AZD6738ATR inhibitor CAS# 1352226-88-0 |
- GDC-0623
Catalog No.:BCC4150
CAS No.:1168091-68-6
- Trametinib DMSO solvate
Catalog No.:BCC2013
CAS No.:1187431-43-1
- Pimasertib (AS-703026)
Catalog No.:BCC2529
CAS No.:1236699-92-5
- SL-327
Catalog No.:BCC1123
CAS No.:305350-87-2
- MEK162 (ARRY-162, ARRY-438162)
Catalog No.:BCC1148
CAS No.:606143-89-9
- Arctigenin
Catalog No.:BCN6291
CAS No.:7770-78-7
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 1352226-88-0 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 54761306 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C20H24N6O2S | M.Wt | 412.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | DMSO : ≥ 38 mg/mL (92.12 mM); | ||
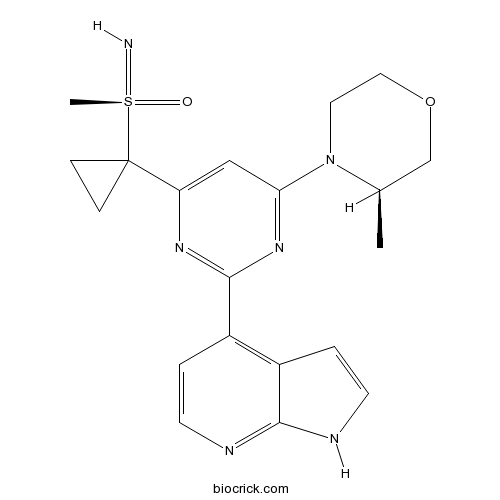
| Chemical Name | imino-methyl-[1-[6-[(3R)-3-methylmorpholin-4-yl]-2-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)pyrimidin-4-yl]cyclopropyl]-oxo-$l^{6}-sulfane | ||
| SMILES | CC1COCCN1C2=NC(=NC(=C2)C3(CC3)S(=N)(=O)C)C4=C5C=CNC5=NC=C4 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | OHUHVTCQTUDPIJ-JYCIKRDWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C20H24N6O2S/c1-13-12-28-10-9-26(13)17-11-16(20(5-6-20)29(2,21)27)24-19(25-17)15-4-8-23-18-14(15)3-7-22-18/h3-4,7-8,11,13,21H,5-6,9-10,12H2,1-2H3,(H,22,23)/t13-,29-/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | AZD6738 is a potent inhibitor of ATR kinase with an IC50 of 1 nM.In Vitro:AZD6738 is a potent inhibitor of ATR kinase activity with an IC50 of 0.001 μM against the isolated enzyme and 0.074 μM against ATR kinase-dependent CHK1 phosphorylation in cells. AZD6738 induces cell death and senescence in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cell lines. AZD6738 impairs viability of four Kras mutant cell lines: H23, H460, A549, and H358. , with the lowest GI50 and greatest maximal inhibition in H460 and H23 cells (1.05 μM, 88.0% and 2.38 μM, 86.2%, respectively). AZD6738 potentiates the cytotoxicity of cisplatin and gemcitabine in NSCLC cell lines with intact ATM kinase signaling, and potently synergizes with cisplatin in ATM-deficient NSCLC cells[1]. AZD6738 inhibits human breast cancer cell lines with IC50 values less than 1 μM using MTT assay. AZD6738 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. It downregulates DNA damage response molecules and cell proliferative signaling molecules[2].In Vivo:Daily administration of AZD6738 and ATR kinase inhibition for 14 consecutive days is tolerated in mice and enhances the therapeutic efficacy of cisplatin in xenograft models. Remarkably, the combination of cisplatin and AZD6738 resolves ATM-deficient lung cancer xenografts[1]. References: | |||||

AZD6738 Dilution Calculator

AZD6738 Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4242 mL | 12.1209 mL | 24.2418 mL | 48.4837 mL | 60.6046 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4848 mL | 2.4242 mL | 4.8484 mL | 9.6967 mL | 12.1209 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2424 mL | 1.2121 mL | 2.4242 mL | 4.8484 mL | 6.0605 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0485 mL | 0.2424 mL | 0.4848 mL | 0.9697 mL | 1.2121 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0242 mL | 0.1212 mL | 0.2424 mL | 0.4848 mL | 0.606 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
AZD6738 is a selective ATR (Ataxia Telangiectasia and RAD3-related) inhibitor, with an IC50 of approximately 30 uM to resting CLL cells [1] [2].
ATR is a PI3K-related kinase. It is involved in the repair of DNA damage. During cell division, it is recruited and activated at sites of single strand DNA breaks to help initiate DNA repair [1].
γH2AX acts as a biomarker of DNA damage. In an in vitro model capable of reproducing, over 70 hours after the initiation of the treatment with AZD6738, the γH2AX signal was sustained [1]. Stalled replication forks may collapse the formation of DNA double stranded breaks and the activation of the ataxia telangiectasia mutated (ATM) kinase. As a single agent across cancer cell line panels, AZD6738 is active. In cell lines lacking ATM-pathway, the sensitivity of AZD6738 was enhanced [3].
