AegelineCAS# 456-12-2 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 456-12-2 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 15558419 | Appearance | White powder |
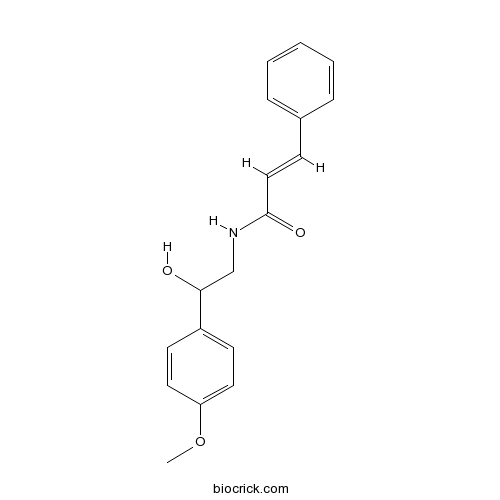
| Formula | C18H19NO3 | M.Wt | 297.4 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Synonyms | Egeline | ||
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO; sparingly soluble in water | ||
| Chemical Name | (E)-N-[2-hydroxy-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)ethyl]-3-phenylprop-2-enamide | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)C(CNC(=O)C=CC2=CC=CC=C2)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | QRFDENJATPJOKG-KPKJPENVSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C18H19NO3/c1-22-16-10-8-15(9-11-16)17(20)13-19-18(21)12-7-14-5-3-2-4-6-14/h2-12,17,20H,13H2,1H3,(H,19,21)/b12-7+ | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Aegeline has anti-diabetic and anti-dyslipidemic activities, it inspired synthesis of novel amino alcohol and thiazolidinedione hybrids with antiadipogenic activity in 3T3-L1 cells, it also inspired synthesis of novel β3-AR agonist improves insulin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo models of insulin resistance. Aegeline mimics the yeast SNARE protein Sec22p in suppressing α-synuclein and Bax toxicity in yeast. |
| Targets | PPARγ | C/EBPα | FAS | hMSCs |
| In vitro | Aegeline, a natural product from the plant Aegle marmelos, mimics the yeast SNARE protein Sec22p in suppressing α-synuclein and Bax toxicity in yeast.[Pubmed: 30579794 ]Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Feb 1;29(3):454-460.Herein, we have identified yeast Sec22p (ySec22p), a SNARE protein essential for endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi trafficking, as a suppressor of Bax-induced yeast apoptosis and corroborated published observations that ySec22p suppresses α-synuclein's toxicity in yeast. It has been suggested that compounds which enhance expression, in neurons, of human homologues of ySec22p (Sec22Bp/Sec22p/Sec22A) would prevent synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's disease. Aegeline inspired synthesis of novel amino alcohol and thiazolidinedione hybrids with antiadipogenic activity in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed: 29220798 ]Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:780-791.Excess adiposity is a hallmark of obesity, which is caused due to an imbalance between energy intake and energy consumed. Obesity is often associated with several metabolic disorders like dyslipidemia, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Earlier, our group had reported natural product Aegeline (amino-alcohol) isolated from the plant Aegle marmelos as an anti-diabetic and anti-dyslipidemic compound. |
| In vivo | Aegeline inspired synthesis of novel β3-AR agonist improves insulin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo models of insulin resistance.[Pubmed: 29524448 ]Metabolism. 2018 Aug;85:1-13.In our drug discovery program of natural product, earlier we have reported Aegeline that is N-acylated-1-amino-2- alcohol, which was isolated from the leaves of Aeglemarmelos showed anti-hyperlipidemic activity for which the QSAR studies predicted the compound to be the β3-AR agonist, but the mechanism of its action was not elucidated. In our present study, we have evaluated the β3-AR activity of novel N-acyl-1-amino-3-arylopropanol synthetic mimics of Aegeline and its beneficial effect in insulin resistance. In this study, we have proposed the novel pharmacophore model using reported molecules for antihyperlipidemic activity. The reported pharmacophore features were also compared with the newly developed pharmacophore model for the observed biological activity.
