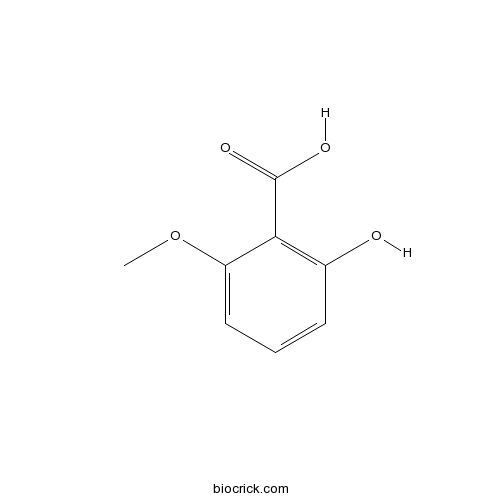
6-Methoxysalicylic AcidCAS# 3147-64-6 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3147-64-6 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 591524 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C8H8O4 | M.Wt | 168 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | 2-hydroxy-6-methoxybenzoic acid | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=CC(=C1C(=O)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AAUQLHHARJUJEH-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C8H8O4/c1-12-6-4-2-3-5(9)7(6)8(10)11/h2-4,9H,1H3,(H,10,11) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Structure Identification | Planta Med. 1988 Jun;54(3):243-5.Alkaloids and Phenolics of Colchicum cilicicum1,2.[Pubmed: 17265262]
|

6-Methoxysalicylic Acid Dilution Calculator

6-Methoxysalicylic Acid Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.9524 mL | 29.7619 mL | 59.5238 mL | 119.0476 mL | 148.8095 mL |
| 5 mM | 1.1905 mL | 5.9524 mL | 11.9048 mL | 23.8095 mL | 29.7619 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.5952 mL | 2.9762 mL | 5.9524 mL | 11.9048 mL | 14.881 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.119 mL | 0.5952 mL | 1.1905 mL | 2.381 mL | 2.9762 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0595 mL | 0.2976 mL | 0.5952 mL | 1.1905 mL | 1.4881 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Mebendazole
Catalog No.:BCC9016
CAS No.:31431-39-7
- 4-Amino-3-nitrobenzophenone
Catalog No.:BCC8682
CAS No.:31431-19-3
- Nocodazole
Catalog No.:BCC3826
CAS No.:31430-18-9
- Isotachioside
Catalog No.:BCN5230
CAS No.:31427-08-4
- IU1
Catalog No.:BCC2086
CAS No.:314245-33-5
- BPTES
Catalog No.:BCC6506
CAS No.:314045-39-1
- (R)-(-)-Apomorphine hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7250
CAS No.:314-19-2
- Evans Blue tetrasodium salt
Catalog No.:BCC6815
CAS No.:314-13-6
- VDM 11
Catalog No.:BCC7044
CAS No.:313998-81-1
- [cPP1-7,NPY19-23,Ala31,Aib32,Gln34] - hPancreatic Polypeptide
Catalog No.:BCC5750
CAS No.:313988-89-5
- PU 02
Catalog No.:BCC6265
CAS No.:313984-77-9
- o-3M3FBS
Catalog No.:BCC7210
CAS No.:313981-55-4
- Sunifiram
Catalog No.:BCC4167
CAS No.:314728-85-3
- Crotaline
Catalog No.:BCN4983
CAS No.:315-22-0
- Allopurinol
Catalog No.:BCC3720
CAS No.:315-30-0
- Testosterone enanthate
Catalog No.:BCC9169
CAS No.:315-37-7
- Acetylheliosupine
Catalog No.:BCN1981
CAS No.:31514-30-4
- PAC-1
Catalog No.:BCC3600
CAS No.:315183-21-2
- Ifflaiamine
Catalog No.:BCN7061
CAS No.:31520-95-3
- Sutherlandin trans-p-coumarate
Catalog No.:BCN5231
CAS No.:315236-68-1
- Isobavachin
Catalog No.:BCN5232
CAS No.:31524-62-6
- 5-Hydroxyseselin
Catalog No.:BCN3428
CAS No.:31525-75-4
- O-Nornuciferine
Catalog No.:BCN7074
CAS No.:3153-55-7
- Matsukaze-lactone
Catalog No.:BCN7580
CAS No.:3153-73-9
Molecularly imprinted polymers with synthetic dummy template for simultaneously selective removal and enrichment of ginkgolic acids from Ginkgo biloba L. leaves extracts.[Pubmed:25441343]
J Chromatogr A. 2014 Nov 14;1368:44-51.
Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers (DMIPs) for simultaneously selective removal and enrichment of ginkgolic acids (GAs) during the processing of Ginkgo biloba leaves have been prepared. Two dummy template molecule with similar structural skeleton to GAs, 6-Methoxysalicylic Acid (MOSA, DT-1) and 6-hexadecyloxysalicylic acid (HOSA, DT-2), have been designed and synthesized. The performance of the DMIPs and NIPs were evaluated including selective recognition capacity, adsorption isotherm, and adsorption kinetics. The selective recognition capacity of the three GAs with four analogues on the sorbents illustrated that the DMIPs sorbents have high specificity for GAs. An efficient method based on DMIP-HOSA coupled with solid-phase extraction (SPE) was developed for simultaneously selective removal and enrichment of ginkgolic acids (GAs) during the processing of Ginkgo biloba leaves. The method showed excellent recoveries (82.5-88.7%) and precision (RSD 0.5-2.6%, n=5) for licorice extracts, Gastrodia elata extracts and pepper extracts spiked at three concentration levels each (50, 100, 200 mug mL(-1)). The results indicated that GAs and standardized Ginkgo biloba leaves extracts could be obtained simultaneously through the DMIP-SPE.
Rapid and sensitive determination of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid in plasma using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry: application to pharmacokinetic study.[Pubmed:19358313]
Biomed Chromatogr. 2009 Sep;23(9):973-9.
A simple and sensitive analytical method using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC/MS/MS) for determination of acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin, ASA) and its major metabolite, salicylic acid (SA), in animal plasma has been developed and validated. Both ASA and SA in plasma samples containing potassium fluoride were extracted using acetonitrile (protein precipitation) with 0.1% formic acid in it. 6-Methoxysalicylic Acid was used as the internal standard (IS). The compounds were separated on a reversed-phase column. The multiple reaction monitoring mode was used with ion transitions of m/z 178.9 --> 136.8, 137.0 --> 93.0 and 167.0 --> 123.0 for ASA, SA and IS, respectively. The lower limits of quantification for ASA and SA were 3 and 30 ng/mL, respectively. The developed method was successfully applied for the evaluation of pharmacokinetics of ASA and SA after p.o. and i.v. administration of 1 mg/kg to rats.
Antinociceptive, hypoglycemic and spasmolytic effects of Brickellia veronicifolia.[Pubmed:18583074]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2008 Aug 13;118(3):448-54.
INTRODUCTION: Brickellia veronicifolia (Kunth) Gray (Asteraceae) (BV) is broadly commercialized for treating gastrointestinal diseases (stomach aches, biliary colics and dyspepsia), arthritis, diabetes and painful inflammatory complaints. AIMS OF THE STUDY: In order to complete the preclinical pharmacological profile of BV, first the antinociceptive effect of an organic extract (BVE) and isolated metabolites on the hot plate and writhing tests was assessed. EXPERIMENTAL: Then, their potential hypoglycemic effects were analyzed in normoglycemic and diabetic rats; in addition, an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was performed. Finally, the spasmolytic activity of BVE was assessed in vivo using the gastrointestinal motility test (GMT) in mice. RESULTS: The results revealed that BVE (100-600 mg/kg), 6-Methoxysalicylic Acid (1), 2-methoxybenzoic acid (2), benzyl-2,6-dimethoxybenzoate (3), and taraxasteryl acetate (4) showed significant analgesic effects. Compounds 2 and 3 were the most active (1-100mg/kg) in the hot plate and writhing tests, respectively. In the antidiabetic assays, BVE (100mg/kg) showed an important hypoglycemic action. Furthermore, at the same dose, it provoked a significant postprandial decrease of blood glucose level after 30 min of a glucose challenge. Finally, the GMT in mice revealed the spasmolytic activity in vivo of BVE (31.6 mg/kg). CONCLUSION: The overall information tends to support the vernacular uses of the plant.


