AG-490JAK2/EGFR inhibitor CAS# 133550-30-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 133550-30-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5328779 | Appearance | Powder |
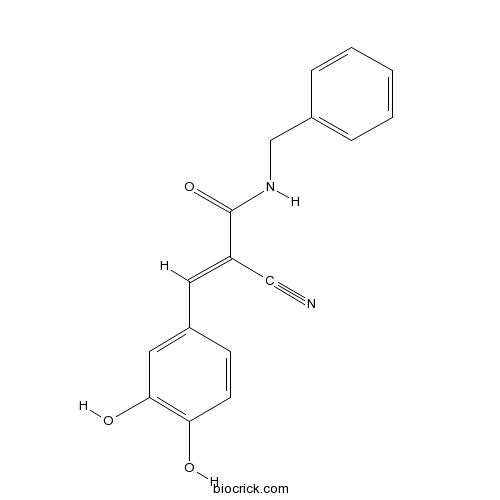
| Formula | C17H14N2O3 | M.Wt | 294.3 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tyrphostin AG 490 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 50 mg/mL (169.89 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-benzyl-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CNC(=O)C(=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)C#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | TUCIOBMMDDOEMM-RIYZIHGNSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C17H14N2O3/c18-10-14(8-13-6-7-15(20)16(21)9-13)17(22)19-11-12-4-2-1-3-5-12/h1-9,20-21H,11H2,(H,19,22)/b14-8+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Selective inhibitor of EGF receptor tyrosine kinase (IC50 values are 2 and 13.5 μM for EGFR and ErbB2 respectively). Inhibitor of JAK2, JAK3/STAT, JAK3/AP-1 and JAK3/MAPK pathways and potently inhibits cytokine-independent cell growth in vitro and tumor cell invasion in vivo. |

AG-490 Dilution Calculator

AG-490 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3979 mL | 16.9895 mL | 33.9789 mL | 67.9579 mL | 84.9473 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6796 mL | 3.3979 mL | 6.7958 mL | 13.5916 mL | 16.9895 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3398 mL | 1.6989 mL | 3.3979 mL | 6.7958 mL | 8.4947 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.068 mL | 0.3398 mL | 0.6796 mL | 1.3592 mL | 1.6989 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.034 mL | 0.1699 mL | 0.3398 mL | 0.6796 mL | 0.8495 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AG-490 is an inhibitor of tyrosine kinases [1].
As a member of the tyrphostin family, AG-490 is reported to have inhibitory activity against many kinases. It can inhibit the hyperactive JAK2 in B cell precursors of ALL patients, inhibit cytokine-induced activation of JAK2 in eosinophils and suppresses the activation of STAT3 in mycosis fungoides-derived T cells. AG-490 is also found to target JAK3 and its downstream STAT and MAPK signaling pathways. In the IL-2-dependent T cell line, D10, AG-490 suppresses IL-2-induced cell proliferation with IC50 value of 25μM without affecting IL-2R chain expression. It also inhibits IL-2-modulated phosphorylation of STAT5a and STAT5b with IC50 value of 50μM-70μM. Moreover, AG-490 reduces IL-2-induced DNA binding by 78%, 65% and 65% for STAT5a/5b, STAT1 and STAT3, respectively. All these show that AG-490 may provide a beneficial therapeutic by suppressing immunopathological states [1].
References:
[1] Wang L H, Kirken R A, Erwin R A, et al. JAK3, STAT, and MAPK signaling pathways as novel molecular targets for the tyrphostin AG-490 regulation of IL-2-mediated T cell response. The Journal of Immunology, 1999, 162(7): 3897-3904.
- Apigenin 4'-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN6181
CAS No.:133538-77-9
- Exendin-3 (9-39) amide
Catalog No.:BCC7257
CAS No.:133514-43-9
- SR 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6309
CAS No.:1335106-03-0
- TAI-1
Catalog No.:BCC5576
CAS No.:1334921-03-7
- Fmoc-Glu(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3492
CAS No.:133464-46-7
- Iloperidone
Catalog No.:BCC2516
CAS No.:133454-47-4
- Heudelotinone
Catalog No.:BCN6180
CAS No.:133453-58-4
- Angophorol
Catalog No.:BCN3965
CAS No.:133442-54-3
- 3'-Geranyl-3-prenyl-2',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1583
CAS No.:1334309-44-2
- PF 1022A
Catalog No.:BCC8064
CAS No.:133413-70-4
- MG-115
Catalog No.:BCC1237
CAS No.:133407-86-0
- MG-132
Catalog No.:BCC1227
CAS No.:133407-82-6
- Tyrphostin B44, (-) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6703
CAS No.:133550-32-0
- AG 555
Catalog No.:BCC6721
CAS No.:133550-34-2
- AG 494
Catalog No.:BCC6722
CAS No.:133550-35-3
- Tyrphostin B44, (+) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6704
CAS No.:133550-37-5
- AG 556
Catalog No.:BCC6720
CAS No.:133550-41-1
- 4,15-Isoatriplicolide methylacrylate
Catalog No.:BCN7935
CAS No.:133559-38-3
- Isoatriplicolide tiglate
Catalog No.:BCN7934
CAS No.:133559-39-4
- Boc-Glutaminol
Catalog No.:BCC3092
CAS No.:133565-42-1
- Boc-Threoninol(Bzl)
Catalog No.:BCC2704
CAS No.:133565-43-2
- Fmoc-Ile-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2584
CAS No.:133565-46-5
- 2-Ethyl-2,6,6-trimethylpiperidin-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN6504
CAS No.:133568-79-3
- 2-Aminoisonicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8550
CAS No.:13362-28-2
High-throughput chemical screening identifies AG-490 as a stimulator of aquaporin 2 membrane expression and urine concentration.[Pubmed:24944200]
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2014 Oct 1;307(7):C597-605.
