CaulophyllogeninCAS# 52936-64-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
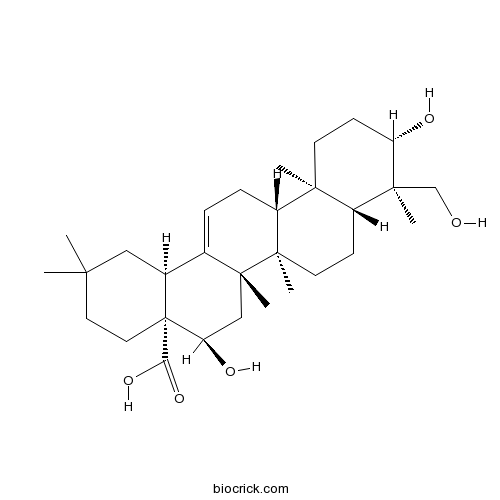
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 52936-64-8 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 104361 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C30H48O5 | M.Wt | 488.7 |
| Type of Compound | Triterpenoids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (4aR,5R,6aR,6aS,6bR,8aR,9R,10S,12aR,14bS)-5,10-dihydroxy-9-(hydroxymethyl)-2,2,6a,6b,9,12a-hexamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,7,8,8a,10,11,12,13,14b-tetradecahydropicene-4a-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2(C(C1)C3=CCC4C5(CCC(C(C5CCC4(C3(CC2O)C)C)(C)CO)O)C)C(=O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | FABOBEOYNMHSHB-UAWZMHPWSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C30H48O5/c1-25(2)13-14-30(24(34)35)19(15-25)18-7-8-21-26(3)11-10-22(32)27(4,17-31)20(26)9-12-28(21,5)29(18,6)16-23(30)33/h7,19-23,31-33H,8-17H2,1-6H3,(H,34,35)/t19-,20+,21+,22-,23+,26-,27-,28+,29+,30+/m0/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | Caulophyllogenin in the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, including IL-12 p40, IL-6, and TNF-α, and for prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases. |
| Targets | TNF-α | IL Recepter |
| In vitro | Inhibitory effects of oleanane-type triterpenes and saponins from the stem bark of Kalopanax pictus on LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.[Reference: WebLink]Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Mar;36(3):327-34.Kalopanax pictus (Araliaceae) is a deciduous tree distributed in Korea, Japan, and China. The stem bark of K. pictus has been functionally used as a traditional crude drug for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases.
|
| Structure Identification | J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jun 8;59(11):6142-9.Triterpenoid glycosides from the leaves of two cultivars of Medicago polymorpha L.[Pubmed: 21526796]The saponin composition of leaves from the Medicago polymorpha cultivars 'Santiago' and 'Anglona' belonging to the botanical varieties brevispina and vulgaris, respectively, was investigated by a combination of chromatographic, spectroscopic, and spectrometric techniques.
