Ac-YVAD-CHOCAS# 143313-51-3 |
- Amyloid β-Protein (1-15)
Catalog No.:BCC1003
CAS No.:183745-81-5
- Beta-Amyloid (1-11)
Catalog No.:BCC1002
CAS No.:190436-05-6
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 143313-51-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 3034818 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H32N4O8 | M.Wt | 492.5 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO | ||
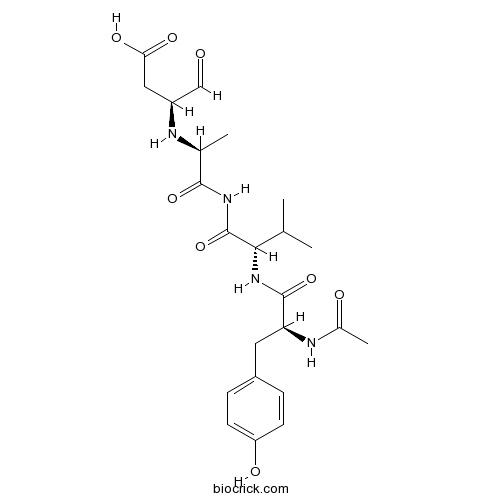
| Chemical Name | (3S)-3-[[(2S)-1-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-acetamido-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]-3-methylbutanoyl]amino]-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-4-oxobutanoic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC(C)C(C(=O)NC(=O)C(C)NC(CC(=O)O)C=O)NC(=O)C(CC1=CC=C(C=C1)O)NC(=O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KQCBPHUOVBKBPQ-SJVNDZIOSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H32N4O8/c1-12(2)20(23(35)27-21(33)13(3)24-16(11-28)10-19(31)32)26-22(34)18(25-14(4)29)9-15-5-7-17(30)8-6-15/h5-8,11-13,16,18,20,24,30H,9-10H2,1-4H3,(H,25,29)(H,26,34)(H,31,32)(H,27,33,35)/t13-,16-,18-,20-/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ac-YVAD-CHO Dilution Calculator

Ac-YVAD-CHO Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0305 mL | 10.1523 mL | 20.3046 mL | 40.6091 mL | 50.7614 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4061 mL | 2.0305 mL | 4.0609 mL | 8.1218 mL | 10.1523 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.203 mL | 1.0152 mL | 2.0305 mL | 4.0609 mL | 5.0761 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0406 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.4061 mL | 0.8122 mL | 1.0152 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0203 mL | 0.1015 mL | 0.203 mL | 0.4061 mL | 0.5076 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
Ac-YVAD-CHO
- H-Chg-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3162
CAS No.:14328-51-9
- RA-XI
Catalog No.:BCN3514
CAS No.:143277-27-4
- AGI-6780
Catalog No.:BCC1331
CAS No.:1432660-47-3
- LDN-212854
Catalog No.:BCC5330
CAS No.:1432597-26-6
- Tin protoporphyrin IX dichloride
Catalog No.:BCC6776
CAS No.:14325-05-4
- Microstegiol
Catalog No.:BCN3157
CAS No.:143246-41-7
- (-)-Isolariciresinol 9'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7708
CAS No.:143236-04-8
- (-)-Lyoniresinol 9'-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN7037
CAS No.:143236-02-6
- Z-2-Nal-OH
Catalog No.:BCC3291
CAS No.:143218-10-4
- Dehydroadynerigenin beta-neritrioside
Catalog No.:BCN4706
CAS No.:143212-60-6
- 7-Geranyloxy-5-methoxycoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN5806
CAS No.:1432075-68-7
- (Z)-3-Hydroxy-5-methoxystilbene
Catalog No.:BCN6688
CAS No.:143207-76-5
- UNC 2400
Catalog No.:BCC5625
CAS No.:1433200-49-7
- RS 56812 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6877
CAS No.:143339-12-2
- SMIP004
Catalog No.:BCC1955
CAS No.:143360-00-3
- Bryostatin 3
Catalog No.:BCC5620
CAS No.:143370-84-7
- Naratriptan
Catalog No.:BCC5053
CAS No.:143388-64-1
- SAR131675
Catalog No.:BCC5097
CAS No.:1433953-83-3
- (Arg)9 peptide
Catalog No.:BCC5336
CAS No.:143413-47-2
- Poriol
Catalog No.:BCN6816
CAS No.:14348-16-4
- Cnidilin
Catalog No.:BCN2731
CAS No.:14348-22-2
- 5,8-Dihydroxypsoralen
Catalog No.:BCC8104
CAS No.:14348-23-3
- LOE 908 hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC7327
CAS No.:143482-60-4
- Emtricitabine
Catalog No.:BCC3774
CAS No.:143491-57-0
Targeting caspase-1 by inhalation-therapy: effects of Ac-YVAD-CHO on IL-1 beta, IL-18 and downstream proinflammatory parameters as detected in rat endotoxaemia.[Pubmed:17384935]
Intensive Care Med. 2007 May;33(5):863-871.
