AZD1981CRTh2 antagonist,potent and selective CAS# 802904-66-1 |
- Ro 31-8220 Mesylate
Catalog No.:BCC4999
CAS No.:138489-18-6
- CHIR-99021 (CT99021)
Catalog No.:BCC1275
CAS No.:252917-06-9
- CHIR-98014
Catalog No.:BCC3751
CAS No.:252935-94-7
- TWS119
Catalog No.:BCC4512
CAS No.:601514-19-6
- GSK-3 inhibitor 1
Catalog No.:BCC4126
CAS No.:603272-51-1
- GSK-3 Inhibitor IX (BIO)
Catalog No.:BCC4510
CAS No.:667463-62-9
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 802904-66-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 11292191 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C19H17ClN2O3S | M.Wt | 388.87 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 31 mg/mL (79.72 mM) *"≥" means soluble, but saturation unknown. | ||
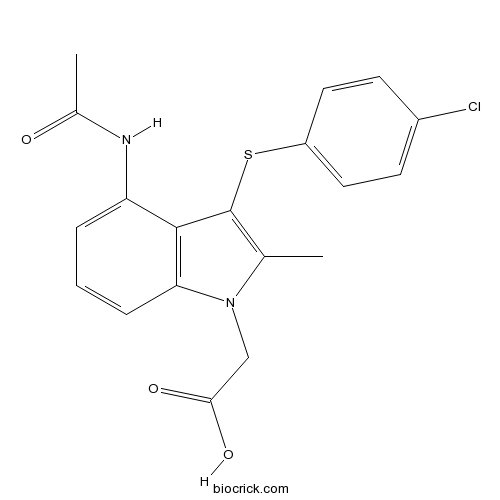
| Chemical Name | 2-[4-acetamido-3-(4-chlorophenyl)sulfanyl-2-methylindol-1-yl]acetic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1=C(C2=C(N1CC(=O)O)C=CC=C2NC(=O)C)SC3=CC=C(C=C3)Cl | ||
| Standard InChIKey | JWYIGNODXSRKGP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C19H17ClN2O3S/c1-11-19(26-14-8-6-13(20)7-9-14)18-15(21-12(2)23)4-3-5-16(18)22(11)10-17(24)25/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,21,23)(H,24,25) | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD1981 is a potent and selective CRTh2 antagonist; displaces radio-labelled PGD2 from human recombinant DP2 with high potency (pIC50 = 8.4).
IC50 value:
Target: GPR44 antagonist
in vitro: AZD1981 produced a concentration-dependent displacement of the [3H]PGD2-specific binding with a mean pIC50 of 8.4 ± 0.1 (n = 25, geometric mean IC50 of 4 nM). AZD1981 had no significant affinity towards recombinant human DP1 receptors with only a mean 27% (range 14–50%; n = 4) displacement of [3H]PGD2-specific binding observed at the highest concentration tested (10 μM). Compared with the binding potency for DP2, AZD1981 showed 10-fold selectivity over rat aldose reductase and 1700-fold selectivity over rat steroid 5α-reductase.In eosinophils, a single concentration of 1 μM, AZD1981 caused a large (20-fold) rightward parallel shift in the 15R-methyl PGD2 E/[A] curve with no evidence of a decrease in the maximal response. The effect of AZD1981 was therefore investigated using a single sub-maximal concentration of agonist (1 μM). AZD1981 produced a concentration-dependent inhibition of eosinophil migration with a pIC50 value of 7.6 ± 0.1 (n = 4) [1].
in vivo: Using the previously described guinea pig hind limb model , 10 nM AZD1981 significantly inhibited DK-PGD2-induced eosinophil mobilization by approximately 50%, and the response was completely inhibited with 100 nM AZD1981 [1].
