LactiflorinCAS# 1361049-59-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

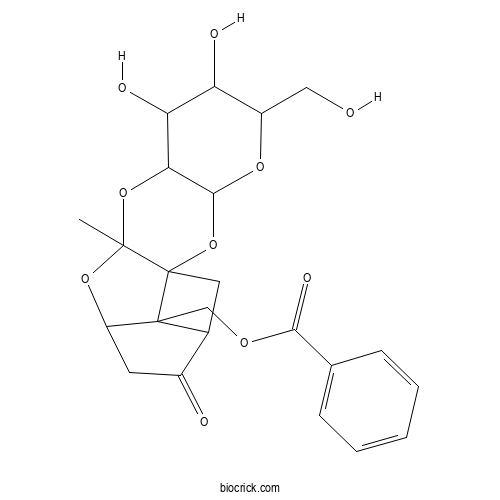
| Cas No. | 1361049-59-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 14605197.0 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C23H26O10 | M.Wt | 462.45 |
| Type of Compound | N/A | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| Chemical Name | [6,7-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)-10-methyl-14-oxo-2,4,9,11-tetraoxapentacyclo[10.4.1.01,10.03,8.015,17]heptadecan-17-yl]methyl benzoate | ||
| SMILES | CC12C3(CC4C3(C(O1)CC4=O)COC(=O)C5=CC=CC=C5)OC6C(O2)C(C(C(O6)CO)O)O | ||
| Standard InChIKey | AGRYIZUKIKYUFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C23H26O10/c1-21-23(33-20-18(32-21)17(27)16(26)14(9-24)30-20)8-12-13(25)7-15(31-21)22(12,23)10-29-19(28)11-5-3-2-4-6-11/h2-6,12,14-18,20,24,26-27H,7-10H2,1H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Lactiflorin Dilution Calculator

Lactiflorin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1624 mL | 10.812 mL | 21.624 mL | 43.2479 mL | 54.0599 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4325 mL | 2.1624 mL | 4.3248 mL | 8.6496 mL | 10.812 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2162 mL | 1.0812 mL | 2.1624 mL | 4.3248 mL | 5.406 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0432 mL | 0.2162 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.865 mL | 1.0812 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0216 mL | 0.1081 mL | 0.2162 mL | 0.4325 mL | 0.5406 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Rotundifuran
Catalog No.:BCX1548
CAS No.:50656-65-0
- Ursonic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1547
CAS No.:989-72-0
- 8-Methyl Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCX1546
CAS No.:3300-25-2
- 7α-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCX1545
CAS No.:566-26-7
- Oleanolic acid -3-O-glucosyl(1-2)xylyl(1-3)glucosiduronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1544
CAS No.:1447508-78-2
- Momordin IIc
Catalog No.:BCX1543
CAS No.:96990-19-1
- Anemarrhenasaponin Ia
Catalog No.:BCX1542
CAS No.:221317-02-8
- N-Desmethyl Galanthamine
Catalog No.:BCX1541
CAS No.:41303-74-6
- Epigalantamine
Catalog No.:BCX1540
CAS No.:1668-85-5
- β-Chamigrenic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1539
CAS No.:1174388-31-8
- 11-epi-morgroside V
Catalog No.:BCX1538
CAS No.:2146088-12-0
- Chrysophanol triglucoside
Catalog No.:BCX1537
CAS No.:120181-07-9
- Dihydrolapachenole
Catalog No.:BCX1550
CAS No.:20213-26-7
- Sibiricaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCX1551
CAS No.:241125-76-8
- Ebeiedinone
Catalog No.:BCX1552
CAS No.:25650-68-4
- Yubeinine
Catalog No.:BCX1553
CAS No.:157478-01-8
- Delavinone
Catalog No.:BCX1554
CAS No.:96997-98-7
- Docosahexaenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1555
CAS No.:6217-54-5
- cis-Myrislignan
Catalog No.:BCX1556
CAS No.:52190-21-3
- Pantolactone
Catalog No.:BCX1557
CAS No.:599-04-2
- 5-Methyl-5H-furan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCX1558
CAS No.:591-11-7
- Lutein laurate-myristate
Catalog No.:BCX1559
CAS No.:117116-36-6
- Lutein monostearate
Catalog No.:BCX1560
CAS No.:115156-87-1
- Lutein monopalmitate
Catalog No.:BCX1561
CAS No.:115182-29-1
Hydroxyethyl Cellulose-Based Hydrogels as Controlled Release Carriers for Amorphous Solid Dispersion of Bioactive Components of Radix Paeonia Alba.[Pubmed:37959739]
Molecules. 2023 Oct 28;28(21):7320.