|

Aegeline Dilution Calculator

Aegeline Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3625 mL | 16.8124 mL | 33.6247 mL | 67.2495 mL | 84.0619 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.6725 mL | 3.3625 mL | 6.7249 mL | 13.4499 mL | 16.8124 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.3362 mL | 1.6812 mL | 3.3625 mL | 6.7249 mL | 8.4062 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0672 mL | 0.3362 mL | 0.6725 mL | 1.345 mL | 1.6812 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0336 mL | 0.1681 mL | 0.3362 mL | 0.6725 mL | 0.8406 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8872
CAS No.:83883-10-7
- Quercetin 3-O-sophoroside-7-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8871
CAS No.:64828-40-6
- N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin
Catalog No.:BCN8870
CAS No.:68573-24-0
- Emodin-1-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN8869
CAS No.:849789-95-3
- Cassiaside B
Catalog No.:BCN8868
CAS No.:119170-51-3
- Piperlonguminine
Catalog No.:BCN8867
CAS No.:5950-12-9
- 7-Ethoxyrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN8866
CAS No.:111200-01-2
- 5,7,3',4',5'-Pentamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8865
CAS No.:53350-26-8
- Isorhamnetin 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8864
CAS No.:6743-96-0
- 7-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN8863
CAS No.:2445-83-2
- Isoarnebin I
Catalog No.:BCN8862
CAS No.:24502-79-2
- Pangelin
Catalog No.:BCN8861
CAS No.:33783-80-1
- Caulophyllogenin
Catalog No.:BCN8874
CAS No.:52936-64-8
- N-trans-Sinapoyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCN8875
CAS No.:200125-11-7
- Sanguisorbigenin
Catalog No.:BCN8876
CAS No.:6812-98-2
- Benzoylgomisin P
Catalog No.:BCN8803
CAS No.:129445-43-8
- Silyamandin
Catalog No.:BCN8804
CAS No.:1009565-36-9
- (+)-δ-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCN8805
CAS No.:119-13-1
- 6-Hydroxykaempferol 3-beta-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8807
CAS No.:205527-00-0
- Syringetin-3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8819
CAS No.:53430-50-5
- Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside-1-2-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8820
CAS No.:55696-57-6
- (3R)-5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-(4'-hydroxybenzyl)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN8842
CAS No.:84638-48-2
- Loureiriol
Catalog No.:BCN8843
CAS No.:479195-44-3
- Hydroxy-γ-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8849
CAS No.:78886-66-5
LOX-1, the Common Therapeutic Target in Hypercholesterolemia: A New Perspective of Antiatherosclerotic Action of Aegeline.[Pubmed:31885819]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2019 Nov 30;2019:8285730.
Background: Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 (LOX-1) is the major receptor for oxidized low-density lipoprotein (Ox-LDL) in the aorta of aged rats. Ox-LDL initiates LOX-1 activation in the endothelium of lipid-accumulating sites of both animal and human subjects of hypercholesterolemia. Targeting LOX-1 may provide a novel diagnostic strategy towards hypercholesterolemia and vascular diseases. Hypothesis: This study was planned to address whether Aegeline (AG) could bind to LOX-1 with a higher affinity and modulate the uptake of Ox-LDL in hypercholesterolemia. Study Design: Thirty-six Wistar rats were divided into six groups. The pathology group rats were fed with high-cholesterol diet (HCD) for 45 days, and the treatment group rats were fed with HCD and Aegeline/atorvastatin (AV) for the last 30 days. In vivo and in vitro experiments were carried out to assay the markers of atherosclerosis like Ox-LDL and LOX-1 levels. Histopathological examination was performed. Oil Red O staining was carried out in the IC-21 cell line. Docking studies were performed. Results: AG administration effectively brought down the lipid levels induced by HCD. The lowered levels of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in AG-administered rats deem it to be a potent antihypercholesterolemic agent. Compared to AV, AG had a pronounced effect in downregulating the expression of lipids evidenced by Oil Red O staining. AG binds with LOX-1 at a higher affinity validated by docking. Conclusion: This study validates AG to be an effective stratagem in bringing down the lipid stress induced by HCD and can be deemed as an antihypercholesterolemic agent.