in vivo: AZD1981 exhibited good cross-species binding activity against mouse, rat, guinea pig, rabbit and dog DP2 . Evaluation in mouse, rat or rabbit cell systems was not possible as they did not respond to DP2 agonists. Agonist responses were seen in guinea pig and dog, and AZD1981 blocked DP2 -mediated eosinophil shape change. Such responses were more robust in the guinea pig, where AZD1981 also blocked DP2 -dependent eosinophil emigration from bone marrow [1]. There was no beneficial clinical effect of AZD1981, at a dose of 1000 mg twice daily for 4 weeks, in patients with moderate to severe COPD. AZD1981 was well tolerated and no safety concerns were identified [3]. References: | |||||

AZD1981 Dilution Calculator

AZD1981 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5716 mL | 12.8578 mL | 25.7155 mL | 51.4311 mL | 64.2888 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5143 mL | 2.5716 mL | 5.1431 mL | 10.2862 mL | 12.8578 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2572 mL | 1.2858 mL | 2.5716 mL | 5.1431 mL | 6.4289 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0514 mL | 0.2572 mL | 0.5143 mL | 1.0286 mL | 1.2858 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0257 mL | 0.1286 mL | 0.2572 mL | 0.5143 mL | 0.6429 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD1981 is a selective, orally bioavailable and potent antagonist of the chemoattractant receptor-homologous expressed on Th2 lymphocytes receptor (CRTh2 or DP2) with an IC50 value of 4 nM [1].
AZD1981 has shown to inhibit eosinophil migration with a pIC50 value of 7.6±0.1. AZD1981 could block chemotaxis of DP2+ T-cell lines with a pIC50 value of 7.5±0.1. AZD1981 has been demonstrated to inhibit PGD2 binding to mouse, rat, rabbit, dog, guinea pig and human DP2. AZD1981 could inhibit shape change induced by DP2 in dog and guinea pig granulocytes as well as in human eosinophils and basophils in blood [2].
References:
[1] Luker T1, Bonnert R, Brough S, Cook AR, Dickinson MR, Dougall I, Logan C, Mohammed RT, Paine S, Sanganee HJ, Sargent C, Schmidt JA,Teague S, Thom S. Substituted indole-1-acetic acids as potent and selective CRTh2 antagonists-discovery of AZD1981. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2011 Nov 1;21(21):6288-92.
[2] Schmidt JA1, Bell FM, Akam E, Marshall C, Dainty IA, Heinemann A, Dougall IG, Bonnert RV, Sargent CA. Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of AZD1981, an orally available selective DP2 antagonist in clinical development for asthma. Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(7):1626-38.
- Artemisinic acid
Catalog No.:BCN4336
CAS No.:80286-58-4
- PHA-848125
Catalog No.:BCC3839
CAS No.:802539-81-7
- Nafamostat hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4188
CAS No.:80251-32-7
- Spiramycin
Catalog No.:BCC4724
CAS No.:8025-81-8
- Casanthranol
Catalog No.:BCC3746
CAS No.:8024-48-4
- 2'-O-Galloylquercitrin
Catalog No.:BCN8225
CAS No.:80229-08-9
- Rosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN8425
CAS No.:80225-53-2
- Glochidionionol C
Catalog No.:BCC2641
CAS No.:
- Roxithromycin
Catalog No.:BCC4842
CAS No.:80214-83-1
- Sorbic acid, 1-p-tolylhydrazide
Catalog No.:BCN2219
CAS No.:802048-02-8
- Helicid
Catalog No.:BCN1056
CAS No.:80154-34-3
- Methyl demethoxycarbonylchanofruticosinate
Catalog No.:BCN1348
CAS No.:80151-89-9
- RG7090
Catalog No.:BCC5499
CAS No.:802906-73-6
- Dehydro-δ-tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCN4573
CAS No.:802909-72-4
- Stevenleaf
Catalog No.:BCN5978
CAS No.:80321-63-7
- Gypenoside XVII
Catalog No.:BCN2339
CAS No.:80321-69-3
- 8-Acetonyldihydronitidine
Catalog No.:BCN3304
CAS No.:80330-39-8
- Tinnevellin glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN3414
CAS No.:80358-06-1
- NSC59984
Catalog No.:BCC6540
CAS No.:803647-40-7
- 2',3,5,6',7-Pentahydroxyflavanone
Catalog No.:BCN4337
CAS No.:80366-15-0
- 8beta-Tigloyloxyreynosin
Catalog No.:BCN7222
CAS No.:80368-31-6
- Obatoclax mesylate (GX15-070)
Catalog No.:BCC2234
CAS No.:803712-79-0
- Z-D-Thr-OH
Catalog No.:BCC2736
CAS No.:80384-27-6
- Protoplumericin A
Catalog No.:BCN4572
CAS No.:80396-57-2
Two Phase II randomized trials on the CRTh2 antagonist AZD1981 in adults with asthma.[Pubmed:27621597]
Drug Des Devel Ther. 2016 Aug 31;10:2759-70.