|

Caulophyllogenin Dilution Calculator

Caulophyllogenin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0462 mL | 10.2312 mL | 20.4625 mL | 40.9249 mL | 51.1561 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4092 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 8.185 mL | 10.2312 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2046 mL | 1.0231 mL | 2.0462 mL | 4.0925 mL | 5.1156 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0409 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.8185 mL | 1.0231 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0205 mL | 0.1023 mL | 0.2046 mL | 0.4092 mL | 0.5116 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Aegeline
Catalog No.:BCN8873
CAS No.:456-12-2
- Hydroxy-alpha-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8872
CAS No.:83883-10-7
- Quercetin 3-O-sophoroside-7-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8871
CAS No.:64828-40-6
- N-(p-Coumaroyl) serotonin
Catalog No.:BCN8870
CAS No.:68573-24-0
- Emodin-1-O-beta-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCN8869
CAS No.:849789-95-3
- Cassiaside B
Catalog No.:BCN8868
CAS No.:119170-51-3
- Piperlonguminine
Catalog No.:BCN8867
CAS No.:5950-12-9
- 7-Ethoxyrosmanol
Catalog No.:BCN8866
CAS No.:111200-01-2
- 5,7,3',4',5'-Pentamethoxyflavone
Catalog No.:BCN8865
CAS No.:53350-26-8
- Isorhamnetin 7-O-glucoside
Catalog No.:BCN8864
CAS No.:6743-96-0
- 7-Methylcoumarin
Catalog No.:BCN8863
CAS No.:2445-83-2
- Isoarnebin I
Catalog No.:BCN8862
CAS No.:24502-79-2
- N-trans-Sinapoyltyramine
Catalog No.:BCN8875
CAS No.:200125-11-7
- Sanguisorbigenin
Catalog No.:BCN8876
CAS No.:6812-98-2
- Benzoylgomisin P
Catalog No.:BCN8803
CAS No.:129445-43-8
- Silyamandin
Catalog No.:BCN8804
CAS No.:1009565-36-9
- (+)-δ-Tocopherol
Catalog No.:BCN8805
CAS No.:119-13-1
- 6-Hydroxykaempferol 3-beta-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8807
CAS No.:205527-00-0
- Syringetin-3-O-rutinoside
Catalog No.:BCN8819
CAS No.:53430-50-5
- Quercetin 3-O-rutinoside-1-2-O-rhamnoside
Catalog No.:BCN8820
CAS No.:55696-57-6
- (3R)-5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methyl-3-(4'-hydroxybenzyl)chroman-4-one
Catalog No.:BCN8842
CAS No.:84638-48-2
- Loureiriol
Catalog No.:BCN8843
CAS No.:479195-44-3
- Hydroxy-γ-sanshool
Catalog No.:BCN8849
CAS No.:78886-66-5
- Astin A
Catalog No.:BCN8851
CAS No.:151201-75-1
Triterpene saponins from Silene gallica collected in North-Eastern Algeria.[Pubmed:31981958]
Phytochemistry. 2020 Apr;172:112274.
Eleven previously undescribed triterpene saponins, named silenegallisaponin A-K (1-11), were isolated from the aerial parts of Silene gallica L. Their structures were elucidated by analysis of 1D and 2D-NMR spectroscopic data and mass spectrometry (HR-ESI-MS). The saponins comprised Caulophyllogenin, echinocystic acid, or quillaic acid substituted at C-3 by a beta-d-glucuronic acid or beta-d-galactopyranosyl-(1 --> 3)-beta-d-glucuronopyranoside and at C-28 by a beta-d-fucopyranose substituted at C-2 by a beta-d-glucose and at C-3 by a beta-d-glucose or a beta-d-quinovose.
Screening of saponins and sapogenins from Medicago species as potential PPARgamma agonists and X-ray structure of the complex PPARgamma/caulophyllogenin.[Pubmed:27283034]
Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 10;6:27658.
A series of saponins and sapogenins from Medicago species were tested for their ability to bind and activate the nuclear receptor PPARgamma by SPR experiments and transactivation assay, respectively. The SPR analysis proved to be a very powerful and fast technique for screening a large number of compounds for their affinity to PPARgamma and selecting the better candidates for further studies. Based on the obtained results, the sapogenin Caulophyllogenin was proved to be a partial agonist towards PPARgamma and the X-ray structure of its complex with PPARgamma was also solved, in order to investigate the binding mode in the ligand binding domain of the nuclear receptor. This is the first known crystal structure of a sapogenin directly interacting with PPARgamma. Another compound of the series, the echinocistic acid, showed antagonist activity towards PPARgamma, a property that could be useful to inhibit the adipocyte differentiation which is a typical adverse effect of PPARgamma agonists. This study confirms the interest on saponins and sapogenins as a valuable natural resource exploitable in the medical and food industry for ameliorating the metabolic syndrome.
Triterpene glucosides from the leaves of Aralia elata and their cytotoxic activities.[Pubmed:23576356]
Chem Biodivers. 2013 Apr;10(4):703-10.
