AG 556EGFR inhibitor CAS# 133550-41-1 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 133550-41-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 5328775 | Appearance | Powder |
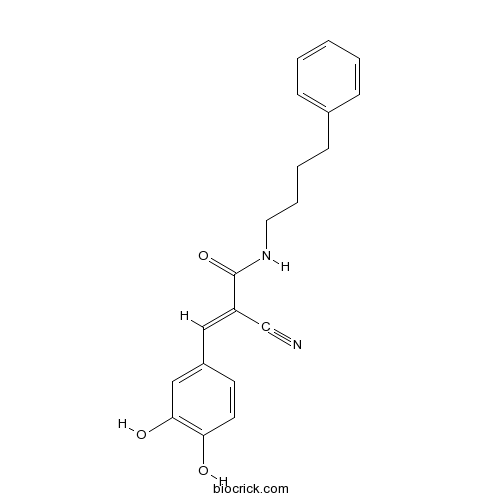
| Formula | C20H20N2O3 | M.Wt | 336.39 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Tyrphostin AG 556 | ||
| Solubility | Soluble to 30 mM in DMSO | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-2-cyano-3-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-N-(4-phenylbutyl)prop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | C1=CC=C(C=C1)CCCCNC(=O)C(=CC2=CC(=C(C=C2)O)O)C#N | ||
| Standard InChIKey | GWCNJMUSWLTSCW-SFQUDFHCSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H20N2O3/c21-14-17(12-16-9-10-18(23)19(24)13-16)20(25)22-11-5-4-8-15-6-2-1-3-7-15/h1-3,6-7,9-10,12-13,23-24H,4-5,8,11H2,(H,22,25)/b17-12+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) kinase inhibitor (IC50 = 1.1 μM). Selective over ErbB2 (IC50 > 500 μM). |

AG 556 Dilution Calculator

AG 556 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.9727 mL | 14.8637 mL | 29.7274 mL | 59.4548 mL | 74.3185 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5945 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9455 mL | 11.891 mL | 14.8637 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2973 mL | 1.4864 mL | 2.9727 mL | 5.9455 mL | 7.4318 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0595 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 1.1891 mL | 1.4864 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0297 mL | 0.1486 mL | 0.2973 mL | 0.5945 mL | 0.7432 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AG 556 is a selective inhibitor of EGFR with IC50 value of 1.1 μM.
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is the cell-surface receptor for epidermal growth factor and plays an important role in tumor invasion and cancer cell proliferation.
AG 556 is a selective EGFR inhibitor. In HEK 293 cells expressing KIR2.3 or Kir2.1, AG556 (10 μM) reversibly reduced KIR2.3 or Kir2.1 currents. Also, AG556 inhibited tyrosine phosphorylation of KIR2.3 or Kir2.1 channels. EGF (100 ng/ml) increased KIR2.3 current, while this effect was inhibited by AG556 [1] [2]. AG556 arrested cells at G1/S phase by 85% and inhibited the activation of Cdk2 by phosphorylating tyrosine 15 on Cdk2 [3].
In a canine model infected with Escherichia coli 0111: B4, AG 556 increased survival times. AG 556 increased mean arterial pressure, oxygen delivery, cardiac output, alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient and left ventricular ejection fraction, which suggested that AG 556 increased survival. Also, AG 556 significantly reduced the levels of serum TNF, which suggested that AG 556 inhibited cell-signaling pathways and cytokine-induced multiorgan failure [4].
References:
[1]. Zhang DY, Zhang YH, Sun HY, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase regulates the human inward rectifier potassium K(IR)2.3 channel, stably expressed in HEK 293 cells. Br J Pharmacol, 2011 Nov, 164(5): 1469-1478 [1].
[2]. Zhang DY, Wu W, Deng XL, et al. Genistein and tyrphostin AG556 inhibit inwardly-rectifying Kir2.1 channels expressed in HEK 293 cells via protein tyrosine kinase inhibition. Biochim Biophys Acta, 2011, 1808(8): 1993-1999.
[3]. Kleinberger-Doron N, Shelah N, Capone R, et al. Inhibition of Cdk2 activation by selected tyrphostins causes cell cycle arrest at late G1 and S phase. Exp Cell Res, 1998, 241(2): 340-351.
[4]. Sevransky JE, Shaked G, Novogrodsky A, et al. Tyrphostin AG 556 improves survival and reduces multiorgan failure in canine Escherichia coli peritonitis. J Clin Invest, 1997, 99(8): 1966-1973.
