AG 555Potent EGFR-kinase inhibitor CAS# 133550-34-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 133550-34-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 680344 | Appearance | Powder |
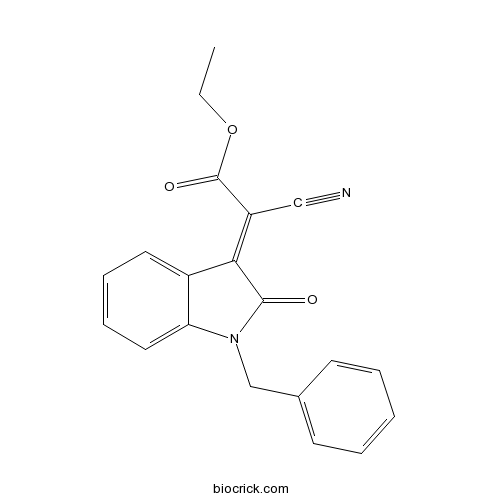
| Formula | C19H18N2O3 | M.Wt | 322.36 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tyrphostin AG 555 | ||
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (310.21 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
| Chemical Name | ethyl (2E)-2-(1-benzyl-2-oxoindol-3-ylidene)-2-cyanoacetate | ||
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)C(=C1C2=CC=CC=C2N(C1=O)CC3=CC=CC=C3)C#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | ILSBZJQRTQRMSR-FBMGVBCBSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H16N2O3/c1-2-25-20(24)16(12-21)18-15-10-6-7-11-17(15)22(19(18)23)13-14-8-4-3-5-9-14/h3-11H,2,13H2,1H3/b18-16+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Potent epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitor (IC50 = 0.7 μM) that displays 50-fold and >140-fold selectivity over ErbB2 and insulin receptor kinase respectively. Induce G1 growth arrest selectively in transformed cells (IC50 values are 6.4 and 9.4 μM in HPV16-immortalized and normal keratinocytes respectively). |

AG 555 Dilution Calculator

AG 555 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.1021 mL | 15.5106 mL | 31.0212 mL | 62.0424 mL | 77.553 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6204 mL | 3.1021 mL | 6.2042 mL | 12.4085 mL | 15.5106 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3102 mL | 1.5511 mL | 3.1021 mL | 6.2042 mL | 7.7553 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.062 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6204 mL | 1.2408 mL | 1.5511 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.031 mL | 0.1551 mL | 0.3102 mL | 0.6204 mL | 0.7755 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AG 555 is a potent and selective inhibitor of EGFR with IC50 value of 0.7 μM.
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is the cell-surface receptor for epidermal growth factor and plays an important role in tumor invasion and cancer cell proliferation.
AG 555 is a potent and selective EGFR inhibitor. In HPV16-immortalized human keratinocytes, AG 555 inhibited the activation of Cdk2 and induced growth arrest at the G1 phase accompanied by 15-20% cell apoptosis [1]. AG556 arrested cells at G1/S phase by 85% and inhibited the activation of Cdk2 by phosphorylating tyrosine 15 on Cdk2 [2]. In A-498, Caki-1 and Caki-2 renal carcinoma cell lines and RT4, J82 and T24 transitional carcinoma cell lines, AG555 inhibited cell proliferation with IC50 values ranging from 3 to 16 μM in a dose-dependent way. AG555 (10-30 μM) completely inhibited cell growth [3]. In NIH/3T3 cells infected with Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV), AG-555 inhibited the viral DNA integrated into the host genome in acutely infected cells. While in chronically infected cells, AG-555 decreased the level of viral RNA and inhibited viral protein synthesis [4].
References:
[1]. Ben-Bassat H, Rosenbaum-Mitrani S, Hartzstark Z, et al. Inhibitors of epidermal growth factor receptor kinase and of cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activation induce growth arrest, differentiation, and apoptosis of human papilloma virus 16-immortalized human keratinocytes. Cancer Res, 1997, 57(17): 3741-3750.
[2]. Kleinberger-Doron N, Shelah N, Capone R, et al. Inhibition of Cdk2 activation by selected tyrphostins causes cell cycle arrest at late G1 and S phase. Exp Cell Res, 1998, 241(2): 340-351.
[3]. Sion-Vardy N, Vardy D, Rodeck U, et al. Antiproliferative effects of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (tyrphostins) on human bladder and renal carcinoma cells. J Surg Res, 1995, 59(6): 675-680.