BACKGROUND: Chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on T helper type 2 (Th2) cell (CRTh2) receptor antagonists is being investigated for asthma. OBJECTIVES: The aim of this study was to assess the effects of the CRTh2 receptor antagonist, AZD1981 (with/without inhaled corticosteroids [ICSs]), on lung function and asthma control. PATIENTS AND METHODS: Adults aged 18-60 years were enrolled in two randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group trials (protocol number: D9830C00003 [study 1, n=209] and protocol number: D9830C00004 [study 2, n=510]). In study 1, patients with stable asthma (forced expiratory volume in 1 second [FEV1]: 65%-110%) were withdrawn from ICS (<400 microg/d) and randomized to AZD1981 1,000 mg twice daily (bid) or placebo. In study 2, patients with uncontrolled asthma (FEV1: 40%-85%) despite ICS therapy (>/=500 microg/d) were randomized to 50 mg, 400 mg, or 1,000 mg bid AZD1981 or placebo. The primary efficacy variable for both trials was the change in morning peak expiratory flow after 4 weeks of treatment. Secondary variables included Asthma Control Questionnaire (ACQ-5) scores, FEV1 assessments, safety, and tolerability. In study 2, efficacy was also assessed according to atopic status. RESULTS: Following 4 weeks of treatment, there was a nonsignificant increase in morning peak expiratory flow on AZD1981 1,000 mg bid (9.5 L/min vs placebo, P=0.086 [study 1] and 12 L/min vs placebo, P=0.16 [study 2]). In study 2, all doses of AZD1981 provided significant improvements in ACQ-5 scores (0.26-0.3 units vs placebo, P=0.010-0.022); however, there was no dose-response relationship. Improved ACQ-5 scores and FEV1 were observed in the majority of atopic patients treated with AZD1981. AZD1981 was well tolerated across treatment groups. CONCLUSION: Further research may be warranted in atopic patients to fully evaluate the clinical efficacy of AZD1981.
Efficacy and safety of AZD1981, a CRTH2 receptor antagonist, in patients with moderate to severe COPD.[Pubmed:23827726]
Respir Med. 2013 Nov;107(11):1722-30.
OBJECTIVE: To evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of the selective CRTh2 (DP2) receptor antagonist AZD1981 compared with placebo in patients with moderate to severe COPD. METHODS: In this multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, phase IIa study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT00690482) patients with moderate to severe COPD received either AZD1981 1000 mg twice daily or matching placebo for 4 weeks. Inhaled terbutaline was used as-needed as reliever medication throughout. The co-primary endpoints were change from baseline to end of treatment in pre-bronchodilator forced expiratory volume in 1 s [FEV1] and the Clinical COPD Questionnaire (CCQ). Additional endpoints included other lung function measures, 6-min walk test (6-MWT), COPD symptom score, reliever medication use and tolerability. RESULTS: 118 patients were randomised to treatment (AZD1981 n = 61; placebo n = 57); 83% of patients were male and the mean age was 63 years (range 43-83). There were no significant differences in the mean difference in change from baseline to end of treatment between AZD1981 and placebo for the co-primary endpoints of pre-bronchodilator FEV1 (AZD1981-placebo: -0.015, 95% CI: -0.10 to 0.070; p = 0.72) and CCQ total score (difference: 0.042, 95% CI: -0.21 to 0.30; p = 0.75). Similarly, no differences were observed between treatments for the other outcomes of lung function, COPD symptom score, 6-MWT, BODE index, and use of reliever medication. AZD1981 was well tolerated. CONCLUSION: There was no beneficial clinical effect of AZD1981, at a dose of 1000 mg twice daily for 4 weeks, in patients with moderate to severe COPD. AZD1981 was well tolerated and no safety concerns were identified.