Radix Paeoniae Alba (RPA) has been used extensively in Chinese traditional medicine to treat gastrointestinal disorders, immune-modulating diseases, cancers, and numerous other conditions. A few of its active components include paeoniflorin, albiflorin, Lactiflorin, and catechin. However, their therapeutic effectiveness is compromised by poor pharmacokinetic profiles, low oral bioavailability, short half-lives, and poor aqueous solubility. In this study, hydroxyethyl cellulose-grafted-2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid (HEC-g-AMPS) hydrogels were successfully prepared for the controlled release of Radix Paeonia Alba-solid dispersion (RPA-SD). A total of 43 compounds were identified in RPA-SD using UHPLC-Q-TOF-MS analysis. The hydrogel network formation was confirmed by FTIR, TGA, DSC, XRD, and SEM. Hydrogels' swelling and drug release were slightly higher at pH 1.2 (43.31% swelling, 81.70% drug release) than at pH 7.4 (27.73% swelling, 72.46% drug release) after 48 h. The gel fraction, drug release time and mechanical strength of the hydrogels increased with increased polymer and monomer concentration. Furthermore, the hydrogels were porous (84.15% porosity) and biodegradable (8.9% weight loss per week). Moreover, the synthesized hydrogels exhibited excellent antimicrobial and antioxidative properties.
Exploring the Mechanism of White Peony in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking.[Pubmed:37139617]
Arch Esp Urol. 2023 Mar;76(2):123-131.
INTRODUCTION: Lupus nephritis (LN) is still a great burden for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, and also one of the most severe complications of SLE. Radix Paeoniae Alba (white peony, WP) is proved with potential efficacy in treating LN. This study was to explore the effective ingredients, potential targets, and pathways of WP in treating LN based on network pharmacology and molecular docking. METHODS: The active ingredients and potential protein targets of WP were gathered on Traditional Chinese Medicine Systematic Pharmacology Database and predicted by Swiss Target Prediction. LN-related therapeutic targets were acquired from multiple databases including Genecards, DisGeNET, OMIM, Drugbank, and PharmGKB. The intersection targets of WP and LN were acquired through Veeny 2.1.0. Protein-Protein Interaction (PPI) network was established by STRING. The results were then visualized by Cytoscape version 3.7.1. to study the mechanisms of WP on LN, gene ontology and functional enrichment analysis were carried out. Finally, molecular docking presented with the binding ability of key targets and major active components. RESULTS: We acquired a total of 13 active ingredients and 260 potential targets of WP. Among them, the intersection with targets of LN were 82 proteins. These targets were regarded as potential therapeutic targets. Through PPI network, we found that the top three proteins were RAC-alpha serine/threonine protein kinase (AKT1), vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA), and transcription factor Jun (JUN), and their corresponding components were kaempferol, paeoniflorin, Lactiflorin, paeoniflorgenone, etc. The results of enrichment analysis suggested that WP treatment for LN mainly involves in signaling pathways in cancer, lipid and atherosclerosis, advanced glycation end product (AGE)-receptor of AGE (RAGE) pathways, C-type lectin receptor and nuclear factor (NF)-kappa B signaling pathways. Molecular docking predicted that the above components have excellent affinity to AKT1, VEGFA, and JUN. CONCLUSIONS: This study gave an insight into the key target proteins and potential underlying pharmacological mechanism of WP in treating LN, which provided evidence for further researches on the mechanism of WP on LN.
Bioassay-Guided Fractionation with Antimalarial and Antimicrobial Activities of Paeonia officinalis.[Pubmed:36500473]
Molecules. 2022 Dec 1;27(23):8382.