OBJECTIVE: We set out to investigate whether the nebulized and inhaled specific caspase-1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO has the potential to attenuate the pulmonary and systemic release of the caspase-1-dependent cytokines interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) and interleukin-18 (IL-18) as well as their downstream enzymes iNOS and COX-2 in rat experimental endotoxaemia. DESIGN AND SETTING: Controlled, randomized animal study in a university research facility. SUBJECT: Male Sprague-Dawley rats (n=32) were randomly treated as follows: Inhaled Ac-YVAD-CHO was administered in eight rats at a inhaled total dosage of 5 mg and in eight rats at a inhaled total dose of 0.5 mg before infusion of lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 5 mg/kg, i.v.). Eight animals received LPS only. Eight animals served as controls without endotoxaemia. MEASUREMENTS AND RESULTS: After 4h of endotoxaemia, levels of IL-1 beta, IL-18 and TNF-alpha in plasma and bronchoalveolar fluid (BALF) were analyzed. Nitric oxide (NO) release from alveolar macrophages was measured by Griess assay. Amounts of iNOS protein in alveolar macrophages and COX-2 protein in lung homogenates were determined by Western blotting. Significant reductions in release of IL-1 beta (-58%, p<0.05) and IL-18 (-51%, p<0.05) in plasma and IL-1 beta (-59%, p<0.05) in BALF were found in animals pretreated with inhaled caspase-1 inhibitor compared with animals without therapy. Expression of iNOS in alveolar macrophages and COX-2 in lung tissue was concurrently decreased in the treatment groups compared with control animals. CONCLUSIONS: Our data demonstrate that administration of the caspase-1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO by inhalation is able to reduce the pulmonary and systemic release of proinflammatory mediators in rat endotoxaemia. These results further underscore that inhalation may constitute an effective route of anti-inflammatory drug administration, beneficial in the clinical setting of ARDS.
Caspase-1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO attenuates quinolinic acid-induced increases in p53 and apoptosis in rat striatum.[Pubmed:15663890]
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2005 Feb;26(2):150-4.
AIM: To study the effects of the caspase-1 inhibitor Ac-YVAD-CHO on quinolinic acid (QA)-induced apoptosis. METHODS: Rats were pre-treated with intrastriatal infusion of Ac-YVAD-CHO (2-8 microg) before intrastriatal injection of QA (60 nmol). Striatal total proteins, genomic DNA, and nuclear proteins were isolated. The effects of Ac-YVAD-CHO on QA-induced caspase-1 activity, internucleosomal DNA fragmentation, IkappaB-alpha degradation, NF-kappaB, and AP-1 activation, and increases in p53 protein levels were measured with enzyme assays, agarose gel electrophoresis, electrophoresis mobility shift assays, and Western blot analysis. RESULTS: Pre-treatment with Ac-YVAD-CHO inhibited QA-induced internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Ac-YVAD-CHO inhibited QA-induced increases in caspase-1 activity and p53 protein levels, but had no effect on QA-induced IkappaB-alpha degradation, NF-kappaB or AP-1 activation. CONCLUSION: Caspase-1 is involved in QA-induced p53 upregulation but not IkappaB-alpha degradation. Inhibition of caspase-1 attenuates QA-induced apoptosis in rat striatum.


