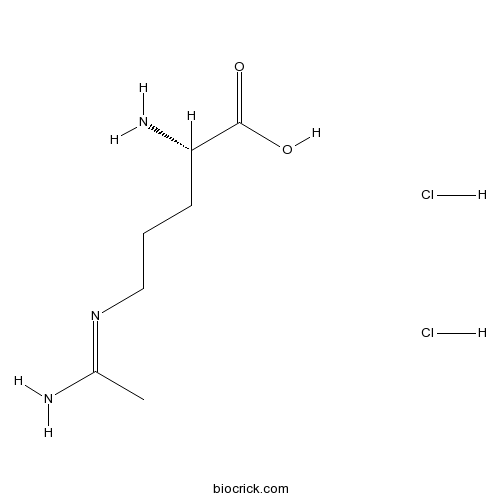
L-NIO dihydrochlorideinhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase CAS# 159190-44-0 |
- GSK1904529A
Catalog No.:BCC1062
CAS No.:1089283-49-7
- PQ 401
Catalog No.:BCC1159
CAS No.:196868-63-0
- BMS-536924
Catalog No.:BCC1177
CAS No.:468740-43-4
- NVP-ADW742
Catalog No.:BCC4553
CAS No.:475488-23-4
- AG-1024
Catalog No.:BCC1242
CAS No.:65678-07-1
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 159190-44-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 2733507 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C7H17Cl2N3O2 | M.Wt | 246.13 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 50 mg/mL (203.14 mM; Need ultrasonic) DMSO : 33.33 mg/mL (135.42 mM; Need ultrasonic) | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S)-2-amino-5-(1-aminoethylideneamino)pentanoic acid;dihydrochloride | ||
| SMILES | CC(=NCCCC(C(=O)O)N)N.Cl.Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | RYCMAAFECCXGHI-ILKKLZGPSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C7H15N3O2.2ClH/c1-5(8)10-4-2-3-6(9)7(11)12;;/h6H,2-4,9H2,1H3,(H2,8,10)(H,11,12);2*1H/t6-;;/m0../s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase. Inhibits iNOS, eNOS and nNOS. Active in vivo. |

L-NIO dihydrochloride Dilution Calculator

L-NIO dihydrochloride Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0629 mL | 20.3145 mL | 40.6289 mL | 81.2579 mL | 101.5723 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8126 mL | 4.0629 mL | 8.1258 mL | 16.2516 mL | 20.3145 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4063 mL | 2.0314 mL | 4.0629 mL | 8.1258 mL | 10.1572 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0813 mL | 0.4063 mL | 0.8126 mL | 1.6252 mL | 2.0314 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0406 mL | 0.2031 mL | 0.4063 mL | 0.8126 mL | 1.0157 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
IC50: 65 M
L-NIO dihydrochloride is an inhibitor of nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS, eNOS and nNOS). An NO synthase is inducible by immunological stimuli such as endotoxin (LPS) and various cytokines, generating nitric oxide (NO) in phagocytic cells including neutrophils and macrophages. Generation of NO by macrophages has been revealed to kill tumour cells due to the inactivation of ironsulphur centres of mitochondrial enzymes.
In vitro: To protect against inflammatory injury stimulated by activated neutrophils, the ability of L-arginine (N-iminoethyl-L-ornithine (L-NIO) was studied in rats, following intradermal or intrapulmonary deposition of immune complexes [1]. The protective effect of L-NIO in the skin was reversed in a dose-dependent manner by the presence of L-arginine, rather than by D-arginine. The protective effects of L-NIO L-Arginine were reversed also in immune complex-induced lung injury, and not associated with reductions in neutrophil accumulation as measured by extraction from tissues of myeloperoxidase. The results demonstrate immune complex induced vascular injury induced by activated macrophage was inhibited effectively by L-NIO as a potent inhibitor [1].
