Momordin IIcCAS# 96990-19-1 |
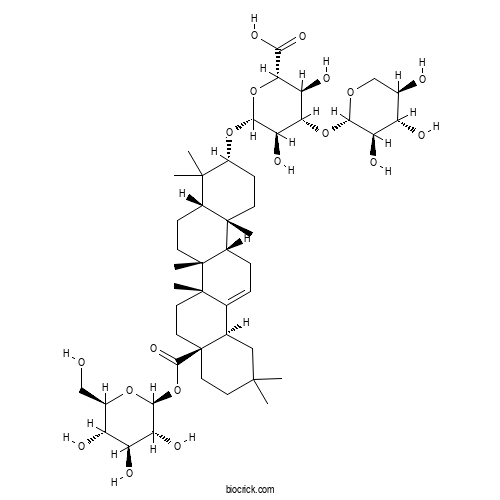
- Momordin II
Catalog No.:BCN3473
CAS No.:95851-41-5
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 96990-19-1 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 134611793.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C47H74O18 | M.Wt | 927.09 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | (2S,3S,4S,5R,6R)-6-[[(3R,4aS,6aR,6bR,8aS,12aR,14aS,14bR)-4,4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-8a-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxycarbonyl-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydropicen-3-yl]oxy]-3,5-dihydroxy-4-[(2S,3R,4S,5R)-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxan-2-yl]oxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||
| SMILES | CC1(CCC2(CCC3(C(=CCC4C3(CCC5C4(CCC(C5(C)C)OC6C(C(C(C(O6)C(=O)O)O)OC7C(C(C(CO7)O)O)O)O)C)C)C2C1)C)C(=O)OC8C(C(C(C(O8)CO)O)O)O)C | ||
| Standard InChIKey | BAJBCZHVQXVBMJ-XUPAPJJXSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C47H74O18/c1-42(2)14-16-47(41(59)65-39-32(54)30(52)29(51)24(19-48)61-39)17-15-45(6)21(22(47)18-42)8-9-26-44(5)12-11-27(43(3,4)25(44)10-13-46(26,45)7)62-40-34(56)35(33(55)36(64-40)37(57)58)63-38-31(53)28(50)23(49)20-60-38/h8,22-36,38-40,48-56H,9-20H2,1-7H3,(H,57,58)/t22-,23-,24-,25-,26+,27-,28+,29-,30+,31-,32-,33+,34-,35+,36+,38+,39+,40-,44+,45+,46-,47+/m1/s1 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Momordin IIc Dilution Calculator

Momordin IIc Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0786 mL | 5.3932 mL | 10.7864 mL | 21.5729 mL | 26.9661 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.2157 mL | 1.0786 mL | 2.1573 mL | 4.3146 mL | 5.3932 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.1079 mL | 0.5393 mL | 1.0786 mL | 2.1573 mL | 2.6966 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1079 mL | 0.2157 mL | 0.4315 mL | 0.5393 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0108 mL | 0.0539 mL | 0.1079 mL | 0.2157 mL | 0.2697 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Anemarrhenasaponin Ia
Catalog No.:BCX1542
CAS No.:221317-02-8
- N-Desmethyl Galanthamine
Catalog No.:BCX1541
CAS No.:41303-74-6
- Epigalantamine
Catalog No.:BCX1540
CAS No.:1668-85-5
- β-Chamigrenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1539
CAS No.:1174388-31-8
- 11-epi-morgroside V
Catalog No.:BCX1538
CAS No.:2146088-12-0
- Chrysophanol triglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1537
CAS No.:120181-07-9
- Chrysophanol-1-O-β-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCX1536
CAS No.:54944-38-6
- Isobutyryl alkannin
Catalog No.:BCX1535
CAS No.:87562-78-5
- Ansamitocin P3
Catalog No.:BCX1534
CAS No.:66584-72-3
- Mexoticin
Catalog No.:BCX1533
CAS No.:18196-00-4
- 31-Norlanostenol
Catalog No.:BCX1532
CAS No.:16910-39-7
- (+)-Dehydroabietic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1531
CAS No.:1231-75-0
- Oleanolic acid -3-O-glucosyl(1-2)xylyl(1-3)glucosiduronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1544
CAS No.:1447508-78-2
- 7α-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCX1545
CAS No.:566-26-7
- 8-Methyl Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCX1546
CAS No.:3300-25-2
- Ursonic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1547
CAS No.:989-72-0
- Rotundifuran
Catalog No.:BCX1548
CAS No.:50656-65-0
- Lactiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX1549
CAS No.:1361049-59-3
- Dihydrolapachenole
Catalog No.:BCX1550
CAS No.:20213-26-7
- Sibiricaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCX1551
CAS No.:241125-76-8
- Ebeiedinone
Catalog No.:BCX1552
CAS No.:25650-68-4
- Yubeinine
Catalog No.:BCX1553
CAS No.:157478-01-8
- Delavinone
Catalog No.:BCX1554
CAS No.:96997-98-7
- Docosahexaenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1555
CAS No.:6217-54-5
Reduction of fat storage in mice fed a high-fat diet long term by treatment with saponins prepared from Kochia scoparia fruit.[Pubmed:16892459]
Phytother Res. 2006 Oct;20(10):877-82.