Three new triterpene glucosides, named congmuyenosides C-E (1-3, resp.), along with four known ones, were isolated from an EtOH extract of Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem. leaves. The structures of the new compounds were identified as 3-O-{beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-[beta-D-glucopyr anosyl-(1-->2)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl}Caulophyllogenin (1), 3-O-{beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-[beta-D-glucopyr anosyl-(1-->2)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl}hederagenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (2), 3-O-{beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-[beta-D-glucopyr anosyl-(1-->2)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl}echinocystic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (3) on the basis of spectral analyses, including MS, (1) H-NMR, (13) C-NMR, DEPT, HSQC, HMBC, NOESY, and HSQC-TOCSY experiments. All isolates obtained were evaluated for their cytotoxic activities against three human tumor cell lines (HepG2, SKOV3, and A549). Compound 3 showed significant cytotoxicity against A549 cell line (IC50 9.9+/-1.5 muM).
Inhibitory effects of oleanane-type triterpenes and saponins from the stem bark of Kalopanax pictus on LPS-stimulated pro-inflammatory cytokine production in bone marrow-derived dendritic cells.[Pubmed:23444041]
Arch Pharm Res. 2013 Mar;36(3):327-34.
Kalopanax pictus (Araliaceae) is a deciduous tree distributed in Korea, Japan, and China. The stem bark of K. pictus has been functionally used as a traditional crude drug for the treatment of various inflammatory diseases. In the present study, we describe the inhibitory effects of oleanane-type triterpenes and saponins isolated from the stem bark of K. pictus on production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells. Of the compounds tested, 16,23,29-trihydroxy-3-oxo-olean-12-en-28-oic acid (1), 4,23,29-trihydroxy-3,4-seco-olean-12-en-3-oate-28-oic acid (2), 3beta,6beta,23-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (3), nipponogenin E (6), 3beta,6beta,23-trihydroxyolean-12-en-28-oic acid (7), and Caulophyllogenin (19) significantly inhibited the production of IL-12 p40 and IL-6 with IC50 values ranging from 3.3 to 9.1 muM. Compounds 2, 3, 7, and 19 significantly suppressed the secretion of TNF-alpha with IC50 ranging from 8.8 to 20.0 muM. These data provide scientific support for the use of K. pictus stem bark and its triterpene and saponin components in the inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion, including IL-12 p40, IL-6, and TNF-alpha, and for prevention and treatment of inflammatory diseases.
Studies on cytotoxic triterpene saponins from the leaves of Aralia elata.[Pubmed:23265478]
Food Chem. 2013 May 1;138(1):208-13.
Aralia elata has long been used as a tonic, anticancer and antidiabetic agent in China and Japan, and is widely consumed as food. Phytochemical investigation of the leaves of A. elata has led to the isolation of four new compounds, 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1 --> 3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl] echinocystic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (congmuyenoside I, 1), 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1 --> 2)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl] hederagenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (congmuyenoside II, 2), 3-O-{[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1 --> 2)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1 --> 3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1 --> 3)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl} echinocystic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (congmuyenoside III, 3) and 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl Caulophyllogenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (congmuyenoside IV, 4), and eight known triterpene saponins (5-12). The structural determination was accomplished with spectroscopic analysis, in particularly (13)C NMR, 2D NMR and HR-ESI-MS techniques. In addition, compounds 5-10 were found for the first time in the genus Aralia. Compounds 1-12 were tested for their inhibition of the growth of HL60, A549 and DU145 cancer cells. In addition, compound 8 showed significant cytotoxic activities against HL60, A549 and DU145 cancer cells with IC(50) values of 15.62, 11.25 and 7.59 muM, respectively.
Cytotoxic triterpene saponins from the leaves of Aralia elata.[Pubmed:22465503]
Fitoterapia. 2012 Jun;83(4):806-11.
