7,8-dimethoxy-5-methylbenzo[e]isoindole-1,3-dione (8a), shows nanomolar IC(50) and obvious phenotype on zebrafish embryo growth associated with the inhibition of GSK-3beta at low micromolar concentration. The interaction mode between 8a and GSK-3beta was characterized by computational modeling.
Characterization and development of novel small-molecules inhibiting GSK3 and activating Wnt signaling.[Pubmed:19823752]
Mol Biosyst. 2009 Nov;5(11):1356-60.
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) is an essential component of the Wnt signaling pathway and plays important roles in regulating cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. As GSK3 is abnormally upregulated in several diseases including type II diabetes, Alzheimer's disease and cancer, it has been regarded as a potential drug target. During zebrafish development, inhibition of GSK3 leads to ectopic activation of the Wnt pathway, resulting in a headless embryo. Using this phenotype as an assay we screened a chemical library of 4000 compounds and identified one novel compound, 3F8, which specifically inhibits eye and forebrain formation in zebrafish embryos, resembling a typical Wnt overexpression phenotype. Cell reporter assays, chemical informatics analysis and in vitro kinase experiments revealed that 3F8 is a selective GSK3 inhibitor, which is more potent than SB216763, a commonly used GSK3 inhibitor. Based on the structure of 3F8, a new generation of compounds inhibiting GSK3 was synthesized and validated by biological assays. Together, 3F8 and its derivatives could be useful as new reagents and potential therapeutic candidates for GSK3 related diseases.