The fresh fruit (Japanese name, Tonburi) of Kochia scoparia has been used as a food garnish in Japanese-style dishes from ancient times, and may prevent metabolic syndromes such as hyperlipidemia, hypertension, obesity and atherosclerosis. This study was performed to clarify whether an ethanol extract of K. scoparia fruit prevented obesity induced in mice by a high-fat diet for 9 weeks. The ethanol extract of K. scoparia fruit prevented the increases in body weight and parametrial adipose tissue weight induced by the high-fat diet. Furthermore, consumption of a high-fat diet containing 1% or 3% K. scoparia extract significantly increased the fecal content and the fecal triacylglycerol level at day 3 compared with those in the high-fat diet group. The ethanol extract (250 mg/kg) and total saponins (100 mg/kg) of K. scoparia inhibited the elevation of the plasma triacylglyccerol level 2 or 3 h after the oral administration of the lipid emulsion. Total saponins, momordin Ic, 2'-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl momordin Ic and 2'-O-beta-d-glucopyranosyl Momordin IIc isolated from K. scoparia fruit inhibited the pancreatic lipase activity (in vitro). These findings suggest that the anti-obesity actions of K. scoparia extract in mice fed a high-fat diet may be partly mediated through delaying the intestinal absorption of dietary fat by inhibiting pancreatic lipase activity.
Glycosides from Bougainvillea glabra.[Pubmed:16286311]
Nat Prod Res. 2006 Jan;20(1):63-7.
Three glycosides were isolated from Bougainvillea glabra and their structures were determined by extensive use of 1D and 2D NMR spectroscopy ((1)H and (13)C). First compound was identical to Momordin IIc (quinoside D) [beta-D-glucopyranosyl 3-O-[beta-D-xylopyranosyl-(1 --> 3)-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyluronic acid)] oleanolate], second compound was quercetin 3-O-alpha-L-(rhamnopyranosyl)(1 --> 6)-[alpha-L-rhamnopy-ranosyl(1 --> 2)]-beta-D-galactopyranoside and third compound was its derivative quercetin 3-O-alpha-L-(4-caffeoylrhamnopyranosyl)(1 --> 6)-[alpha-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1 --> 2)]-beta-D-galactopyranoside, a new natural product.
Effects of oleanolic acid glycosides on gastrointestinal transit and ileus in mice.[Pubmed:10428392]
Bioorg Med Chem. 1999 Jun;7(6):1201-5.
The effects of various oleanolic acid glycosides obtained from medicinal herbs on gastrointestinal transit (GIT) and ileus were investigated in fasted mice. Ileus was induced by the peritoneal-irritation or by the laparotomy with manipulation. One hour after the oral administration, three oleanolic acid 3-O-monodesmosides (oleanolic acid 3-O-glucuronide (3, 50 mg/kg), momordin Ic (4, 25 and 50 mg/kg), and momordin I (6, 25 mg/kg)) significantly accelerated GIT, but two oleanolic acid 3-O-monodesmosides (28-deglucosyl-chikusetsusaponins IV (8) and V (10)), oleanolic acid 3,28-O-bisdesmosides (Momordin IIc (5), chikusetsusaponins IV (7) and V (9)), and their common aglycon (oleanolic acid (1)) (50 mg/kg) showed no significant effect. On the other hand, oleanolic acid 28-O-monodesmoside (compound O (2, 50 mg/kg)) significantly inhibited GIT. 4 (5-25 mg/kg) and 6 (12.5 and 25 mg/kg) also significantly prevented the inhibition of GIT induced by the peritoneal injection of acetic acid. 2 and 9 (50 mg/kg) significantly potentiated the inhibition of GIT, whereas 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, and 10 (50 mg/kg) showed no significant effect. 3, 4, 6, and 10 (50 mg/kg) significantly prevented the inhibition of GIT induced by laparotomy with manipulation, while 1, 2, 5, 7, 8, and 9 (50 mg/kg) showed no significant effect. These results indicate that the 3-O-glycoside moiety seems to be essential to show the GIT accelerating activity, and the 28-O-glucoside moiety reduce the activity. The accelerations of GIT by 3, 4, and 6 were completely abolished by the pretreatment with streptozotocin (100 mg/kg, i.v.), but not by the pretreatment with capsaicin (75 mg/kg in total, s.c.). These results suggest that sympathetic nervous system, but not capsaicin-sensitive sensory nerves, be involved in the enhancements of GIT by 3, 4, and 6. It is worthy to study their therapeutical effect in the prevention of the inhibition of GIT, including ileus, in clinic.