Phytochemical investigation of the leaves of Aralia elata has led to the isolation of four new compounds, 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl oleanolic acid (1), 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)]-beta-d-glucopyranosyl hederagenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (2), 3-O-{[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)]-[beta-d-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)-beta-d-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl} oleanolic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (3) and 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-beta-d-glucopyranosyl Caulophyllogenin (4) and two known compounds, 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)-alpha-l-arabinopyranosyl]-echinocystic acid (5) and 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl echinocystic acid (6). The structural determination was accomplished with spectroscopic analysis, in particular (13)C-NMR, 2D-NMR and HR-ESI-MS techniques. Compounds 1-6 were tested for their inhibition of the growth of HL60, A549 and DU145 cancer cells. Compound 1 showed significant cytotoxic activity against HL60 and A549 cancer cells with IC(50) values of 6.99muM and 7.93muM respectively. In addition, compounds 5 and 6 showed significant cytotoxic activity against HL60 cancer cells with IC(50) values of 5.75muM and 7.51muM, respectively.
Triterpenoid glycosides from the leaves of two cultivars of Medicago polymorpha L.[Pubmed:21526796]
J Agric Food Chem. 2011 Jun 8;59(11):6142-9.
The saponin composition of leaves from the Medicago polymorpha cultivars 'Santiago' and 'Anglona' belonging to the botanical varieties brevispina and vulgaris, respectively, was investigated by a combination of chromatographic, spectroscopic, and spectrometric techniques. Several compounds were detected and quantitated by HPLC analysis using the external standard method. Twelve triterpene saponins (1-12) were purified by reverse-phase chromatography and their structures elucidated by spectroscopic (1D and 2D NMR, ESI-MS/MS) and chemical methods. They were identified as glycosides of echinocystic acid, hederagenin, Caulophyllogenin, bayogenin, and soyasapogenol B. Two of them (2, 10) were previously reported in M. polymorpha; five of them (4, 6, 7, 9, 12) were already identified in other Medicago species; and three of them (1, 8, 11) were found in other plant genera. The two saponins identified as 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-28-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)beta-D-glucopyrano side] echinocystic acid (3) and 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-28-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside echinocystic acid (5) are newly identified natural compounds. The presence of echinocystic acid is reported here for the first time in the genus Medicago. Saponins from the cultivar 'Anglona' were characterized by a higher amount of echinocystic acid glycosydes, whereas saponins from the cultivar 'Santiago' were characterized by a higher amount of hederagenin glycosydes.
Leiyemudanosides A-C, three new bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponins from the roots of Caulophyllum robustum.[Pubmed:19720119]
Fitoterapia. 2010 Apr;81(3):200-4.
Three new oleanane bidesmosidic triterpenoid saponins, named leiyemudanosides A-C (1-3) were isolated from the roots of Caulophyllum robustum Maxim. Their structures were established by chemical and detailed spectroscopic analysis as 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-Caulophyllogenin-28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)- beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (1), 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-Caulophyllogenin-28-O- alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranos yl ester (2), and 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-echinocystic acid-28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-gl ucopyranosyl ester (3), respectively.
Activity-guided isolation of saponins from Kalopanax pictus with anti-inflammatory activity.[Pubmed:12130847]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 2002 Jul;50(7):900-3.
By bioassay-guided separation, a known saponin, kalopanaxsaponin A (1) and a new saponin, pictoside A (2) were isolated from the stem bark of Kalopanax pictus as anti-inflammatory components when evaluated by vascular permeability test. Another novel saponin, pictoside B (3) was also isolated but was inactive in the test system used. The structures of pictosides A and B were elucidated as Caulophyllogenin 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (2) and pictogenin (3beta,6beta,16alpha,23-tetrahydroxyolean-12-ene-28-oic acid) 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (3), respectively, by spectral analysis and by chemical degradation. Kalopanaxsaponin A and pictoside A showed significant anti-inflammatory activity at the oral doses of 50 mg/kg.
Characterization of the triterpene saponins of the roots and rhizomes of blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides).[Pubmed:11743794]
J Agric Food Chem. 2001 Dec;49(12):5969-74.