In ATM-deficient but not ATM-proficient in vivo models, treatment with AZD6738 alone significantly inhibited the activity of tumors in equivalent, tolerated doses. Ionizing radiation (IR) is a DNA damaging inducing agent. When AZD6738 and IR were used together, regression or anti-tumor growth inhibitory activity was observed. In tumor tissue, AZD6738 is associated with a persistent γH2AX staining increase. In normal gut tissue or bone marrow, treatment with AZD6738 only transiently increased the γH2AX staining [3].
References:
[1]. Choi MY, Fecteau JF, Brown J, et al. Induction of proliferation sensitizes chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells to apoptosis mediated by the ATR inhibitor AZD6738. Cancer Research, 2014, 74(19 Supplement): 5485-5485.
[2]. Checkley S, MacCallum L, Yates J, et al. Bridging the gap between in vitro and in vivo: Dose and schedule predictions for the ATR inhibitor AZD6738. Scientific reports, 2015, 5.
[3]. Guichard SM, Brown E, Odedra R, et al. The pre-clinical in vitro and in vivo activity of AZD6738: A potent and selective inhibitor of ATR kinase. Cancer Research, 2013, 73(8 Supplement): 3343-3343.
- Schineolignin B
Catalog No.:BCN3623
CAS No.:1352185-26-2
- AMG232
Catalog No.:BCC3992
CAS No.:1352066-68-2
- 3Beta-acetoxy-eupha-7,25-dien-24(R)-ol
Catalog No.:BCN1580
CAS No.:1352001-09-2
- Sanggenol P
Catalog No.:BCN4766
CAS No.:1351931-30-0
- H-Val-OtBu.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC3143
CAS No.:13518-40-6
- GNE-7915
Catalog No.:BCC5304
CAS No.:1351761-44-8
- HG-10-102-01
Catalog No.:BCC4271
CAS No.:1351758-81-0
- ONO-4059
Catalog No.:BCC6463
CAS No.:1351635-67-0
- 21,23:24,25-Diepoxy-21,23-dimethoxytirucall-7-en-3-one
Catalog No.:BCN1581
CAS No.:1351617-74-7
- Amooracetal
Catalog No.:BCN6876
CAS No.:1351617-73-6
- Sarpogrelate hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC5247
CAS No.:135159-51-2
- H-DL-Ala-OMe.HCl
Catalog No.:BCC2854
CAS No.:13515-97-4
- Pindolol
Catalog No.:BCC6881
CAS No.:13523-86-9
- Trijuganone C
Catalog No.:BCN3685
CAS No.:135247-94-8
- Pulchinenoside B
Catalog No.:BCN6554
CAS No.:135247-95-9
- EW-7197
Catalog No.:BCC6467
CAS No.:1352608-82-2
- 2''-O-Rhamnosylicariside II
Catalog No.:BCN3464
CAS No.:135293-13-9
- MEN 10376
Catalog No.:BCC7133
CAS No.:135306-85-3
- 8,8'-Bibaicalein
Catalog No.:BCN6549
CAS No.:135309-02-3
- 5,7,3',4'-Tetrahydroxy-3-methoxy-8,5'-diprenylflavone
Catalog No.:BCN6848
CAS No.:1353676-65-9
- Isojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7492
CAS No.:135378-08-4
- 4'-Hydroxyisojasminin
Catalog No.:BCN7383
CAS No.:135378-09-5
- 12alpha-Methoxygrandiflorenic acid
Catalog No.:BCN7771
CAS No.:135383-94-7
- 8-Prenyldaidzein
Catalog No.:BCN4711
CAS No.:135384-00-8
Anti-tumor activity of the ATR inhibitor AZD6738 in HER2 positive breast cancer cells.[Pubmed:27501113]
Int J Cancer. 2017 Jan 1;140(1):109-119.
Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) proteins are sensors of DNA damage, which induces homologous recombination (HR)-dependent repair. ATR is a master regulator of DNA damage repair (DDR), signaling to control DNA replication, DNA repair and apoptosis. Therefore, the ATR pathway might be an attractive target for developing new drugs. This study was designed to investigate the antitumor effects of the ATR inhibitor, AZD6738 and its underlying mechanism in human breast cancer cells. Growth inhibitory effects of AZD6738 against human breast cancer cell lines were studied using a 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium, MTT) assay. Cell cycle analysis, Western blotting, immunofluorescence and comet assays were also performed to elucidate underlying mechanisms of AZD6738 action. Anti-proliferative and DDR inhibitory effects of AZD6738 were demonstrated in human breast cancer cell lines. Among 13 cell lines, the IC50 values of nine cell lines were less than 1 mumol/L using MTT assay. Two cell lines, SK-BR-3 and BT-474, were chosen for further evaluation focused on human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive breast cancer cells. Sensitive SK-BR-3 but not the less sensitive BT-474 breast cancer cells showed increased level of apoptosis and S phase arrest and reduced expression levels of phosphorylated check-point kinase 1 (CHK1) and other repair markers. Decreased functional CHK1 expression induced DNA damage accumulation due to HR inactivation. AZD6738 showed synergistic activity with cisplatin. Understanding the antitumor activity and mechanisms of AZD6738 in HER2-positive breast cancer cells creates the possibility for future clinical trials targeting DDR in HER2-positive breast cancer treatment.
