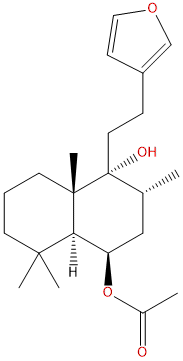
RotundifuranCAS# 50656-65-0 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 50656-65-0 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C22H34O4 | M.Wt | 362.51 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Rotundifuran Dilution Calculator

Rotundifuran Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7585 mL | 13.7927 mL | 27.5854 mL | 55.1709 mL | 68.9636 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.5517 mL | 2.7585 mL | 5.5171 mL | 11.0342 mL | 13.7927 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2759 mL | 1.3793 mL | 2.7585 mL | 5.5171 mL | 6.8964 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0552 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5517 mL | 1.1034 mL | 1.3793 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0276 mL | 0.1379 mL | 0.2759 mL | 0.5517 mL | 0.6896 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Ursonic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1547
CAS No.:989-72-0
- 8-Methyl Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCX1546
CAS No.:3300-25-2
- 7α-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCX1545
CAS No.:566-26-7
- Oleanolic acid -3-O-glucosyl(1-2)xylyl(1-3)glucosiduronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1544
CAS No.:1447508-78-2
- Momordin IIc
Catalog No.:BCX1543
CAS No.:96990-19-1
- Anemarrhenasaponin Ia
Catalog No.:BCX1542
CAS No.:221317-02-8
- N-Desmethyl Galanthamine
Catalog No.:BCX1541
CAS No.:41303-74-6
- Epigalantamine
Catalog No.:BCX1540
CAS No.:1668-85-5
- β-Chamigrenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1539
CAS No.:1174388-31-8
- 11-epi-morgroside V
Catalog No.:BCX1538
CAS No.:2146088-12-0
- Chrysophanol triglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1537
CAS No.:120181-07-9
- Chrysophanol-1-O-β-gentiobioside
Catalog No.:BCX1536
CAS No.:54944-38-6
- Lactiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX1549
CAS No.:1361049-59-3
- Dihydrolapachenole
Catalog No.:BCX1550
CAS No.:20213-26-7
- Sibiricaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCX1551
CAS No.:241125-76-8
- Ebeiedinone
Catalog No.:BCX1552
CAS No.:25650-68-4
- Yubeinine
Catalog No.:BCX1553
CAS No.:157478-01-8
- Delavinone
Catalog No.:BCX1554
CAS No.:96997-98-7
- Docosahexaenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1555
CAS No.:6217-54-5
- cis-Myrislignan
Catalog No.:BCX1556
CAS No.:52190-21-3
- Pantolactone
Catalog No.:BCX1557
CAS No.:599-04-2
- 5-Methyl-5H-furan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCX1558
CAS No.:591-11-7
- Lutein laurate-myristate
Catalog No.:BCX1559
CAS No.:117116-36-6
- Lutein monostearate
Catalog No.:BCX1560
CAS No.:115156-87-1
Rotundifuran Induces Ferroptotic Cell Death and Mitochondria Permeability Transition in Lung Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:38540189]
Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):576.
Rotundifuran (RF), a potent anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer compound, is a natural compound predominantly present in Vitex Rotundifolia. Herein, we investigated the effects of RF on the growth of lung cancer cells. Our findings suggested that RF inhibits cell growth, highlighting its potential as a therapeutic agent for cancer treatment. Interestingly, we observed that cell growth inhibition was not due to apoptosis, as caspases were not activated and DNA fragmentation did not occur. Furthermore, we found that intracellular vacuoles and autophagy were induced, but RF-induced cell death was not affected when autophagy was inhibited. This prompted us to investigate other possible mechanisms underlying cell growth inhibition. Through a cDNA chip analysis, we confirmed changes in the expression of ferroptosis-related genes and observed lipid peroxidation. We further examined the effect of ferroptosis inhibitors and found that they alleviated cell growth inhibition induced by RF. We also observed the involvement of calcium signaling, ROS accumulation, and JNK signaling in the induction of ferroptosis. Our findings suggested that RF is a potent anti-cancer drug and further studies are needed to validate its clinal use.
The Cyr61 Is a Potential Target for Rotundifuran, a Natural Labdane-Type Diterpene from Vitex trifolia L., to Trigger Apoptosis of Cervical Cancer Cells.[Pubmed:34234887]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 May 22;2021:6677687.
Cervical cancer is a common female malignant tumor that seriously threatens human health. This study explored the anticervical cancer effects and potential mechanisms of Rotundifuran (RTF), a natural product isolated from Vitex trifolia L. In this study, we found that RTF can suppress the proliferation of cervical cancer cell lines, including HeLa and SiHa cells (with the IC(50) less than 10 muM), via induction of apoptosis in vitro, and the antitumor effect of RTF is further confirmed on the HeLa cell-inoculated xenograft model. In addition, our results proved that the antitumor effects of RTF might be related with the reactive oxygen species- (ROS-) induced mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis through MAPK and PI3K/Akt signal pathways. Using proteomics analysis and the drug affinity responsive target stability- (DARTS-) combined mass spectrometry (DARTS-MS), Cyr61 was indicated as a potential target for RTF in cervical cancer cells. Our present study would be beneficial for the development of RTF as a candidate for treatment of cervical cancer in the future.