A reduction or loss of plasma membrane aquaporin 2 (AQP2) in kidney principal cells due to defective vasopressin (VP) signaling through the VP receptor causes excessive urine production, i.e., diabetes insipidus. The amount of AQP2 on the plasma membrane is regulated by a balance of exocytosis and endocytosis and is the rate limiting step for water reabsorption in the collecting duct. We describe here a systematic approach using high-throughput screening (HTS) followed by in vitro and in vivo assays to discover novel compounds that enhance vasopressin-independent AQP2 membrane expression. We performed initial chemical library screening with a high-throughput exocytosis fluorescence assay using LLC-PK1 cells expressing soluble secreted yellow fluorescent protein and AQP2. Thirty-six candidate exocytosis enhancers were identified. These compounds were then rescreened in AQP2-expressing cells to determine their ability to increase AQP2 membrane accumulation. Effective drugs were then applied to kidney slices in vitro. Three compounds, AG-490, beta-lapachone, and HA14-1 increased AQP2 membrane accumulation in LLC-PK1 cells, and both AG-490 and beta-lapachone were also effective in MDCK cells and principal cells in rat kidney slices. Finally, one compound, AG-490 (an EGF receptor and JAK-2 kinase inhibitor), decreased urine volume and increased urine osmolality significantly in the first 2-4 h after a single injection into VP-deficient Brattleboro rats. In conclusion, we have developed a systematic procedure for identifying new compounds that modulate AQP2 trafficking using initial HTS followed by in vitro assays in cells and kidney slices, and concluding with in vivo testing in an animal model.
Primary effusion lymphoma cell death induced by bortezomib and AG 490 activates dendritic cells through CD91.[Pubmed:22412839]
PLoS One. 2012;7(3):e31732.
To understand how cytotoxic agent-induced cancer cell death affects the immune system is of fundamental importance to stimulate immune response to counteract the high mortality due to cancer. Here we compared the immunogenicity of Primary Effusion Lymphoma (PEL) cell death induced by anticancer drug Bortezomib (Velcade) and Tyrphostin AG 490, a Janus Activated Kinase 2/signal trasducer and activator of transcription-3 (JAK2/STAT3) inhibitor. We show that both treatments were able to induce PEL apoptosis with similar kinetics and promote dendritic cells (DC) maturation. The surface expression of molecules involved in immune activation, namely calreticulin (CRT), heat shock proteins (HSP) 90 and 70 increased in dying cells. This was correlated with DC activation. We found that PEL cell death induced by Bortezomib was more effective in inducing uptake by DC compared to AG 490 or combination of both drugs. However the DC activation induced by all treatments was completely inhibited when these cells were pretreated with a neutralizing antiboby directed against the HSP90/70 and CRT common receptor, CD91. The activation of DC by Bortezomib and AG 490 treated PEL cells, as seen in the present study, might have important implications for a combined chemo and immunotherapy in such patients.
Inhibition of Janus kinases by tyrosine phosphorylation inhibitor, Tyrphostin AG-490.[Pubmed:26017266]
J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2015;33(11):2368-79.
Janus kinases (JAKs) belong to a crucial family of tyrosine kinases, implicated in the patho-physiology of multiple cancer types, and serve as striking therapeutic targets. To date, many potent, either ATP-competitive (PTK domain) or non-ATP-competitive JAK inhibitors have been identified. Among them, Tyrphostin AG-490 (2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-(phenylmethyl)-2-propenamide) is a well-known ATP-competitive inhibitor. However, its mode of action, details of interacting residues, and induced conformational changes in JAK-specific binding sites remain elusive. Here, through comparative structure analysis, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics simulation assays, we explored comparative binding patterns of AG-490 against JAK1, JAK2, and JAK3. Our results entail noteworthy observations about the binding affinity of AG-490 by illustrating distinctive amino acid residues lying at the conserved ATP-binding domains of JAK family members. By subsequent assessment of their structural homology and conserved structural folds, we highlight intriguing prospects to design more specific and potent inhibitors for selective targeting of JAK family members. Our comparative study provides a platform for the rational design of precise and potent inhibitor for selective targeting of JAK family members.
