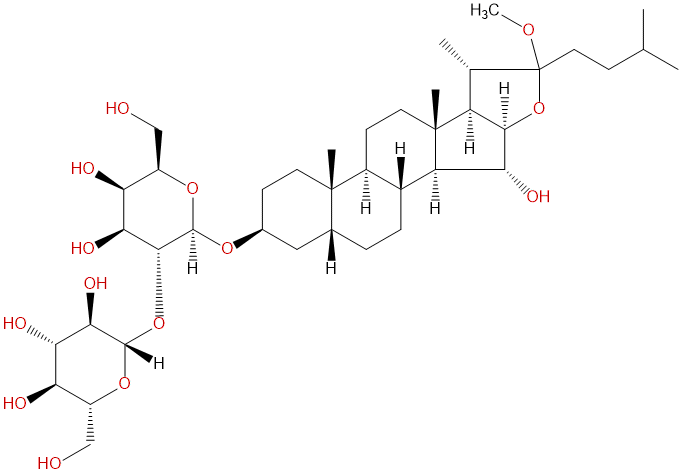
Anemarrhenasaponin IaCAS# 221317-02-8 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 221317-02-8 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C40H68O14 | M.Wt | 772.97 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Anemarrhenasaponin Ia Dilution Calculator

Anemarrhenasaponin Ia Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2937 mL | 6.4686 mL | 12.9371 mL | 25.8742 mL | 32.3428 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2587 mL | 1.2937 mL | 2.5874 mL | 5.1748 mL | 6.4686 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1294 mL | 0.6469 mL | 1.2937 mL | 2.5874 mL | 3.2343 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0259 mL | 0.1294 mL | 0.2587 mL | 0.5175 mL | 0.6469 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0129 mL | 0.0647 mL | 0.1294 mL | 0.2587 mL | 0.3234 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- N-Desmethyl Galanthamine
Catalog No.:BCX1541
CAS No.:41303-74-6
- Epigalantamine
Catalog No.:BCX1540
CAS No.:1668-85-5
- β-Chamigrenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1539
CAS No.:1174388-31-8
- 11-epi-morgroside V
Catalog No.:BCX1538
CAS No.:2146088-12-0
- Chrysophanol triglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1537
CAS No.:120181-07-9
- Chrysophanol-1-O-β-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCX1536
CAS No.:54944-38-6
- Isobutyryl alkannin
Catalog No.:BCX1535
CAS No.:87562-78-5
- Ansamitocin P3
Catalog No.:BCX1534
CAS No.:66584-72-3
- Mexoticin
Catalog No.:BCX1533
CAS No.:18196-00-4
- 31-Norlanostenol
Catalog No.:BCX1532
CAS No.:16910-39-7
- (+)-Dehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1531
CAS No.:1231-75-0
- d-Epigalbacin
Catalog No.:BCX1530
CAS No.:84709-25-1
- Momordin IIc
Catalog No.:BCX1543
CAS No.:96990-19-1
- Oleanolic acid -3-O-glucosyl(1-2)xylyl(1-3)glucosiduronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1544
CAS No.:1447508-78-2
- 7α-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCX1545
CAS No.:566-26-7
- 8-Methyl Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCX1546
CAS No.:3300-25-2
- Ursonic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1547
CAS No.:989-72-0
- Rotundifuran
Catalog No.:BCX1548
CAS No.:50656-65-0
- Lactiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX1549
CAS No.:1361049-59-3
- Dihydrolapachenole
Catalog No.:BCX1550
CAS No.:20213-26-7
- Sibiricaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCX1551
CAS No.:241125-76-8
- Ebeiedinone
Catalog No.:BCX1552
CAS No.:25650-68-4
- Yubeinine
Catalog No.:BCX1553
CAS No.:157478-01-8
- Delavinone
Catalog No.:BCX1554
CAS No.:96997-98-7
Study on the Effects of Chinese Materia Medica Processing on the Hypoglycemic Activity and Chemical Composition of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma.[Pubmed:34712345]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Oct 19;2021:6211609.