Compounds from the Fruits of the Popular European Medicinal Plant Vitex agnus-castus in Chemoprevention via NADP(H):Quinone Oxidoreductase Type 1 Induction.[Pubmed:23662135]
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:432829.
As part of our continuing efforts in the search for potential biologically active compounds from medicinal plants, we have isolated 18 compounds including two novel nitrogen containing diterpenes from extracts of the fruits of Vitex agnus-castus. These isolates, along with our previously obtained novel compound vitexlactam A (1), were evaluated for potential biological effects, including cancer chemoprevention. Chemically, the nitrogenous isolates were found to be two labdane diterpene alkaloids, each containing an alpha , beta -unsaturated gamma -lactam moiety. Structurally, they were elucidated to be 9 alpha -hydroxy-13(14)-labden-16,15-amide (2) and 6 beta -acetoxy-9 alpha -hydroxy-13(14)-labden-15,16-amide (3), which were named vitexlactams B and C, respectively. The 15 known isolates were identified as vitexilactone (4), Rotundifuran (5), 8-epi-manoyl oxide (6), vitetrifolin D (7), spathulenol (8), cis-dihydro-dehydro-diconiferylalcohol-9-O- beta -D-glucoside (9), luteolin-7-O-glucoside (10), 5-hydroxy-3,6,7,4'-tetramethoxyflavone (11), casticin (12), artemetin (13), aucubin (14), agnuside (15), beta -sitosterol (16), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (17), and p-hydroxybenzoic acid glucose ester (18). All compound structures were determined/identified on the basis of 1D and/or 2D NMR and mass spectrometry techniques. Compounds 6, 8, 9, and 18 were reported from a Vitex spieces for the first time. The cancer chemopreventive potentials of these isolates were evaluated for NADP(H):quinone oxidoreductase type 1 (QR1) induction activity. Compound 7 demonstrated promising QR1 induction effect, while the new compound vitexlactam (3) was only slightly active.
Evaluation of the estrogenic activity of the constituents in the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia L. for the potential treatment of premenstrual syndrome.[Pubmed:17883902]
J Pharm Pharmacol. 2007 Sep;59(9):1307-12.
The ethanol extract of the fruits of Vitex rotundifolia (VRE) and its four major compounds (casticin, luteolin, Rotundifuran and agnuside) were tested for their estrogen-like activity by using the modified cell proliferation assay (E-SCREEN assessment system), as well as the estrogen receptor (ER(alpha)), estrogen receptor-regulated progesterone receptor and pS2 mRNA expression in MCF-7 cells. The results showed that only agnuside and Rotundifuran could stimulate the proliferation of MCF-7 cells. These actions were dose dependent (range from 100 nM to 10 microM) and could be significantly inhibited by the specific estrogen receptor antagonist ICI 182,780. The estrogen receptor ER(alpha) and the estrogen receptor-regulated progesterone receptor and pS2 mRNA levels were increased by treatment with Rotundifuran and agnuside within 24 h, and the effects could be reversed by ICI 182,780. The standardization of the extract and constituents were carried out by means of a high-performance liquid chromatography-fingerprint. It was concluded that VRE and its compounds showed estrogen-like activity and that the estrogenic effects of Rotundifuran and agnuside were mediated by the estrogen inducible gene, which may be useful in regulating the hormone levels to treat related diseases. However, further studies are required to assess the physiological significance of VRE in animals and man.
Diterpenoids and flavonoids from the fruits of Vitex agnus-castus and antioxidant activity of the fruit extracts and their constituents.[Pubmed:17262892]
Phytother Res. 2007 Apr;21(4):391-4.
From the n-hexane fraction of the fruits of Vitex agnus-castus, two labdane-type diterpenes, vitetrifolin B and C, were isolated by means of multiple chromatographic separations, together with the previously identified Rotundifuran, vitexilactone and the sesquiterpene spathulenol. From the EtOAc fraction, eupatorin was identified for the first time, besides the known casticin, penduletin, vitexin and orientin. The n-hexane, EtOAc and MeOH-H(2)O fractions of the MeOH extract of Agni-casti fructus were subjected to in vitro antioxidant assays. The EtOAc extract displayed a significant concentration-dependent effect when tested by 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrasyl (DPPH) free radical assay (IC(50) = 68 microg/mL) and against the autooxidation of a standard rat brain homogenate (IC(50) = 14 microg/mL). The MeOH-H(2)O fraction was less active with 3643 microg/mL (DPPH test) and IC(50) = 125 microg/mL (rat brain homogenate), while the n-hexane phase proved to be inactive. The main flavonoid constituents of the EtOAc extract, casticin, vitexin and orientin were assayed for antioxidant activity and found that only casticin possesses a marked lipid peroxidation inhibitory effect (IC(50) = 0.049 mm) compared with that of the positive control ascorbic acid (IC(50) = 0.703 mm).