Bioassay-guided fractionation technique of roots of Paeonia officinalis led to isolation and structure elucidation of seven known compounds, including four monoterpene glycosides: Lactiflorin (1), paeoniflorin (4), galloyl paeoniflorin (5), and (Z)-(1S,5R)-beta-pinen-10-yl beta-vicianoside (7); two phenolics: benzoic acid (2) and methyl gallate (3); and one sterol glycoside: beta-sitosterol 3-O-beta-D-glucopyranoside (6). The different fractions and the isolated compounds were evaluated for their antimicrobial and antimalarial activities. Fraction II and III showed antifungal activity against Candida neoformans with IC(50) values of 28.11 and 74.37 microg/mL, respectively, compared with the standard fluconazole (IC(50) = 4.68 microg/mL), and antibacterial potential against Pseudomonas aeruginosa (IC(50) = 20.27 and 24.82 microg/mL, respectively) and Klebsiella pneumoniae (IC(50) = 43.21 and 94.4 microg/mL, respectively), compared with the standard meropenem (IC(50) = 28.67 and 43.94 microg/mL, respectively). Compounds 3 and 5 showed antimalarial activity against Plasmodium falciparum D6 with IC(50) values of 1.57 and 4.72 microg/mL and P. falciparum W2 with IC(50) values of 0.61 and 2.91 microg/mL, respectively, compared with the standard chloroquine (IC(50) = 0.026 and 0.14 microg/mL, respectively).
Metabolism of Paeoniae Radix Rubra and its 14 constituents in mice.[Pubmed:36267278]
Front Pharmacol. 2022 Oct 4;13:995641.
Objective: Paeoniae Radix Rubra (PRR) is a commonly used traditional Chinese medicine with the effects of clearing away heat, cooling the blood, and relieving blood stasis. To 1) elucidate the metabolites and metabolic pathways of PRR and its 14 main constituents in mice and 2) reveal the possible origins of the known effective forms of PRR and their isomers, the metabolism of PRR in mice was systematically studied for the first time. Methods: PRR and its 14 constituents were administered to mice by gavage once a day for seven consecutive days, respectively. All urine and feces were collected during the 7 days of dosing, and blood was collected at 1 h after the last dose. Metabolites were detected and identified using high performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector and combined with electrospray ionization ion trap time-of-flight multistage mass spectrometry (HPLC-DAD-ESI-IT-TOF-MS(n)). Results: In total, 23, 16, 24, 17, 18, 30, 27, 17, 22, 17, 33, 3, 8, 24, and 31 metabolites of paeoniflorin, albiflorin, oxypaeoniflorin, benzoylpaeoniflorin, hydroxybenzoylpaeoniflorin, benzoyloxypaeoniflorin, galloylpaeoniflorin, Lactiflorin, epicatechin gallate, catechin gallate, catechin, ellagic acid, 3,3'-di-O-methylellagic acid, methylgallate, and PRR were respectively identified in mice; after eliminating identical metabolites, a total of 195 metabolites remained, including 8, 11, 25, 17, 18, 30, 27, 17, 21, 17, 1, 2, 8, 20, and 20 newly identified metabolites, respectively. The metabolic reactions of PRR and its 14 main constituents in mice were primarily methylation, hydrogenation, hydrolysis, hydroxylation, glucuronidation, and sulfation. Conclusion: We elucidated the metabolites and metabolic pathways of PRR and its 14 constituents (e.g., paeoniflorin, catechin, ellagic acid, and gallic acid) in mice and revealed the possible origins of the 10 known effective forms of PRR and their isomers. The findings are of great significance to studying the mechanism of action and quality control of PRR.
Network pharmacology-based prediction of inhibiting leukocyte recruitment and angiogenesis of total glucosides of peony against rheumatoid arthritis.[Pubmed:36226643]
Ann Palliat Med. 2022 Oct;11(10):3085-3101.
BACKGROUND: Total glucosides of peony (TGP) is extracted from Paeonia lactiflora Pallas, which has been approved for rheumatoid arthritis (RA) treatment. There were approximately 15 monoterpene glycosides identified in TGP. Pervious researches focused on the effects of TGP and the major ingredient paeoniflorin (PF), but the functions of other monoterpene glycosides and their interactions were not clear. Network pharmacology has been one of the new strategies for multi-target drug discovery. In this study, we investigate the functions of all components of TGP and their interactions in RA treatment based on network pharmacology methods. METHODS: The components of TGP were searched out the Web of Science, PubMed, China National Knowledge Infrastructure databases; then we identified the potential targets based of chemical similarity in the Similarity Ensemble Approach. The molecular related with RA were obtained from DrugBank, GeneCards, DisGeNET and Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) databases. The components-targets-disease network was constructed and analyzed with Cytoscape software; Gene Ontology (GO) and the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) enrichment analyses were conducted with R for function analysis. The hub components-targets interactions were validated with Autodock Vina. RESULTS: Twenty potential targets of TGP were predicted for RA treatment. The major components of TGP, PF and albiflorin (AF) had more predicted targets. Hub targets of TGP were LGALS3/9, VEGFA, FGF1, FGF2, IL-6, IL-2, SELP, PRKCA and ERAP1. These targets ameliorated RA mainly through inhibiting leukocyte recruitment and angiogenesis. Enriched pathways including VEGFR pathway, signaling by interleukins, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, platelet activation, extracellular matrix organization, and so on. The combination of PF, AF and Lactiflorin (LF) with the hub targets was further validated using docking program. CONCLUSIONS: We investigated the comprehensive mechanism of TGP for RA treatment. We analyzed the different targets of the components in TGP and predicted the new effects of TGP on inhibiting leukocyte recruitment and angiogenesis. This study provides a better understanding of TGP on the RA treatment.
