AR 231453GPR119 agonist,potent and selective CAS# 733750-99-7 |
- BCX 1470
Catalog No.:BCC1413
CAS No.:217099-43-9
- A 205804
Catalog No.:BCC3944
CAS No.:251992-66-2
- A 286982
Catalog No.:BCC3946
CAS No.:280749-17-9
- AEBSF.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC1219
CAS No.:30827-99-7
- Nafamostat
Catalog No.:BCC4187
CAS No.:81525-10-2
- Nafamostat Mesylate(FUT-175)
Catalog No.:BCC1228
CAS No.:82956-11-4
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 733750-99-7 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 24939268 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C21H24FN7O5S | M.Wt | 505.52 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | H2O : 60 mg/mL (118.69 mM; Need ultrasonic and warming) DMSO : ≥ 60 mg/mL (118.69 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
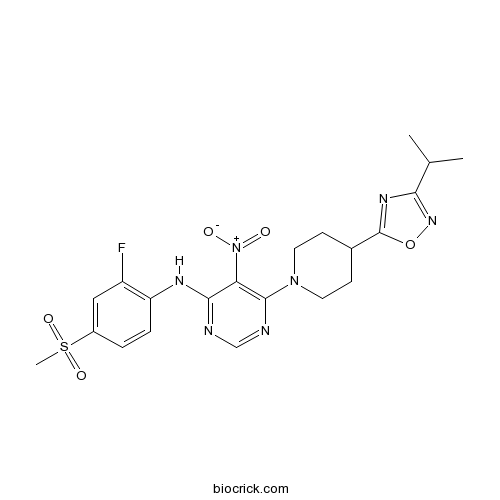
| Chemical Name | N-(2-fluoro-4-methylsulfonylphenyl)-5-nitro-6-[4-(3-propan-2-yl-1,2,4-oxadiazol-5-yl)piperidin-1-yl]pyrimidin-4-amine | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C1=NOC(=N1)C2CCN(CC2)C3=C(C(=NC=N3)NC4=C(C=C(C=C4)S(=O)(=O)C)F)[N+](=O)[O-] | ||
| Standard InChIKey | DGBKNTVAKIFYNU-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C21H24FN7O5S/c1-12(2)18-26-21(34-27-18)13-6-8-28(9-7-13)20-17(29(30)31)19(23-11-24-20)25-16-5-4-14(10-15(16)22)35(3,32)33/h4-5,10-13H,6-9H2,1-3H3,(H,23,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AR231453 is a potent and selective small molecule agonist of GPR119 that enhances glucose-dependent insulin secretion and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) release; Antidiabetic agent.
IC50 value:
Target: GPR119
in vitro: The GPR119-specific agonist AR231453 significantly increased cAMP accumulation and insulin release in both HIT-T15 cells and rodent islets. In both cases, loss of GPR119 rendered AR231453 inactive [1]. In GLUTag cells, a well-established model of intestinal L-cell function, the potent GPR119 agonist AR231453 stimulated cAMP accumulation and GLP-1 release [2].
in vivo: AR231453 also enhanced glucose-dependent insulin release in vivo and improved oral glucose tolerance in wild-type mice but not in GPR119-deficient mice. Diabetic KK/A(y) mice were also highly responsive to AR231453. Orally active GPR119 agonists may offer significant promise as novel antihyperglycemic agents acting in a glucose-dependent fashion [1]. When administered in mice, AR231453 increased active GLP-1 levels within 2 min after oral glucose delivery and substantially enhanced total glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide levels. Blockade of GLP-1 receptor signaling with exendin(9-39) reduced the ability of AR231453 to improve glucose tolerance in mice [2]. References: | |||||

AR 231453 Dilution Calculator

AR 231453 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9782 mL | 9.8908 mL | 19.7816 mL | 39.5632 mL | 49.454 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.3956 mL | 1.9782 mL | 3.9563 mL | 7.9126 mL | 9.8908 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1978 mL | 0.9891 mL | 1.9782 mL | 3.9563 mL | 4.9454 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0396 mL | 0.1978 mL | 0.3956 mL | 0.7913 mL | 0.9891 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0198 mL | 0.0989 mL | 0.1978 mL | 0.3956 mL | 0.4945 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AR 231453 is an agonist of GPR119 with EC50 value of 0.68nM [1].