Structure-related inhibitory activity of oleanolic acid glycosides on gastric emptying in mice.[Pubmed:10218824]
Bioorg Med Chem. 1999 Feb;7(2):323-7.
We examined the effects of various oleanolic acid oligoglycosides obtained from traditional herbs on gastric emptying in non-nutrient meal- or nutrient meal-loaded mice. Test samples were given orally to fasted mice 0.5 h before loading of test meals. Oleanolic acid 3-O-monodesmosides [oleanolic acid 3-O-glucuronide (3, 12.5-50 mg/kg), momordin Ic (4, 25 and 50 mg/kg), momordin I (6, 12.5-50 mg/kg), and 28-O-deglucosyl-chikusetsusaponins IV (8, 12.5-50 mg/kg) and V (10, 50 mg/kg)] were found to show inhibitory effects on gastric emptying in 1.5% CMC-Na test meal-loaded mice. 4, 6, and 8 also inhibited gastric emptying in mice given 40% glucose test meal, milk test meal, and 60% ethanol test meal. 3 inhibited gastric emptying in mice given milk test meal or 60% ethanol test meal, but lacked significant inhibition in 40% glucose test meal-loaded mice. 10 (50 mg/kg) also slightly inhibited gastric emptying in milk test meal-loaded mice, but lacked the significant inhibition in mice given 40% glucose or 60% ethanol test meal. Whereas oleanolic acid 3,28-0-bisdesmosides [Momordin IIc (5), chikusetsusaponins IV (7) and V (9)], oleanolic acid 28-O-monodesmoside [compound O (2)], and their common aglycon [oleanolic acid (1)] showed no such effects at dose of 50 mg/kg. 28-O-Deglucosyl-chikusetsusaponin V (10) showed a little inhibition in these experiments. These results indicate that both the 3-O-monodesmoside structure and 28-carboxyl group were confirmed to be essential for such activity, and the 28-ester glucoside moiety and 2'-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside moiety reduce the activity.
Protective effects of oleanolic acid oligoglycosides on ethanol- or indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal lesions in rats.[Pubmed:9808070]
Life Sci. 1998;63(17):PL245-50.
We examined the effects of various oleanolic acid oligoglycosides obtained from traditional herbs on ethanol- or indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal lesions in rats and on gastric secretion in pylorus-ligated rats. Test samples were given orally to fasted rats 1 h before absolute ethanol (1.5 ml/rat, p.o.) or indomethacin (30 mg/kg, s.c.) treatment, or ligation of the pylorus. Oleanolic acid 3-O-monodesmosides [oleanolic acid 3-O-glucuronide (1, 20-50 mg/kg), momordin Ic (2, 5-50 mg/kg), and 28-O-deglucosyl-chikusetsusaponins IV (5, 10-50 mg/kg) and V (7, 10-50 mg/kg)] were found to show protective effects on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesions, whereas oleanolic acid 3,28-O-bisdesmosides [Momordin IIc (3), chikusetsusaponins IV (4) and V (6)], oleanolic acid 28-O-monodesmoside [compound O (8)], and their common aglycon [oleanolic acid (9)] showed no such effects. Oleanolic acid 3-O-monodesmosides (1, 2, and 5) also showed protective effects on indomethacin-induced gastric mucosal lesions. 28-O-Deglucosyl-chikusetsusaponin V (7) did not inhibit the indomethacin-induced lesions, while chikusetsusaponins V (6, 50 mg/kg) had the gastroprotective effect. These active saponins (1, 2, 4-7, 10-50 mg/kg) did not decrease the gastric secretion by oral administration in pylorus-ligated rats.
Triterpenoid glycosides from the fruits of Kochia scoparia.[Pubmed:7480207]
Planta Med. 1995 Oct;61(5):450-2.
From the fruits of Kochia scoparia (L.) Schrad, five triterpenoid glycosides were isolated for the first time from this plant. They were elucidated as momordin Ic, the 6'-methyl ester of momordin Ic, Momordin IIc, 2'-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylmomordin Ic, and 2'-O-beta-D-glucopyranosylMomordin IIc on the basis of spectral and chemical methods. The last two saponins are new natural products.