Network Pharmacology, Molecular Docking, and Experimental Validation to Unveil the Molecular Targets and Mechanisms of Compound Fuling Granule to Treat Ovarian Cancer.[Pubmed:36062197]
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022 Aug 23;2022:2896049.
BACKGROUND: Compound fuling granule (CFG) is a traditional Chinese medicine formula that is used for more than twenty years to treat ovarian cancer (OC) in China. However, the underlying processes have yet to be completely understood. This research is aimed at uncovering its molecular mechanism and identifying possible therapeutic targets. METHODS: Significant genes were collected from Therapeutic Target Database and Database of Gene-Disease Associations. The components of CFG were analyzed by LC-MS/MS, and the active components of CFG were screened according to their oral bioavailability and drug-likeness index. The validated targets were extracted from PharmMapper and PubChem databases. Venn diagram and STRING website diagrams were used to identify intersection targets, and a protein-protein interaction network was prepared using STRING. The ingredient-target network was established using Cytoscape. Molecular docking was performed to visualize the molecule-protein interactions using PyMOL 2.3. Enrichment and pathway analyses were performed using FunRich software and Reactome pathway, respectively. Experimental validations, including CCK-8 assay, wound-scratch assay, flow cytometry, western blot assay, histopathological examination, and immunohistochemistry, were conducted to verify the effects of CFG on OC cells. RESULTS: A total of 56 bioactive ingredients of CFG and 185 CFG-OC-related targets were screened by network pharmacology analysis. The potential therapeutic targets included moesin, glutathione S-transferase kappa 1, ribonuclease III (DICER1), mucin1 (MUC1), cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (CDK2), E1A binding protein p300, and transcription activator BRG1. Reactome analysis showed 51 signaling pathways (P < 0.05), and FunRich revealed 44 signaling pathways that might play an important role in CFG against OC. Molecular docking of CDK2 and five active compounds (baicalin, ignavine, Lactiflorin, neokadsuranic acid B, and deoxyaconitine) showed that baicalin had the highest affinity to CDK2. Experimental approaches confirmed that CFG could apparently inhibit OC cell proliferation and migration in vitro; increase apoptosis; decrease the protein expression of MUC1, DICER1, and CDK2; and suppress the progression and distant metastasis of OC in vivo. DICER1, a tumor suppressor, is essential for microRNA synthesis. Our findings suggest that CFG may impair the production of miRNAs in OC cells. CONCLUSION: Based on network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experimental validation, the potential mechanism underlying the function of CFG in OC was explored, which supplies the theoretical groundwork for additional pharmacological investigation.
Zhen-Wu decoction and lactiflorin, an ingredient predicted by in silico modelling, alleviate uremia induced cardiac endothelial injury via Nrf2 activation.[Pubmed:35963415]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Nov 15;298:115579.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Cardiorenal syndrome type 4 (CRS type 4), with high rates of morbidity and mortality, has become a social and economic problem worldwide over the last few decades. Zhen-Wu decoction, a traditional medicine used in East Asia, has been widely used in the treatment of cardiovascular disease and kidney disease, and has shown potential therapeutic effects for the clinical treatment of CRS type 4. However, the underlying mechanism has not been extensively explored. AIM OF THE STUDY: The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect and underlying mechanism of Zhen-Wu decoction on uremic cardiomyopathy, offering a potential target for clinical treatment of CRS type 4. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Five/six nephrectomized mice were utilized for experiments in vivo. The cardioprotective effects of Zhen-Wu decoction were evaluated by echocardiography and tissue staining. RNA-Seq data were used to investigate the potential pharmacological mechanism. The prediction of targets and active components was based on our previous strategy. Subsequently, the protective effect of the selected compound was verified in experiments in vitro. RESULTS: Zhen-Wu decoction alleviated cardiac dysfunction and endothelial injury in 5/6 nephrectomized mice, and the mechanism may involve the inflammatory process and oxidative stress. The activation of the Nrf2 signaling pathway was predicted to be a potential target of Zhen-Wu decoction in protecting endothelial cells. Through our machine learning strategy, we found that Lactiflorin as an ingredient in Zhen-Wu decoction, alleviates IS-induced endothelial cell injury by blocking Keap1 and activating Nrf2. CONCLUSIONS: The present study demonstrated that Zhen-Wu decoction and Lactiflorin could protect endothelial cells against oxidative stress in mice after nephrectomy by activating the Nrf2 signaling pathway.