PURPOSE: To compare the hypoglycemic effects of different extracts of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma (AR) before and after being stir-baked with salt water on the diabetic mice and to detect the contents of 8 components in the corresponding active parts simultaneously using the UPLC-MS method, in order to screen the better extracts for diabetes and to clear the material basis for enhancing hypoglycemic activity of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma stir-baked with salt water (SAR). METHODS: Taking spontaneous type II diabetic db/db mice as models and fasting blood glucose (FBG), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), glycated hemoglobin or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbAlc), serum resistin (RESISTEIN), fasting insulin (FINS), superoxide dismutase (SOD), malondialdehyde (MDA), and nitric oxide (NO) as indicators, the hypoglycemic effects of different active parts of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma were evaluated. The chromatographic separation was performed on a Waters BEH C18 (2.1 mm x 50 mm, 1.7 mum) column using acetonitrile (B) and 0.1% formic acid in water (A) as mobile phases, and the flow rate was 0.3 ml/min. The column temperature was set as 28 degrees C, and the injection volume was 10 muL. A mass spectrometer was connected to the UPLC system via an electrospray ionization (ESI) interface. Full-scan data acquisition was performed in the negative ion mode. RESULT: In the study of pharmacodynamics, the hypoglycemic effect of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma stir-baked with salt water is better than that of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma and the hypoglycemic effect of ethanol extract of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma is more remarkable than that of the decoction. The measured components all have a good linear relationship within their respective linear ranges (r >/= 0.9990); the average recovery rates are 98.86%-100.69%, RSD <2.90%. Compared with the raw Anemarrhenae Rhizoma, the contents of Timosaponin AIII, Timosaponin BII, Timosaponin BIII, Anemarrhenasaponin I, Anemarrhenasaponin Ia, and Mangiferin of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma stir-baked with salt water are all higher, the changes of Timosaponin AI and Anemarrhenasaponin AII are not obvious, and all the contents of chemical composition in the ethanol extract of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma and Anemarrhenae Rhizoma stir-baked with salt water were obviously higher compared with the water decoction. CONCLUSION: The processing method, stir-baking with salt water, can increase the contents of active compositions in Anemarrhenae Rhizoma and strengthen the hypoglycemic effect. The ethanol extract of Anemarrhenae Rhizoma stir-baked with salt water is the better active site.
Steroidal saponins from Anemarrhena asphodeloides and their effects on superoxide generation.[Pubmed:10617410]
Planta Med. 1999 Oct;65(7):661-3.
A new steroidal saponin, timosaponin F, along with six known compounds was isolated from the rhizomes of Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bge. On the basis of chemical and spectroscopic evidence, the structure of timosaponin F was elucidated as (5beta, 25 S):-spirostan-3beta,15alpha,23alpha-triol-3-O-beta- glucopyranosyl-(1--->2)-beta-galactopyranoside. The six known compounds were anemarrhenasaponin I, Anemarrhenasaponin Ia, timosaponin BI, timosaponin BII, timosaponin B, timosaponin AIII; their effects on superoxide generation are also reported.
Effect of six steroidal saponins isolated from anemarrhenae rhizoma on platelet aggregation and hemolysis in human blood.[Pubmed:10556655]
Clin Chim Acta. 1999 Nov;289(1-2):79-88.
Six steroidal saponins were isolated from Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge (Liliaceae), a traditional chinese medicine, and named anemarrhenasaponin I (An-I), Anemarrhenasaponin Ia (An-Ia), timosaponin B-I (TB-I), timosaponin B-II (TB-II), timosaponin B-III (TB-III), and timosaponin A-III (TA-III). The effects of these six compounds on platelet aggregation and hemolysis in human blood were studied. All these compounds provoked remarkable inhibiting effect on platelet aggregation, and activated partial thromboplastin times (APTT) are sensitive to the presence of these six compounds. Using an in vitro system, APTT was delayed with the increment of the concentrations of these six compounds. In these six compounds, only timosaponin A-III appeared a strong effect on hemolysis, and Anemarrhenasaponin Ia had a slight effect on hemolysis, other had no effect on hemolysis. These results suggested that these steroidal saponins isolated from Anemarrhena asphodeloides Bunge (Liliaceae) might be used as a novel antithrombotic therapeutic agents in post-myocardial infarction.