- Tyrphostin B44, (+) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6704
CAS No.:133550-37-5
- AG 494
Catalog No.:BCC6722
CAS No.:133550-35-3
- AG 555
Catalog No.:BCC6721
CAS No.:133550-34-2
- Tyrphostin B44, (-) enantiomer
Catalog No.:BCC6703
CAS No.:133550-32-0
- AG-490
Catalog No.:BCC2193
CAS No.:133550-30-8
- Apigenin 4'-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN6181
CAS No.:133538-77-9
- Exendin-3 (9-39) amide
Catalog No.:BCC7257
CAS No.:133514-43-9
- SR 1001
Catalog No.:BCC6309
CAS No.:1335106-03-0
- TAI-1
Catalog No.:BCC5576
CAS No.:1334921-03-7
- Fmoc-Glu(OAll)-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3492
CAS No.:133464-46-7
- Iloperidone
Catalog No.:BCC2516
CAS No.:133454-47-4
- Heudelotinone
Catalog No.:BCN6180
CAS No.:133453-58-4
- 4,15-Isoatriplicolide methylacrylate
Catalog No.:BCN7935
CAS No.:133559-38-3
- Isoatriplicolide tiglate
Catalog No.:BCN7934
CAS No.:133559-39-4
- Boc-Glutaminol
Catalog No.:BCC3092
CAS No.:133565-42-1
- Boc-Threoninol(Bzl)
Catalog No.:BCC2704
CAS No.:133565-43-2
- Fmoc-Ile-ol
Catalog No.:BCC2584
CAS No.:133565-46-5
- 2-Ethyl-2,6,6-trimethylpiperidin-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN6504
CAS No.:133568-79-3
- 2-Aminoisonicotinic acid
Catalog No.:BCC8550
CAS No.:13362-28-2
- Exoticin
Catalog No.:BCN6182
CAS No.:13364-94-8
- 1-Allyl-3,5-Dimethylpyrazole
Catalog No.:BCC8450
CAS No.:13369-74-9
- GSK 2193874
Catalog No.:BCC8009
CAS No.:1336960-13-4
- Ebenifoline E-II
Catalog No.:BCN3097
CAS No.:133740-16-6
- Suavioside A
Catalog No.:BCN6963
CAS No.:133740-37-1
The effect of tyrphostin AG-556 on intimal thickening in a mouse model of arterial injury.[Pubmed:15924877]
Exp Mol Pathol. 2005 Jun;78(3):233-8.
BACKGROUND: Inflammation has been shown to play an important role in promoting the response to arterial injury and proinflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha, are candidate mediators. AG-556 is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor proven to be effective in a model of multiple sclerosis-like syndrome in mice due to its immunomodulating effect. In the current study, we investigated the effect of the tyrphostin AG-556 on neointimal thickening and cytokine profile in a model of arterial injury in the mouse. METHODS: Injury was induced by external cuff placement on the left femoral artery of wild-type C57BL/6 mice. AG-556 dissolved in DMSO was injected intraperitoneally daily to the injured mice in a dosage of 2 mg/mouse. Control mice received DMSO injections. Histological analysis was carried out to assess neointimal formation. Splenocytes were cultured in the absence and presence of a mitogen for evaluation of thymidine incorporation and cytokine production. RESULTS: AG-556 treatment significantly attenuated intimal thickening (43,000+/-17,000 microm2; n=11) when compared to DMSO administration (286,000+/-127,000 microm2; n=10; P<0.05). Basal interferon-gamma production by splenocytes from AG-556-treated mice was increased by approximately 20-fold in comparison with levels in DMSO-treated animals, whereas Con-A induced secretion of the cytokine was similar between both groups. Levels of TNF-alpha, IL-4 and IL-10 in the culture supernatant from treated and non-treated animals did not differ significantly. CONCLUSION: The tyrosine kinase inhibitor AG-556 may have a role in the reduction of intimal thickening. The effect could be mediated via an immune modulating effect involving a significant increase in the smooth muscle cell inhibitory cytokine IFN-gamma.
The effect of early and late treatment with the tyrphostin AG-556 on the progression of experimental autoimmune myocarditis.[Pubmed:15126106]
Exp Mol Pathol. 2004 Jun;76(3):234-41.
Experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM) in rats is a T-cell-mediated disorder; the involvement of TNF-alpha in this disorder has been demonstrated. EAM represents a model for human autoimmune myocarditis, a condition for which no optimal treatment is currently available. Tyrphostins AG-126 and AG-556 were previously shown to reduce TNF-alpha production and its end-organ cytotoxicity, thus proving beneficial in animal models of septic shock and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. To study the effects of AG-126 and AG-556 on EAM, we induced the disorder in male Lewis rats through immunization against myosin and subsequently treated the rats with both agents or the control DMSO both before and after the appearance of myocardial inflammation. AG-556 administered daily for 21 days from the day of EAM induction, significantly reduced the severity of myocarditis. Similarly, AG-556 administered for an additional 10 days after myosin immunization (when signs of inflammation are already present) attenuated the progression of myocarditis, though AG-126 did not. TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma production by in vitro sensitized splenocytes from AG-556-treated rats was significantly diminished as compared with control cells from EAM animals. Thus, AG-556 may represent a novel strategy of ameliorating the progression of myocarditis without non-selectively compromising the immune system.
Investigation of tyrphostin AG 556 for testicular torsion-induced ischemia reperfusion injury in rat.[Pubmed:24070787]
J Pediatr Urol. 2014 Apr;10(2):223-9.