An S-warfarin and AZD1981 interaction: in vitro and clinical pilot data suggest the N-deacetylated amino acid metabolite as the primary perpetrator.[Pubmed:27558866]
Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2017 Feb;83(2):381-392.
AIM: AZD1981 is an orally bioavailable chemoattractant receptor-homologous molecule expressed on Th2 cells (CRTh2) receptor antagonist progressed to phase II trials for the treatment of allergic asthma. Previously performed in vitro human hepatocyte incubations identified N-deacetylated AZD1981 as a primary metabolite. We report on metabolite exposure from a clinical excretion balance, on in vitro studies performed to determine the likelihood of a metabolite-dependent drug-drug interaction (DDI) and on a clinical warfarin DDI study. The aim was to demonstrate that N-deacetylated AZD1981 is responsible for the observed interaction. METHODS: The excretion and biotransformation of [(14) C]-AZD1981 were studied in healthy male volunteers, and subsequently in vitro cytochrome P450 (CYP) inhibition and hepatocyte uptake investigations were carried out with metabolites and the parent drug. A clinical DDI study using coadministered twice-daily 100 mg and 400 mg AZD1981 with 25 mg warfarin was performed. RESULTS: The excretion balance study showed N-deacetylated AZD1981 to be the most abundant metabolite present in plasma. In vitro data revealed the metabolite to be a weak CYP2C9 time-dependent inhibitor, subject to more active hepatic uptake than the parent molecule. Clinically, the S-warfarin area under the plasma concentration-time curve increased, on average, 1.4-fold [95% confidence interval (CI) 1.22, 1.50] and 2.4-fold (95% CI 2.11, 2.64) after 100 mg (n = 13) and 400 mg (n = 11) AZD1981 administration, respectively. In vitro CYP inhibition and hepatocyte uptake data were used to explain the interaction. CONCLUSIONS: N-deacetylated AZD1981 can be added to the small list of drug metabolites reported as sole contributors to clinical drug-drug interactions, with weak time-dependent inhibition exacerbated by efficient hepatic uptake being the cause.
Biochemical and pharmacological characterization of AZD1981, an orally available selective DP2 antagonist in clinical development for asthma.[Pubmed:23146091]
Br J Pharmacol. 2013 Apr;168(7):1626-38.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The discovery of DP2 as a second receptor for PGD2 has prompted the search for antagonists as potential novel therapies based on the associations between PGD2 and disease. Here we describe the biochemical and pharmacological properties of 4-(acetylamino)-3-[(4-chlorophenyl)thio]-2-methyl-1H-indole-1-acetic acid (AZD1981), a novel DP2 receptor antagonist. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Binding to DP2 , functional receptor pharmacology and selectivity were studied in both human and animal systems. KEY RESULTS: AZD1981 displaced radio-labelled PGD2 from human recombinant DP2 with high potency (pIC50 = 8.4). Binding was reversible, non-competitive and highly selective against a panel of more than 340 other enzymes and receptors, including DP1 (>1000-fold selective). AZD1981 inhibited DP2 -mediated shape change and CD11b up-regulation in human eosinophils, shape change in basophils and chemotaxis of human eosinophils and Th2 cells with similar potency. AZD1981 exhibited good cross-species binding activity against mouse, rat, guinea pig, rabbit and dog DP2 . Evaluation in mouse, rat or rabbit cell systems was not possible as they did not respond to DP2 agonists. Agonist responses were seen in guinea pig and dog, and AZD1981 blocked DP2 -mediated eosinophil shape change. Such responses were more robust in the guinea pig, where AZD1981 also blocked DP2 -dependent eosinophil emigration from bone marrow. CONCLUSIONS AND IMPLICATIONS: AZD1981 is a DP2 antagonist that blocks functional responses in eosinophils, Th2 cells and basophils. It exhibited similar potency irrespective of the cell type, DP2 agonist or species used. This selective orally active agent is currently under clinical evaluation as a potential therapeutic agent in respiratory diseases including asthma.