Pharmacokinetics and Tissue Distribution of Aegeline after Oral Administration in Mice.[Pubmed:30754052]
Planta Med. 2019 Apr;85(6):491-495.
Aegeline is claimed to be a biologically active constituent of Aegle marmelos. Preclinical studies have reported possible therapeutic potential for Aegeline against obesity and diabetes. In recent years, Aegeline has been added to several weight loss products. However, the consumption of Aegeline-containing supplements such as OxyELITE Pro and VERSA-1 has been linked to multiple cases of acute and chronic liver failure. This study was carried out to evaluate the pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of Aegeline in ND4 mice. Two doses of Aegeline, a human equivalent dose (1x) 30 mg/kg and a 10x dose (300 mg/kg), were orally administered to the mice, and blood and tissue samples were collected over 8 h. The quantitative analysis of plasma and tissue homogenates (liver, kidney, and brain) was done by UHPLC-QTOF to determine Aegeline concentrations. The peak plasma level of Aegeline was achieved at a Tmax of 0.5 h, indicating its rapid absorption from the gastrointestinal tract. Aegeline was not detected in the plasma at 8 h after oral administration, with a half-life of 1.4 +/- 0.01 and 1.3 +/- 0.07 h for the 30 and 300 mg/kg doses, respectively. The half-life of Aegeline in the liver was 1.2 h and 1.7 h for 30 and 300 mg/kg doses, respectively, with a Tmax of 1.9 h, which indicates relatively fast elimination of Aegeline from the liver.
Aegeline, a natural product from the plant Aegle marmelos, mimics the yeast SNARE protein Sec22p in suppressing alpha-synuclein and Bax toxicity in yeast.[Pubmed:30579794]
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019 Feb 1;29(3):454-460.
Herein, we have identified yeast Sec22p (ySec22p), a SNARE protein essential for endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi trafficking, as a suppressor of Bax-induced yeast apoptosis and corroborated published observations that ySec22p suppresses alpha-synuclein's toxicity in yeast. It has been suggested that compounds which enhance expression, in neurons, of human homologues of ySec22p (Sec22Bp/Sec22p/Sec22A) would prevent synucleinopathies, such as Parkinson's disease. With the aim of finding a small molecule that would mimic ySec22p, a library of natural products consisting of 394-compounds was screened using yeast cells that express either human alpha-synuclein or human Bax. The antioxidant Aegeline, an alkaloid-amide occurring in the leaves of the plant Aegle marmelos Correa, was the only molecule that overcame apoptosis induced by both alpha-synuclein and Bax in yeast. Besides, Aegeline also prevented growth block in cells expressing the more toxic A53T alpha-synuclein mutant. Restoration of cell growth occurred through inhibition of increased ROS levels, mitochondrial membrane potential loss and nuclear DNA fragmentation, characteristics of apoptosis manifested in alpha-synuclein or Bax-expressing cells. These results highlight the importance of yeast systems to identify rapidly molecules that may prevent the onset of apoptosis that occurs in Parkinson's disease.
Aegeline inspired synthesis of novel beta3-AR agonist improves insulin sensitivity in vitro and in vivo models of insulin resistance.[Pubmed:29524448]
Metabolism. 2018 Aug;85:1-13.