In vivo: A dose-dependent increase in mean systemic arterial blood pressure accompanied by bradycardia was induced at the administration of L-NIO (0.03-300 mgkg-1, i.v.). L-NIO (100 mgkg-, i.v.) has an effect inhibitor of the hypotensive responses to ACh and bradykinin. L-arginine (30-100 mg kg- 1, i.v.) in a dose-dependent manner reversed the increase in blood pressure and bradycardia produced by these compounds. It was enantiomer specific for all of these effects. These facts indicate that L-NIO can inhibit NO synthase as inhibitors in the vascular endothelium and verify that L-NIO plays an important role for NO synthesis in the maintenance of vascular tone and blood pressure [2].
Clinical trial: So far, no clinical study has been conducted.
References:
[1]. Mulligan MS, Moncada S, Ward PA. Protective effects of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase in immune complex-induced vasculitis. Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1159-62.
[2]. Rees DD, Palmer RM, Schulz R, Hodson HF, Moncada S.Br J Pharmacol. Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo.1990 Nov;101 (3):746-52.
- MM 77 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6854
CAS No.:159187-70-9
- L-755,507
Catalog No.:BCC7282
CAS No.:159182-43-1
- CARIPORIDE
Catalog No.:BCC6432
CAS No.:159138-80-4
- 3F8
Catalog No.:BCC6112
CAS No.:159109-11-2
- F1839-I
Catalog No.:BCN6450
CAS No.:159096-49-8
- 6-Benzyloxyindole
Catalog No.:BCC8769
CAS No.:15903-94-3
- Wedelobatin B
Catalog No.:BCN6730
CAS No.:1589488-35-6
- Wedelobatin A
Catalog No.:BCN6731
CAS No.:1589488-34-5
- Secoisolarisiresinol Diglucoside
Catalog No.:BCC9140
CAS No.:158932-33-3
- Boc-D-Tryptophanol
Catalog No.:BCC2698
CAS No.:158932-00-4
- APC 366
Catalog No.:BCC7392
CAS No.:158921-85-8
- GR 231118
Catalog No.:BCC7085
CAS No.:158859-98-4
- Isokaempferide
Catalog No.:BCN3790
CAS No.:1592-70-7
- PNU 22394 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7285
CAS No.:15923-42-9
- MPDC
Catalog No.:BCC6873
CAS No.:159262-32-5
- Everolimus (RAD001)
Catalog No.:BCC3594
CAS No.:159351-69-6
- N-Acetyl-O-phosphono-Tyr-Glu-Glu-Ile-Glu
Catalog No.:BCC5853
CAS No.:159439-02-8
- Enfuvirtide
Catalog No.:BCC5641
CAS No.:159519-65-0
- Fluconazole mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4236
CAS No.:159532-41-9
- GR 55562 dihydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6913
CAS No.:159533-25-2
- Daminozide
Catalog No.:BCC1514
CAS No.:1596-84-5
- 3,4-Secotirucalla-4(28,7,24-triene-3),26-dioic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1549
CAS No.:159623-48-0
- Saropyrone
Catalog No.:BCN7692
CAS No.:159650-12-1
- Wikstrol A
Catalog No.:BCN7938
CAS No.:159736-35-3
Endothelial dysfunction impairs vascular neurotransmission in tail arteries.[Pubmed:25447765]
Neurochem Int. 2015 Jan;80:7-13.