AZD6738, A Novel Oral Inhibitor of ATR, Induces Synthetic Lethality with ATM Deficiency in Gastric Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:28138034]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Apr;16(4):566-577.
Ataxia telangiectasia and Rad3-related (ATR) can be considered an attractive target for cancer treatment due to its deleterious effect on cancer cells harboring a homologous recombination defect. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential use of the ATR inhibitor, AZD6738, to treat gastric cancer.In SNU-601 cells with dysfunctional ATM, AZD6738 treatment led to an accumulation of DNA damage due to dysfunctional RAD51 foci formation, S phase arrest, and caspase 3-dependent apoptosis. In contrast, SNU-484 cells with functional ATM were not sensitive to AZD6738. Inhibition of ATM in SNU-484 cells enhanced AZD6738 sensitivity to a level comparable with that observed in SNU-601 cells, showing that activation of the ATM-Chk2 signaling pathway attenuates AZD6738 sensitivity. In addition, decreased HDAC1 expression was found to be associated with ATM inactivation in SNU-601 cells, demonstrating the interaction between HDAC1 and ATM can affect sensitivity to AZD6738. Furthermore, in an in vivo tumor xenograft mouse model, AZD6738 significantly suppressed tumor growth and increased apoptosis.These findings suggest synthetic lethality between ATR inhibition and ATM deficiency in gastric cancer cells. Further clinical studies on the interaction between AZD 6738 and ATM deficiency are warranted to develop novel treatment strategies for gastric cancer. Mol Cancer Ther; 16(4); 566-77. (c)2017 AACR.
Radiosensitization by the ATR Inhibitor AZD6738 through Generation of Acentric Micronuclei.[Pubmed:28062704]
Mol Cancer Ther. 2017 Jan;16(1):25-34.
AZD6738 is an orally active ATR inhibitor (ATRi) currently in phase I clinical trials. We found in vitro growth inhibitory activity of this ATRi in a panel of human cancer cell lines. We demonstrated radiosensitization by AZD6738 to single radiation fractions in multiple cancer cell lines independent of both p53 and BRCA2 status by the clonogenic assay. Radiosensitization by AZD6738 to clinically relevant doses of fractionated radiation was demonstrated in vitro using a 3D tumor spheroid model and, in vivo, AZD6738 radiosensitized by abrogating the radiation-induced G2 cell-cycle checkpoint and inhibiting homologous recombination. Mitosis with damaged DNA resulted in mitotic catastrophe as measured by micronucleus formation by live-cell fluorescent-ubiquitination cell-cycle imaging of cell-cycle progression and nuclear morphology. Induction of micronuclei was significantly more prominent for AZD6738 compared with inhibition of the downstream kinase CHK1 alone at isoeffective doses. Micronuclei were characterized as acentric chromosomal fragments, which displayed characteristics of increased DNA damage and cell-cycle dyssynchrony when compared with the primary nucleus. Mol Cancer Ther; 16(1); 25-34. (c)2016 AACR.
LC-MS/MS assay for the simultaneous quantitation of the ATM inhibitor AZ31 and the ATR inhibitor AZD6738 in mouse plasma.[Pubmed:28213176]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 May 10;138:158-165.
The ATM kinase inhibitor AZ31 and ATR kinase inhibitor AZD6738 are in various phases of preclinical and clinical evaluation for their ability to potentiate chemoradiation. To support the preclinical evaluation of their pharmacokinetics, we developed and validated an LC-MS/MS assay for the simultaneous quantification of AZ31 and AZD6738 in mouse plasma. A "dilute and shoot" method was used to precipitate proteins from a sample volume of 50muL. Chromatographic separation was achieved using a Phenomenex Polar-RP column and a gradient mobile phase consisting of methanol-water with 0.1% formic acid. Detection was accomplished using a Waters Quattro Micro mass spectrometer in positive ionization mode. The assay utilizing 50muL sample was linear from 10 to 5000ng/mL and determined to be both accurate (-8.2 to 8.6%) and precise (<5.4% CV) and achieved the criteria for U.S. FDA guidance for bioanalytical method validation. Quantification was achieved in mouse tissue homogenate using a separate 200muL sample preparation. This LC-MS/MS assay will be essential for determining the tissue distribution and pharmacokinetics in future mouse studies.