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: In our drug discovery program of natural product, earlier we have reported Aegeline that is N-acylated-1-amino-2- alcohol, which was isolated from the leaves of Aeglemarmelos showed anti-hyperlipidemic activity for which the QSAR studies predicted the compound to be the beta3-AR agonist, but the mechanism of its action was not elucidated. In our present study, we have evaluated the beta3-AR activity of novel N-acyl-1-amino-3-arylopropanol synthetic mimics of Aegeline and its beneficial effect in insulin resistance. In this study, we have proposed the novel pharmacophore model using reported molecules for antihyperlipidemic activity. The reported pharmacophore features were also compared with the newly developed pharmacophore model for the observed biological activity. EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH: Based on 3D pharmacophore modeling of known beta3AR agonist, we screened 20 synthetic derivatives of Aegeline from the literature. From these, the top scoring compound 10C was used for further studies. The in-slico result was further validated in HEK293T cells co-trransfected with human beta3-AR and CRE-Luciferase reporter plasmid for beta3-AR activity.The most active compound was selected and beta3-AR activity was further validated in white and brown adipocytes differentiated from human mesenchymal stem cells (hMSCs). Insulin resistance model developed in hMSC derived adipocytes was used to study the insulin sensitizing property. 8week HFD fed C57BL6 mice was given 50mg/Kg of the selected compound and metabolic phenotyping was done to evaluate its anti-diabetic effect. RESULTS: As predicted by in-silico 3D pharmacophore modeling, the compound 10C was found to be the most active and specific beta3-AR agonist with EC50 value of 447nM. The compound 10C activated beta3AR pathway, induced lipolysis, fatty acid oxidation and increased oxygen consumption rate (OCR) in human adipocytes. Compound 10C induced expression of brown adipocytes specific markers and reverted chronic insulin induced insulin resistance in white adipocytes. The compound 10C also improved insulin sensitivity and glucose tolerance in 8week HFD fed C57BL6 mice. CONCLUSION: This study enlightens the use of in vitro insulin resistance model close to human physiology to elucidates the insulin sensitizing activity of the compound 10C and edifies the use of beta3AR agonist as therapeutic interventions for insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Aegeline inspired synthesis of novel amino alcohol and thiazolidinedione hybrids with antiadipogenic activity in 3T3-L1 cells.[Pubmed:29220798]
Eur J Med Chem. 2018 Jan 1;143:780-791.
Excess adiposity is a hallmark of obesity, which is caused due to an imbalance between energy intake and energy consumed. Obesity is often associated with several metabolic disorders like dyslipidemia, cardiovascular diseases and type 2 diabetes. Earlier, our group had reported natural product Aegeline (amino-alcohol) isolated from the plant Aegle marmelos as an anti-diabetic and anti-dyslipidemic compound. With this background, we synthesized a series of novel amino alcohol and thiazolidinedione hybrid molecules and studied their antiadipogenic activity. As a result, we have identified a potent hybrid compound 12c as an inhibitor of adipocyte differentiation. The compound 12c inhibits lipid accumulation and adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocyte cell line. Exposure of compound 12c blocks mitotic clonal expansion and arrests cells in S-phase of cell cycle. Detailed analysis showed that compound 12c decreases expression of two major transcription factors that are involved in adipocyte differentiation, PPARgamma, C/EBPalpha, and other adipogenesis associated genes like aP2 and FAS. Thus, we concluded that compound 12c shows potential ability to inhibit adipocyte differentiation which can be used therapeutically for the treatment of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders.
Lipid lowering agents of natural origin: An account of some promising chemotypes.[Pubmed:28987600]
Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Nov 10;140:331-348.
The role of natural products in the drug development and discovery has been phenomenal. There has been an enormous interest in exploring all possible natural sources to identify structures exhibiting pronounced hypolipidemic activity albeit with no toxicity. The present review describes the profile of some interesting naturally occurring compounds and their derivatives as potential hypolipidemic agents. Some of the interesting natural chemotypes that can control the increased levels of plasma lipids and discussed in this review are compactin, lovastatin, gugglesterone, berberine, lupeol, phytol, polyprenol, Aegeline, 4-hydroxyisoleucine, alpha-asarone, resveratrol, esculeoside A, swertiamarin, rutin, saucerneol B, curcumin and a clerodane diterpene.
Overview of regulation of dietary supplements in the USA and issues of adulteration with phenethylamines (PEAs).[Pubmed:27259162]
Drug Test Anal. 2017 Mar;9(3):500-517.