OBJECTIVE: To investigate the effects of tyrphostin AG 556, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) in an experimental model of testicular ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury. MATERIAL AND METHODS: Twenty-four adult male rats were randomly divided into four groups (n = 6): sham, torsion/detorsion (T/D), T/D + dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) (vehicle group), and T/D + DMSO + tyrphostin AG 556. Testicular torsion was achieved by rotating the left testis 720 degrees clockwise for 4 h. Thirty minutes before detorsion, 3 mg/kg tyrphostin AG 556 was injected transperitoneally in the AG 556 group and DMSO was injected transperitoneally in the DMSO group. After 2 h of reperfusion arterial blood samples were collected for biochemical analysis for malondialdehyde (MDA), ischemia modified albumin (IMA), SCUBE1 (signal peptide-CUB [complement C1r/C1s, Uegf, and Bmp1] and EGF [epidermal growth factor] like domain-containing protein 1), total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), and oxidative stress index (OSI) parameters, and ipsilateral orchiectomies were performed for histopathological examination based on the semi-quantitative Johnsen's mean testicular biopsy score (MTBS) in all groups. RESULTS: Tyrphostin AG 556 exhibited a protective effect against I/R injury in testicular torsion. Of the biochemical parameters evaluated as a result of testicular I/R, IMA, MDA, and TOS levels were significantly elevated. There was no significant difference in terms of these biochemical parameters between the sham and AG 556 groups. Significant histopathological injury was determined by comparing the T/D and sham groups. According to histopathological injury scores, significant differences were determined between T/D and AG 556 groups and between AG 556 and sham groups. AG 556 had a superior improving effect on Johnsen's scores than DMSO. CONCLUSIONS: Our results suggest that the use of tyrphostin AG 556 prior to testicular reperfusion has a protective effect against testicular I/R injury.
The effects of tyrphostine Ag 556 on experimental spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury.[Pubmed:14706378]
Surg Neurol. 2004 Jan;61(1):45-54; discussion 54.
BACKGROUND: To investigate the effects of Tyrphostin AG 556 on spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. METHODS: The inhibition of tyrosine kinase may represent a novel approach in the treatment of spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. Recently, a family of tyrosine kinase inhibitors, the tyrphostins, has been successfully used in models of endotoxemia, peritonitis, and hypovolemic shock. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Twenty-four Wistar rats were used in the study. Rats were divided into 4 groups of 6 animals. The groups were named as sham operated group, injury group, vehicle group, and treatment group. Clamping of the abdominal aorta was performed for 45 minutes with all of the groups except sham-operated group. All of the rats were sacrificed 24 hours after the operation for biochemical and ultrastructural studies. RESULTS: Tyrphostin AG 556 treatment was found effective on experimental spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury. The Malondialdehyde (MDA) values of the treatment group were statistically significant lower then the other reperfusion injury groups. The histologic examination showed better cellular structure in the treatment group than the other reperfusion injury groups. The neurologic scores of the treatment group also improved after treatment. CONCLUSIONS: Tyrphostin AG 556 alters spinal cord ischemia reperfusion injury by inhibiting protein kinases. Further investigations will be required to determine the long-term effects of this drug.
Secondary dimerization between members of the epidermal growth factor receptor family.[Pubmed:9115272]
J Biol Chem. 1997 May 2;272(18):12052-6.
Growth factor receptors of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor family play pivotal roles in the regulation of cell proliferation and differentiation and are involved in the development of human cancers. It has been well documented that these receptors undergo growth factor-stimulated homo- and heterodimerization as a first step in the initiation of signaling cascades. Here we provide evidence for a new mechanism for growth factor-stimulated receptor dimer formation, designated secondary dimerization. The growth factor-induced dimerization and ensuing receptor trans-autophosphorylation results in the dissociation of the original (primary) receptor dimer. Each phosphorylated receptor monomer then interacts with a new (nonphosphorylated) receptor to form a secondary dimer. Treatment of cells with EGF yields Neu-ErbB3 secondary dimers, and heregulin treatment induces the formation of Neu-EGF receptor (secondary) dimers. The ability of EGF and heregulin to stimulate a cascade of dimerization events points to a novel mechanism by which multiple signaling activities and diverse biological responses are initiated by members of the EGF receptor family.
Tyrphostins. 2. Heterocyclic and alpha-substituted benzylidenemalononitrile tyrphostins as potent inhibitors of EGF receptor and ErbB2/neu tyrosine kinases.[Pubmed:1676428]
J Med Chem. 1991 Jun;34(6):1896-907.
We have previously described a novel series of low molecular weight protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors which we named tyrphostins. The characteristic active pharmacophore of these compounds was the hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitrile moiety. In this article we describe three novel groups of tyrphostins: (i) one group has the phenolic moiety of the cis-benzylidenemalononitrile replaced either with other substituted benzenes or with heteroaromatic rings, (ii) another is a series of conformationally constrained derivatives of hydroxy-cis-benzylidenemalononitriles in which the malononitrile moiety is fixed relative to the aromatic ring, and (iii) two groups of compounds in which the position trans to the benzenemalononitrile has been substituted by ketones and amides. Among the novel tyrphostins examined we found inhibitors which discriminate between the highly homologous EGF receptor kinase (HER1) and ErbB2/neu kinase (HER2). These findings may lead to selective tyrosine kinase blockers for the treatment of diseases in which ErbB2/neu is involved.