The polycythemia vera-associated Jak2 V617F mutant induces tumorigenesis in nude mice.[Pubmed:19327411]
Int Immunopharmacol. 2009 Jul;9(7-8):870-7.
The somatic Jak2 mutation (V617F) was identified in most patients with polycythemia vera (PV). Here, we show that the activating Jak2 V617F mutant completely protected Ba/F3 cells from cytokine withdrawal-induced apoptotic cell death. Interestingly, Ba/F3 cells expressing Jak2 V617F mutant induced rapid tumorigenesis in nude mice, leading to rapid death. Whereas an injection of Ba/F3 cells expressing wild-type Jak2 had no effect, an injection of Ba/F3 cells expressing Jak2 V617F mutant promptly invaded and spread into various distinct organs, such as the liver and spleen. Strikingly, Jak2 inhibitor, AG490 potently inhibited cytokine-independent cell growth induced by the Jak2 V617F mutant. Also, treatment with AG490 effectively delayed Jak2 V617F mutant-induced tumorigenesis in nude mice. Thus, our results both in vitro and in vivo suggest that Jak2 harboring V617F mutation is a potent oncogene able to promote cell transformation and tumorigenesis.
JAK3, STAT, and MAPK signaling pathways as novel molecular targets for the tyrphostin AG-490 regulation of IL-2-mediated T cell response.[Pubmed:10201908]
J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):3897-904.
AG-490 is a member of the tyrphostin family of tyrosine kinase inhibitors. While AG-490 has been considered to be a Janus kinase (JAK)2-specific inhibitor, these conclusions were primarily drawn from acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells that lack readily detectable levels of JAK3. In the present study, evidence is provided that clearly demonstrates AG-490 potently suppresses IL-2-induced T cell proliferation, a non-JAK2-dependent signal, in a dose-dependent manner in T cell lines D10 and CTLL-2. AG-490 blocked JAK3 activation and phosphorylation of its downstream counterpart substrates, STATs. Inhibition of JAK3 by AG-490 also compromised the Shc/Ras/Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways as measured by phosphorylation of Shc and extracellular signal-related kinase 1 and 2 (ERK1/2). AG-490 effectively inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation and DNA binding activities of several transcription factors including STAT1, -3, -5a, and -5b and activating protein-1 (AP-1) as judged by Western blot analysis and electrophoretic mobility shift assay. These data suggest that AG-490 is a potent inhibitor of the JAK3/STAT, JAK3/AP-1, and JAK3/MAPK pathways and their cellular consequences. Taken together, these findings support the notion that AG-490 possesses previously unrecognized clinical potential as an immunotherapeutic drug due to its inhibitory effects on T cell-derived signaling pathways.
Inhibition of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia by a Jak-2 inhibitor.[Pubmed:8628398]
Nature. 1996 Feb 15;379(6566):645-8.
Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL) is the most common cancer of childhood. Despite the progress achieved in its treatment, 20% of cases relapse and no longer respond to chemotherapy. The most common phenotype of ALL cells share surface antigens with very early precursors of B cells and are therefore believed to originate from this lineage. Characterization of the growth requirement of ALL cells indicated that they were dependent on various cytokines, suggesting paracrine and/or autocrine growth regulation. Because many cytokines induce tyrosine phosphorylation in lymphoid progenitor cells, and constitutive tyrosine phosphorylation is commonly observed in B-lineage leukaemias, attempts have been made to develop protein tyrosine kinase (PTK) blockers of leukaemia cell growth. Here we show that leukaemic cells from patients in relapse have constitutively activated Jak-2 PTK. Inhibition of Jak-2 activity by a specific tyrosine kinase blocker, AG-490, selectively blocks leukaemic cell growth in vitro and in vivo by inducing programmed cell death, with no deleterious effect on normal haematopoiesis.
Tyrphostins. 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and ErbB2/neu tyrosine kinases.[Pubmed:1676428]
J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1896-907.
We have previously described a novel series of low molecular weight protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors which we named tyrphostins. The characteristic active pharmacophore of these compounds was the hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitrile moiety. In this article we describe three novel groups of tyrphostins: (i) one group has the phenolic moiety of the cis-benzylidenemalononitrile replaced either with other substituted benzenes or with heteroaromatic rings, (ii) another is a series of conformationally constrained derivatives of hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitriles in which the malononitrile moiety is fixed relative to the aromatic ring, and (iii) two groups of compounds in which the position trans to the benzenemalononitrile has been substituted by ketones and amides. Among the novel tyrphostins examined we found inhibitors which discriminate between the highly homologous EGF receptor kinase (HER1) and ErbB2/neu kinase (HER2). These findings may lead to selective tyrosine kinase blockers for the treatment of diseases in which ErbB2/neu is involved.