[4]. Seri I, Aflalo E, Gazit A, et al. Tyrphostin AG-555 inhibits early and late stages of Moloney murine leukemia virus replication cycle. Int J Oncol, 1997, 10(6): 1185-1189.
- Tyrphostin B44, (-) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6703
CAS No.:133550-32-0
- AG-490
Catalog No.:BCC2193
CAS No.:133550-30-8
- Apigenin 4'-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN6181
CAS No.:133538-77-9
- Exendin-3 (9-39) amide
Catalog No.:BCC7257
CAS No.:133514-43-9
- SR 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6309
CAS No.:1335106-03-0
- TAI-1
Catalog No.:BCC5576
CAS No.:1334921-03-7
- Fmoc-Glu(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3492
CAS No.:133464-46-7
- Iloperidone
Catalog No.:BCC2516
CAS No.:133454-47-4
- Heudelotinone
Catalog No.:BCN6180
CAS No.:133453-58-4
- Angophorol
Catalog No.:BCN3965
CAS No.:133442-54-3
- 3'-Geranyl-3-prenyl-2',4',5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN1583
CAS No.:1334309-44-2
- PF 1022A
Catalog No.:BCC8064
CAS No.:133413-70-4
- AG 494
Catalog No.:BCC6722
CAS No.:133550-35-3
- Tyrphostin B44, (+) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6704
CAS No.:133550-37-5
- AG 556
Catalog No.:BCC6720
CAS No.:133550-41-1
- 4,15-Isoatriplicolide methylacrylate
Catalog No.:BCN7935
CAS No.:133559-38-3
- Isoatriplicolide tiglate
Catalog No.:BCN7934
CAS No.:133559-39-4
- Boc-Glutaminol
Catalog No.:BCC3092
CAS No.:133565-42-1
- Boc-Threoninol(Bzl)
Catalog No.:BCC2704
CAS No.:133565-43-2
- Fmoc-Ile-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2584
CAS No.:133565-46-5
- 2-Ethyl-2,6,6-trimethylpiperidin-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN6504
CAS No.:133568-79-3
- 2-Aminoisonicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8550
CAS No.:13362-28-2
- Exoticin
Catalog No.:BCN6182
CAS No.:13364-94-8
- 1-Allyl-3,5-Dimethylpyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8450
CAS No.:13369-74-9
Tyrphostin AG 555 inhibits bovine papillomavirus transcription by changing the ratio between E2 transactivator/repressor function.[Pubmed:12867421]
J Biol Chem. 2003 Sep 26;278(39):37306-13.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor (tyrphostin) AG 555 selectively interferes with viral transcription in bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV-1)-transformed fibroblasts and induces suppression of cyclin-dependent kinase activity and cell cycle arrest. Concomitant with inhibition of viral transcription, c-Jun was strongly up-regulated, which was consistent with the observation that AG 555 treatment also led to an activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway by enhancing phosphorylation of JNK and p38. Increased JNK and p38 activity resulted in higher phosphorylation of the AP-1 family members c-Jun and activating transcription factor 2. Scanning the BPV-1 genome for potential binding sequences, an intragenic AP-1 site (BAP-1) within the E7 open reading frame was detected. Enhanced dimerization of phosphorylated activating transcription factor 2 together with c-Jun and binding to BAP-1 seem to be responsible for viral dysregulation because both suppression of BPV-1 and induction of c-Jun mRNA could be almost entirely abrogated by simultaneous treatment with SB 203580, an inhibitor of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Moreover, dissecting the complex transcriptional pattern of episomal BPV-1 with specific primer sets for reverse transcription-PCR analysis, the repressive effect could be attributed to a selective down-regulation of the mRNA encoding the E2 transactivator function in favor of the E2 repressor, whose mRNA level remained constant during AG 555 treatment. These data indicate that tyrphostin AG 555 disturbs the balance of negative and positive regulatory factors necessary to maintain the homeostasis of a virus-transformed phenotype.
Tyrphostin AG-555 inhibits early and late stages of Moloney murine leukemia virus replication cycle.[Pubmed:21533502]
Int J Oncol. 1997 Jun;10(6):1185-9.