Seven triterpene saponins were isolated from n-butanol fractions of blue cohosh (Caulophyllum thalictroides) roots and rhizomes. Their structures were established by spectral ((1)H NMR, (13)C NMR, 2D-NMR, and APCI-MS) techniques and chemical reactions as hederagenin 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (1); Caulophyllogenin 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (2); hederagenin 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranoside (3); 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-hederagenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyr anoside (4); 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl- Caulophyllogenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyr anoside (5); 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl- echinocystic acid 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyr anoside (6); 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-hederagenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyr anoside (7). All seven compounds were identified in this species for the first time.
Five saponins from the root bark of Aralia elata.[Pubmed:11261582]
Phytochemistry. 2001 Mar;56(5):491-7.
Five saponins, 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-oleanolic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (aralia-saponin V), 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-echinocystic acid 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (aralia-saponin VI), 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->3)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-hederagenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (aralia-saponin VII), 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)-[beta-D-glucopyr anosyl-(1-->2)]-beta-D-glucopyranosyl]-Caulophyllogenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (aralia-saponin VIII), 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl (1-->2)-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl(1-->3)]-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl]-hederagenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl ester (aralia-saponin IX), were isolated from the root bark of Aralia elata (Miq.) Seem., together with four known compounds. Their structures were determined on the basis of chemical and spectroscopic methods.
Leonticins D-H, five triterpene saponins from Leontice kiangnanensis.[Pubmed:9014373]
Phytochemistry. 1997 Feb;44(3):497-504.
Five new triterpene saponins, leonticins D-H, were isolated from the tubers of Leontice kiangnanensis. Based on a combination of chemical degradation and spectroscopic analysis (negative ion FAB mass spectrometry and 2D NMR experiments), their structures were characterized as 3-O-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-Caulophyllogenin 28 -O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6-beta-D- glucopyranoside, 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl -(1-->3)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl- (1-->2)]-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-oleanolic acid 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl- (1-->4)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 3-O-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->3)]-[beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->2)]-alph a-L -arabinopyranosyl-hederagenin 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D- glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, 3-O-beta-D-xylopyranosyl- (1-->3)-beta-D-galactopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D- glucopyranosyl-(-->3)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl-echinocystic acid 28-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->4)-beta-D- glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside, respectively.
Two new triterpenoidal glycosides from Medicago polymorpha L.[Pubmed:8069980]
Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1994 Jun;42(6):1339-41.
Two new triterpenoid glycosides called medicago-saponins P1 (1) and P2 (2) were isolated together with five known glycosides from the aerial parts of Medicago polymorpha L. (Leguminosae). The structures of 1 and 2 were determined to be 3-O-alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(1-->2)-alpha-L-arabinopyranosyl Caulophyllogenin 28-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-(1-->6)-beta-D-glucopyranoside and the desglucoside of 1.
[Structure of chrysantellin B, a new saponin isolated from Chrysanthellum procumbens Rich (author's transl)].[Pubmed:7408850]
Eur J Biochem. 1980;108(1):271-7.
A new saponin, chrysantellin B, has been found in a tropical plant Chrysanthellum procumbens Rich as a minor companion of chrysantellin A which was previously studied. The structure of chrysantellin B was determined by mass spectrometry, proton and 13C nuclear-magnetic resonance. The aglycone part is a triterpene: 3 beta, 16 alpha, 23-trihydroxy-olean-12-en-28-oic acid or Caulophyllogenin. Carbohydrate components are D-glucose, D-oxylose and L-rhamnose in a molar ratio 1:2:2. The structure of chrysantellin B was established as 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl[L-rhamnopyranosyl-(alpha 1 leads to 3)-D-xylopyranosyl-(beta 1 leads to 4)-L-rhamnopyranosyl-(alpha 1 leads to 2)-D-xylopyranosyl-(beta 1 leads to 28)]Caulophyllogenin.