Labdane-type diterpenes as new cell cycle inhibitors and apoptosis inducers from Vitex trifolia L.[Pubmed:15621610]
J Asian Nat Prod Res. 2005 Apr;7(2):95-105.
Five labdane-type diterpenes, vitexilactone (1), (rel 5S,6R,8R,9R,10S)-6-acetoxy-9-hydroxy-13(14)-labden-16,15-olide (2), Rotundifuran (3), vitetrifolin D (4), and vitetrifolin E (5), have been isolated from Vitex trifolia L., a Chinese folk medicine used to treat cancers, as new cell cycle inhibitors and apoptosis inducers through a bioassay-guided separation procedure and were identified by spectroscopic methods. Compounds 1-5 dramatically induced apoptosis both on tsFT210 and K562 cells at higher concentrations while at lower concentrations they inhibited the cell cycle progression of both tsFT210 and K562 cells at the G0/G1 phase. MIC values for 1-5 for inducing apoptosis and concentration regions for 1-5 for inhibiting cell cycle both on tsFT210 and K562 cells have also been determined. Furthermore, the inhibitory effects of 1-5 on the proliferation of tsFT210 and K562 cells have been evaluated by MTT assay to obtain IC50 values to confirm that 1-5 are anticancer components of Vitex trifolia L., which exert their anti-proliferative effect on cancer cells through inducing apoptosis and inhibiting the cell cycle. The present results provide labdane-type diterpenes, 1-5, as a new class of cell cycle inhibitors and compounds 1, 2, 4, and 5 as new apoptosis inducers, which also explains, for the first time, the usage of Vitex trifolia L. by Chinese people to treat cancers.
Rotundifuran, a labdane type diterpene from Vitex rotundifolia, induces apoptosis in human myeloid leukaemia cells.[Pubmed:11536386]
Phytother Res. 2001 Sep;15(6):535-7.
The inhibitory effect of Rotundifuran, a labdane type diterpene isolated from the fruit of Vitex rotundifolia, on the proliferation of human myeloid leukaemia HL-60 cells was examined. The concentration required for 50% inhibition of the growth after 96 h was 22.5 microM. The mode of cell death induced by Rotundifuran was found to be apoptosis, which was judged by the morphological alteration of the cells and by the detection of DNA fragmentation using agarose gel electrophoresis. The degree of apoptosis was quantified by a sandwich enzyme immunoassay and flow cytometric analysis. These results suggest that Rotundifuran may be used as a potential chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent.
Diterpenoids from the fruits of Vitex trifolia.[Pubmed:11140517]
Phytochemistry. 2000 Dec;55(8):873-7.
An abietane-type diterpene, named vitetrifolin A, and two labdane-type diterpenes, named vitetrifolins B and C, were isolated from the acetone extract of the fruits of Vitex trifolia L. (Viticis Fructus; Verbenaceae) along with three known diterpenes, Rotundifuran, dihydrosolidagenone and abietatriene 3beta-ol. The structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic analysis, X-ray crystallographic analysis and chemical evidence.
Quantitative high performance liquid chromatographic analysis of diterpenoids in agni-casti fructus.[Pubmed:10865453]
Planta Med. 2000 May;66(4):352-5.
Pharmacological data have indicated that part of the dopaminergic activity of Vitex agnus-castus is attributed to the labdan diterpenoids found in the fruits. Therefore an analytical method for the standardization of Rotundifuran (1), vitexilactone (2) and 6 beta,7 beta-diacetoxy-13-hydroxy-labda-8,14-diene (3) was developed. Because of the time-consuming and expensive isolation of the diterpenoids, p-cymene was chosen as an internal standard. The concentration of Rotundifuran in different extracts and trade samples of the drug varies between 0.04 and 0.30% in the drug and between 1.04 and 2.23% in the extract. The concentration of vitexilactone was generally lower between 0.016 and 0.167% for the drug and between 0.34 and 1.01% for the extract. The determined concentration of 6 beta,7 beta-diacetoxy-13-hydroxy-labda-8,14-diene in the drug was in the range of 0.02 and 0.10% and in the extract in the range of 0.18 and 0.80%. Determination of the factors of correction of p-cymene gave 5.63 for Rotundifuran, 2.73 for vitexilactone and 3.74 for 6 beta,7 beta-diacetoxy-13-hydroxy-labda-8,14-diene.