We have previously shown that certain tyrphostin derivatives, known as protein tyrosine blockers, inhibited Moloney murine leukemia virus (Mo-MuLV) replication in acutely and chronically infected NIH/3T3 cells, without affecting cell viability or growth. In our present work, we examined the stages in the viral life cycle that are affected by tyrphostin AG-555. We found that this drug inhibited the integration of the viral DNA into the host genome in acutely infected cells. This compound also reduced the level of viral RNA and specifically inhibited viral protein synthesis in NIH/3T3/Mo-MuLV chronically infected cells while no effect on the cellular beta-actin was observed. Since tyrphostin AG-555 inhibited both the early stages (integration process) and the late stages (viral protein synthesis) in the virus life cycle, it offers a potential advantage over other compounds which affect only one stage in the viral life cycle. Therefore, tyrphostin AG-555 may be considered as a potent antiretroviral drug.
Tyrphostins that suppress the growth of human papilloma virus 16-immortalized human keratinocytes.[Pubmed:10454524]
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1999 Sep;290(3):1442-57.
Human papilloma virus 16 (HPV16) is considered to be the causative agent for cervical cancer, which ranks second to breast cancer in women's malignancies. In an attempt to develop drugs that inhibit the malignant transformation of HPV16-immortalized epithelial cells, we examined the effect of tyrphostins on such cells. We examined the effect of tyrphostins from four different families on the growth of HPV16-immortalized human keratinocytes (HF-1) cells. We found that they alter their cell cycle distribution, their morphology, and induce cell death by apoptosis. The effects of tyrphostins on HF-1 cells are different from their effects on normal keratinocytes. Growth suppression by AG555 and AG1478 is accompanied by 30% apoptosis in HF-1 cells, but this is not observed in normal keratinocytes. Tyrphostin treatment produces distinctive morphological changes in HF-1 cells and in normal keratinocytes; however, the culture organization of normal keratinocytes is less disrupted. These differential effects of the tyrphostins on HPV16-immortalized keratinocytes compared with their effects on normal keratinocytes suggests that these compounds are suitable candidates for the treatment of papilloma. Previous and present results indicate that group 1 tyrphostins, which inhibit Cdk2 activation, and group 2 tyrphostins, represented by AG1478, a potent epidermal growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor, induce cell cycle arrest; and, in the case of HF-1 cells, apoptosis and differentiation. Cells accumulate in the G(1) phase of the cell cycle at the expense of S and G(2) + M. These compounds block the growth of normal keratinocytes without inducing apoptosis or differentiation, causing them to accumulate in G(1). AG17, which belongs to group 4, exerts its antiproliferative effect mainly by increasing the fractions of cells in G(1) with a concomitant decrease in the fraction of cells in S and G(2) + M.
Tyrosine kinase inhibition: an approach to drug development.[Pubmed:7892601]
Science. 1995 Mar 24;267(5205):1782-8.
Protein tyrosine kinases (PTKs) regulate cell proliferation, cell differentiation, and signaling processes in the cells of the immune system. Uncontrolled signaling from receptor tyrosine kinases and intracellular tyrosine kinases can lead to inflammatory responses and to diseases such as cancer, atherosclerosis, and psoriasis. Thus, inhibitors that block the activity of tyrosine kinases and the signaling pathways they activate may provide a useful basis for drug development. This article summarizes recent progress in the development of PTK inhibitors and demonstrates their potential use in the treatment of disease.
Tyrphostins. 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and ErbB2/neu tyrosine kinases.[Pubmed:1676428]
J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1896-907.
We have previously described a novel series of low molecular weight protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors which we named tyrphostins. The characteristic active pharmacophore of these compounds was the hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitrile moiety. In this article we describe three novel groups of tyrphostins: (i) one group has the phenolic moiety of the cis-benzylidenemalononitrile replaced either with other substituted benzenes or with heteroaromatic rings, (ii) another is a series of conformationally constrained derivatives of hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitriles in which the malononitrile moiety is fixed relative to the aromatic ring, and (iii) two groups of compounds in which the position trans to the benzenemalononitrile has been substituted by ketones and amides. Among the novel tyrphostins examined we found inhibitors which discriminate between the highly homologous EGF receptor kinase (HER1) and ErbB2/neu kinase (HER2). These findings may lead to selective tyrosine kinase blockers for the treatment of diseases in which ErbB2/neu is involved.