The multi-billion dollar dietary supplement industry is global in reach. The industry has been criticized for problems related to poor quality control, safety, misbranding, and adulteration. In this review, we describe how the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates dietary supplements within the framework of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C Act). The Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA), which amended the FD&C Act, gave the FDA the authority to promulgate Good Manufacturing Practices for dietary supplements and required that manufacturers provide the FDA information supporting a conclusion that the ingredients are reasonably expected to be safe if the dietary ingredients were not marketed in the USA before 15 October 1994. Recent amendments to the FD&C Act require that serious dietary-supplement-related adverse events be reported to the FDA and provide the agency with mandatory recall authority. We discuss the presence of naturally occurring (e.g. Ephedra, Citrus aurantium, Acacia) and synthetic (e.g. beta-methylphenethylamines, methylsynephrine, alpha-ethyl-phenethylamine) biologically active phenethylamines (PEAs) in dietary supplements and of PEA drugs (e.g. clenbuterol, fenfluramine, sibutramine, lorcaserin) in weight-loss products. Regulatory actions against manufacturers of products labelled as dietary supplements that contain the aliphatic amines 1,3-dimethylamine and 1,3-dimethylbutylamine, and PEAs such as beta-methylphenethylamine, Aegeline, and Dendrobium illustrate the FDA's use of its authority under the FD&C Act to promote dietary supplement safety. Published 2016. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Simultaneous Determination of Aegeline and Six Coumarins from Different Parts of the Plant Aegle marmelos Using UHPLC-PDA-MS and Chiral Separation of Aegeline Enantiomers Using HPLC-ToF-MS.[Pubmed:27054911]
Planta Med. 2016 Apr;82(6):580-8.
A fast UHPLC-PDA method was developed for the simultaneous analysis of one alkaloid, Aegeline, and six coumarins, viz., umbelliferone, scopoletin, marmesinin, 8-hydroxypsoralen, angelicin, and marmelosin, from the leaf, fruit, root, and bark of Aegle marmelos. The UHPLC method was validated for linearity, accuracy, repeatability, limits of detection and limits of quantification. The linearity range (r(2) > 0.99) of the seven compounds was found to be 0.5-250 microg/mL, and the limits of detection and limits of quantification for the seven compounds were found to be 0.1 and 0.5 microg/mL, respectively. The developed UHPLC method is simple, fast, and especially suitable for quality control analysis of coumarins and Aegeline from A. marmelos and commercial dietary supplements. Single quadrupole mass spectrometry was used for the identification and confirmation of coumarins and Aegeline from different plant parts and dietary supplements. In addition, a novel chiral HPLC-ToF-MS method was developed for the resolution of Aegeline enantiomers. By applying this chiral method, the distribution of enantiomers of Aegeline from different parts of A. marmelos and Aegeline-containing dietary supplements is reported for the first time.
Two new cytotoxic furoquinoline alkaloids isolated from Aegle marmelos (Linn.) Correa.[Pubmed:26729368]
Nat Prod Res. 2016 Nov;30(22):2559-2566.
Two new cytotoxic furoquinoline alkaloids were isolated from the leaves of Aegle marmelos (Linn.) Correa; one from the total alkaloidal fraction (acid/base shake-out method) of the CHCl3 extract and identified as 7,8-dihydroxy-4-hydrofuroquinoline and named trivially as Aegelbine-A. The other new alkaloid isolated from the pet. ether extract and identified as 4-hydro-7-hydroxy-8-prenyloxyfuroquinoline and named trivially as Aegelbine-B, together with a known alkaloid; Aegeline and a known phenolic acid; rho-hydroxybenzoic acid. The structures of all the isolated compounds were established based on 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy and HR-ESI/MS. The cytotoxic activity of the isolated compounds was evaluated in vitro against HepG-2, PC3, A549 and MCF-7 cell lines. The obtained results revealed promising activity with structure-based relationship which is discussed briefly.
The Role of Adverse Event Reporting in the FDA Response to a Multistate Outbreak of Liver Disease Associated with a Dietary Supplement.[Pubmed:26327730]
Public Health Rep. 2015 Sep-Oct;130(5):526-32.