The present study intends to clarify if endothelium dysfunction impairs vascular sympathetic neurotransmission. Electrically-evoked tritium overflow (100 pulses/5 Hz) was evaluated in arteries (intact and denuded) or exhibiting some degree of endothelium dysfunction (spontaneously hypertensive arteries), pre-incubated with [(3)H]-noradrenaline in the presence of enzymes (nitric oxide synthase (NOS); nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase; xanthine oxidase; cyclooxygenase; adenosine kinase) inhibitors and a nucleoside transporter inhibitor. Inhibition of endothelial nitric oxide synthase with L-NIO dihydrochloride reduced tritium overflow in intact arteries whereas inhibition of neuronal nitric oxide synthase with Nomega-Propyl-L-arginine hydrochloride was devoid of effect showing that only endothelial nitric oxide synthase is involved in vascular sympathetic neuromodulation. Inhibition of enzymes involved in reactive oxygen species or prostaglandins production with apocynin and allopurinol or indomethacin, respectively, failed to alter tritium overflow. A facilitation or reduction of tritium overflow was observed in the presence of 8-cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) or of 5-iodotubericidin, respectively, but only in intact arteries. These effects can be ascribed to a tonic inhibitory effect mediated by A1 receptors. In denuded and hypertensive arteries, 7-(2-phenylethyl)-5-amino-2-(2-furyl)-pyrazolo-[4,3-e]-1,2,4-triazolo[1,5-c] pyrimidine (SCH 58261) reduced tritium overflow, suggesting the occurrence of a tonic activation of A2A receptors. When endogenous adenosine bioavailability was increased by the nucleoside transporter inhibitor, S-(4-Nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine, tritium overflow increased in intact, denuded and hypertensive arteries. Among the endothelium-derived substances studied that could alter vascular sympathetic transmission only adenosine/adenosine receptor mediated mechanisms were clearly impaired by endothelium injury/dysfunction.
Protective effects of inhibitors of nitric oxide synthase in immune complex-induced vasculitis.[Pubmed:1281719]
Br J Pharmacol. 1992 Dec;107(4):1159-62.
1. The ability of analogues of L-arginine (N-iminoethyl-L-ornithine (L-NIO), NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA), NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) and NG-nitro-L-arginine (L-NNA)) to protect against inflammatory injury induced by activated neutrophils was investigated in rats following intradermal or intrapulmonary deposition of immune complexes. 2. The descending order of potency for protective effects of these analogues was: L-NIO > L-NMMA > L-NNA = L-NAME. The approximate IC50 value for L-NIO in the dermal vasculitis model was 65 microM. For all other compounds, the IC50 values were > 5 mM. 3. The protective effect of L-NIO in the skin was reversed in a dose-dependent manner by the presence of L-arginine, but not by D-arginine. L-Arginine also reversed the protective effects of L-NIO in immune complex-induced lung injury. 4. The protective effects of L-NIO were not associated with reductions in neutrophil accumulation, as measured by extraction from tissues of myeloperoxidase. 5. These data demonstrate that L-NIO has the most potent protective effects against immune complex-induced vascular injury induced by activated macrophages. Furthermore, they indicate that this injury is dependent upon the generation of nitric oxide.
Characterization of three inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in vitro and in vivo.[Pubmed:1706208]
Br J Pharmacol. 1990 Nov;101(3):746-52.
1. Three analogues of L-arginine were characterized as inhibitors of endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase by measuring their effect on the endothelial NO synthase from porcine aortae, on the vascular tone of rings of rat aorta and on the blood pressure of the anaesthetized rat. 2. NG-monomethyl-L-arginine (L-NMMA), N-iminoethyl-L-ornithine (L-NIO) and NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; all at 0.1-100 microM) caused concentration-dependent inhibition of the Ca2(+)-dependent endothelial NO synthase from porcine aortae. 3. L-NMMA, L-NIO and L-NAME caused an endothelium-dependent contraction and an inhibition of the endothelium-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine (ACh) in aortic rings. 4. L-NMMA, L-NIO and L-NAME (0.03-300 mg kg-1, i.v.) induced a dose-dependent increase in mean systemic arterial blood pressure accompanied by bradycardia. 5. L-NMMA, L-NIO and L-NAME (100 mg kg-1, i.v.) inhibited significantly the hypotensive responses to ACh and bradykinin. 6. The increase in blood pressure and bradycardia produced by these compounds were reversed by L-arginine (30-100 mg kg-1, i.v.) in a dose-dependent manner. 7. All of these effects were enantiomer specific. 8. These results indicate that L-NMMA, L-NIO and L-NAME are inhibitors of NO synthase in the vascular endothelium and confirm the important role of NO synthesis in the maintenance of vascular tone and blood pressure.