AR 231453 is the first subnanomolar agonist of GPR119. It is highly selective against GPR119 over a 76 receptor and enzyme profiling panel (CEREP) including the known incretin receptors. It also has no activity to 140 known and orphan GPCRs in melanophore dispersion assays. Besides that, AR 231453 is reported to stimulate cAMP production via endogenously expressed GPR119 in HIT-T15 cell line with EC50 value of 4.7nM [1].
In vivo assay shows that AR 231453 has activity in rodents. It can enhance glucose-dependent insulin release and improve oral glucose tolerance in wild-type C57/bl6J mice but not in GPR119-deficient mice at a dose of 20 mg/kg. Due to its activity to active GPR119, AR 231453 is expected to be a potent anti-diabetic agent [1].
References:
[1] Semple G, Fioravanti B, Pereira G, Calderon I, Uy J, Choi K, Xiong Y, Ren A, Morgan M, Dave V, Thomsen W, Unett DJ, Xing C, Bossie S, Carroll C, Chu ZL, Grottick AJ, Hauser EK, Leonard J, Jones RM. Discovery of the first potent and orally efficacious agonist of the orphan G-protein coupled receptor 119. J Med Chem. 2008 Sep 11;51(17):5172-5.
- SB 706375
Catalog No.:BCC6256
CAS No.:733734-61-7
- SCH 50911
Catalog No.:BCC5692
CAS No.:733717-87-8
- Niclosamide monohydrate
Catalog No.:BCC5212
CAS No.:73360-56-2
- 9-O-Acetyl-4,4'-di-O-methyllariciresinol
Catalog No.:BCN1367
CAS No.:73354-15-1
- Albanin A
Catalog No.:BCN3290
CAS No.:73343-42-7
- Macbecin I
Catalog No.:BCC7551
CAS No.:73341-72-7
- 3-Hydroxy-9,10-Dimethoxypterocarpan
Catalog No.:BCC8101
CAS No.:73340-41-7
- Methylnissolin
Catalog No.:BCN1368
CAS No.:733-40-4
- BAY 61-3606
Catalog No.:BCC1406
CAS No.:732983-37-8
- Deoxynojirimycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCN2626
CAS No.:73285-50-4
- 1,4-Dihydro-1,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid
Catalog No.:BCN1369
CAS No.:73281-83-1
- 5-O-Caffeoylshikimic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7929
CAS No.:73263-62-4
- Norandrostenedione
Catalog No.:BCC9103
CAS No.:734-32-7
- Dehydrobruceine A
Catalog No.:BCN7620
CAS No.:73435-47-9
- 1-Deoxymannojirimycin hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6995
CAS No.:73465-43-7
- Tetrachyrin
Catalog No.:BCN4776
CAS No.:73483-88-2
- 7-Acetyllycopsamine
Catalog No.:BCN2000
CAS No.:73544-48-6
- cis-ACBD
Catalog No.:BCC6587
CAS No.:73550-55-7
- Mevastatin
Catalog No.:BCN2568
CAS No.:73573-88-3
- 27-p-Coumaroyloxyursolic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4288
CAS No.:73584-67-5
- Omeprazole
Catalog No.:BCC1254
CAS No.:73590-58-6
- (-)-Bicuculline methobromide
Catalog No.:BCC6555
CAS No.:73604-30-5
- 3-Hydroxybenzylamine
Catalog No.:BCN1804
CAS No.:73604-31-6
- Xylazine
Catalog No.:BCC5167
CAS No.:7361-61-7
Theoretical Cross Sections of the Inelastic Fine Structure Transition M((2)P1/2) + Ng <--> M((2)P3/2) + Ng for M = K, Rb, and Cs and Ng = He, Ne, and Ar.[Pubmed:28368614]
J Phys Chem A. 2017 May 11;121(18):3340-3351.