OBJECTIVE: Liver disease is a potential complication from using dietary supplements. This study investigated an outbreak of non-viral liver disease associated with the use of OxyELITE Pro(TM), a dietary supplement used for weight loss and/or muscle building. METHODS: Illness details were ascertained from MedWatch reports submitted to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) describing consumers who ingested OxyELITE Pro alone or in combination with other dietary supplements. FDA's Forensic Chemistry Center analyzed samples of OxyELITE Pro. RESULTS: From February 2012 to February 2014, FDA received 114 reports of adverse events of all kinds involving consumers who ingested OxyELITE Pro. The onset of illness for the first report was December 2010 and for the last report was January 2014. Thirty-three states, two foreign nations, and Puerto Rico submitted reports. Fifty-five of the reports (48%) described liver disease in the absence of viral infection, gallbladder disease, autoimmune disease, or other known causes of liver damage. A total of 33 (60%) of these patients were hospitalized, and three underwent liver transplantation. In early 2013, OxyELITE Pro products entered the market with a formulation distinct from products sold previously. The new formulation replaced 1,3-dimethylamylamine with Aegeline. However, the manufacturer failed to submit to FDA a required "new dietary ingredient" notice for the use of Aegeline in OxyELITE Pro products. Laboratory analysis identified no drugs, poisons, pharmaceuticals, toxic metals, usnic acid, N-Nitroso-fenfluramine, pyrrolizidine alkaloids, aristocholic acid, or phenethylamines in the products. CONCLUSIONS: Vigilant surveillance is required for adverse events linked to the use of dietary supplements.
Inhibition of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 by Aegle marmelos and its constituents.[Pubmed:26247834]
Xenobiotica. 2016;46(2):117-25.
1. Aegle marmelos (bael) is a popular tree in India and other Southeast Asian countries. The fruit is usually consumed as dried, fresh or juice, and is reported to have a high nutritional value and many perceived health benefits. Despite its edible nature and therapeutic properties, no studies are reported regarding its effects on major drug metabolizing enzymes. 2. This study was aimed to evaluate the inhibitory potential of methanolic extract of A. marmelos fruit and its constituents (three furanocoumarins, namely marmelosin, marmesinin and 8-hydroxypsoralen, and 1 alkaloid, Aegeline) towards major Cytochrome P450 enzymes (CYP3A4, 2D6, 1A2, 2C9 and 2C19) using human liver microsomes and recombinant CYPs. 3. The methanolic extract and marmelosin was found to be competitive and time-dependant inhibitor of CYP3A4. While reversible and non-competitive inhibition was observed for CYP1A2. Time-dependent inhibition of CYP3A4 was not affected by the addition of reduced glutathione. Marmesinin showed moderate inhibition of CYP3A4 and 1A2, while Aegeline was a very weak inhibitor of CYP3A4 and showed no inhibition for CYP1A2 isoform. No significant inhibition of recombinant CYP2D6, 2C9, and 2C19 was seen with the extract or its constituents. 4. This is the first report of CYP3A4 and CYP1A2 inhibition by A. marmelos extract and one of its furanocoumarins, marmelosin. Further studies are warranted to determine if acute or prolonged use of bael fruit could affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs that are substrates of CYP3A4 or CYP1A2.
Aegeline from Aegle marmelos stimulates glucose transport via Akt and Rac1 signaling, and contributes to a cytoskeletal rearrangement through PI3K/Rac1.[Pubmed:26102565]
Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Sep 5;762:419-29.
Aegeline is an alkaloidal-amide, isolated from the leaves of Aegle marmelos and have shown antihyperglycemic as well as antidyslipidemic activities in the validated animal models of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Here we delineate, Aegeline enhanced GLUT4 translocation mediated 2-deoxy-glucose uptake in both time and concentration-dependent manner. 2-deoxy-glucose uptake was completely stymied by the transport inhibitors (wortmannin and genistein) in C2C12 myotubes. Pharmacological inhibition of Akt (also known as protein kinase B) and Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) suggest that both Akt and Rac1 operate Aegeline-stimulated glucose transport via distinct parallel pathways. Moreover, Aegeline activates p21 protein-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and cofilin (an actin polymerization regulator). Rac1 inhibitor (Rac1 inhib II) and PAK1 inhibitor (IPA-3) completely blocked Aegeline-induced phosphorylation of cofilin and p21 protein-activated kinase 1 (PAK1). In summary, these findings suggest that Aegeline stimulates the glucose transport through Akt and Rac1 dependent distinct parallel pathways and have cytoskeletal roles via stimulation of the PI3-kinase-Rac1-PAK1-cofilin pathway in the skeletal muscle cells. Therefore, multiple targets of Aegeline in the improvement of insulin sensitivity of the skeletal muscle cells may be suggested.