Scattering matrix elements of the inelastic fine structure transition M((2)P1/2) + Ng <--> M((2)P3/2) + Ng are computed using the channel packet method (CPM) for alkali-metal atoms M = K, Rb, and Cs, as they collide with noble-gas atoms Ng = He, Ne, and Ar. The calculations are performed within the block Born-Oppenheimer approximation where excited state VA(2)Pi1/2(R), VA(2)Pi3/2(R), and VB(2)Sigma1/2(R) adiabatic potential energy surfaces are used together with a Hund's case (c) basis to construct a 6 x 6 diabatic representation of the electronic Hamiltonian. Matrix elements of the angular kinetic energy of the nuclei incorporate Coriolis coupling and, together with the diabatic representation of the electronic Hamiltonian, yield a 6 x 6 effective potential energy matrix. This matrix is diagonal in the asymptotic limit of large internuclear separation with eigenvalues that correlate to the (2)Pj alkali atomic energy levels. Scattering matrix elements are computed using the CPM by preparing reactant and product wave packets on the effective potential energy surfaces that correspond to the excited (2)Pj alkali states of interest. The reactant wave packet is then propagated forward in time using the split operator method together with a unitary transformation between the adiabatic and diabatic representations. The Fourier transformation of the correlation function between the evolving reactant wave packet and stationary product wave packet yields state-to-state scattering matrix elements as a function of energy for a particular choice of total angular momentum J. Calculations are performed for energies that range from 0.0 to 0.01 hartree and values of J that start with a minimum of J = 0.5 for all M + Ng pairs up to a maximum that ranges from J = 450.5 for KAr to J = 100.5 for CsAr. A sum over J together with an average over energy is used to compute thermally averaged cross sections for a temperature range of T = 0-400 K.
Simulation of carbon nanotube welding through Ar bombardment.[Pubmed:28365822]
J Mol Model. 2017 Apr;23(4):148.
Single-walled carbon nanotubes show promise as nanoscale transistors for nanocomputing applications. This use will require appropriate methods for creating electrical connections between distinct nanotubes, analogous to welding of metallic wires at larger length scales, but methods for performing nanoscale chemical welding are not yet sufficiently understood. This study examines the effect of Ar bombardment on the junction of two crossed single-walled carbon nanotubes, to understand the value and limitations of this method for generating connections between nanotubes. A geometric criterion was used to assess the quality of the junctions formed, with the goal of identifying the most productive conditions for experimental ion bombardment. In particular, the effects of nanotube chirality, Ar impact kinetic energy, impact particle flux and fluence, and annealing temperature were considered. The most productive bombardment conditions, leading to the most crosslinking of the tubes with the smallest loss of graphitic (i.e., conductive) character, were found to be at relatively mild impact energies (100 eV), with low flux and high-temperature (3000 K) annealing. Particularly noteworthy for experimental application, a high junction quality is maintained for a relatively broad range of fluences, from 3 x 10(19) m(-2) to at least 1 x 10(20) m(-2).
Lack of beta2-AR Increases Anxiety-Like Behaviors and Rewarding Properties of Cocaine.[Pubmed:28348522]
Front Behav Neurosci. 2017 Mar 13;11:49.
It is well known that beta-adrenoceptors (beta-ARs) play a critical role in emotional arousal and stressful events, but the specific contributions of the beta2-AR subtype to the psychological disorders are largely unknown. To investigate whether beta2-AR are involved in anxiety-like behavior and reward to addictive drugs, we conducted a series of behavioral tests on beta2-AR knock-out (KO) mice. beta2-AR KO mice exhibited increased preference for the dark compartment and closed arm in tests of Light/Dark box and elevated plus maze, indicating that beta2-AR deletion elevates level of anxiety or innate fear. beta2-AR KO mice also showed decreased immobility in tail suspension test (TST), suggesting that beta2-AR deletion inhibits depression-like behavior. Interestingly, beta2-AR ablation did not change basal locomotion but significantly increased locomotor activity induced by acute cocaine administration. beta2-AR KO mice showed enhanced place preference for cocaine, which could be attenuated by beta1-selective AR antagonist betaxolol. Consistently, beta2-AR agonist suppressed cocaine-conditioned place preference (CPP). These data indicate that beta2-AR deletion enhances acute response and reward to cocaine. Our results suggest that beta2-AR regulates anxiety level, depression-like behavior and hedonic properties of cocaine, implicating that beta2-AR are the potential targets for the treatment of emotional disorders and cocaine addiction.
Explained Variance and Intraclass Correlation in a Two-Level AR(1) Model.[Pubmed:28375685]
Multivariate Behav Res. 2017 Jul-Aug;52(4):403-415.
The total variance of a first-order autoregressive AR(1) time series is well known in time series literature. However, despite the increased use and interest in two-level AR(1) models, an equation for the total variance of these models does not exist. This paper presents an approximation of this total variance. It will be used to compute the unexplained and explained variance at each level of the model, the proportion of explained variance, and the intraclass correlation (ICC). The use of these variances and the ICC will be illustrated using an example concerning structured diary data about the positive affect of 96 married women.