Phytochemical identification of Xiaoer Huanglong Granule and pharmacokinetic study in the rat using its seven major bioactive components.[Pubmed:35662416]
J Sep Sci. 2022 Aug;45(15):2804-2818.
Xiaoer Huanglong Granule is the only Chinese Patent Medicine widely used for treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. However, not much is known about the bioactive components and pharmacokinetics of Xiaoer Huanglong Granule even after it was successfully introduced into clinical use. This study analyzed the components in the medication and rat plasma after oral administration with the help of the UNIFI platform and Masslynx. A total of 119 and 37 components were detected in the medication and plasma, respectively, using an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometer. We established a rapid and sensitive simultaneous determination of one triterpene saponin, three monoterpene glycosides, and three lignans in rat plasma by solid-phase extraction. The determination was accomplished within 7.50 min via gradient elution. The values of the lower limit of quantitation were validated at 0.08 ng/ml for tenuifolin, 0.8 ng/ml for Lactiflorin, 1.828 ng/ml for albiflorin, 2 ng/ml for paeoniflorin, gomisin B, and gomisin D, 10 ng/ml for schisandrin. The results from validations of other methods were all acceptable (relative standard deviation Lactiflorin was studied for the first time.
Comparative Elucidation of Age, Diameter, and "Pockmarks" in Roots of Paeonia lactiflora Pall. (Shaoyao) by Qualitative and Quantitative Methods.[Pubmed:35154191]
Front Plant Sci. 2022 Jan 26;12:802196.
Paeonia lactiflora Pall. is a world-famous ornamental plant, whose roots have been used as an important traditional Chinese medicine, Shaoyao, to treat diseases for more than 1,000 years. Because of the excellent curative effect of Shaoyao, its quality has attracted wide attention, however, there is a lack of comprehensive research on the different influencing factors of quality of Shaoyao. In this study, ultra-performance liquid chromatography-quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UPLC-Q/TOF-MS) and high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detection (HPLC-DAD) were utilized to systematically analyze the Shaoyao of different ages, diameters and roots with "pockmarks." 60 metabolites were detected and identified from Shaoyao using the UPLC-Q/TOF-MS, of which 20 potential quality markers of dissected roots with and without "pockmarks" were selected for the first time using the orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) and the variable importance for projection (VIP) plot. Then, a selective and accurate HPLC-DAD quantitative assay has been developed for the simultaneous determination of 11 bioactive components in Shaoyao. The results showed that the total content of five monoterpene glycosides including oxypaeoniflorin, albiflorin, paeoniflorin, Lactiflorin, and benzoylpaeoniflorin and six phenols including gallic acid, catechin, methyl gallate, ethyl gallate, apiopaeonoside and benzoic acid in the 3-year-old Shaoyao was higher than that of 4-year-old and 5-year-old Shaoyao. In Shaoyao of the same age, the total content of five monoterpene glycosides and six phenols decreased with an increase in diameter. In addition, regardless of whether it is a whole or a divided root, the contents of five monoterpene glycosides and six phenols in Shaoyao with "pockmarks" were higher than those of Shaoyao without "pockmarks." In summary, this work has explored several factors that might affect the quality of Shaoyao, and provide a guide for more comprehensive quality evaluation in its further production, processing, and rational utilization.
Exploration of chemical composition and absorption characteristics of Chaigui granules based on UHPLC-Q-orbitrap-MS/MS.[Pubmed:32446142]
J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2020 Aug 5;187:113293.
Established qualitative analysis method for Chaigui granules based on UHPLC-Q-orbitrap-MS/MS and applied to its absorption properties studies. The LC-MS method was established to identify the structures of the components and metabolites. And then biosamples of rats after administration, e.g. intestinal solution, serum and brain microdialysate, were detected in rats with same method. Xcalibur 3.2 software was used for mass spectrum analysis and identification. Compound discover 3.0 was used for metabolite analysis. 95 chemical constituents were identified from Chaigui granules, including sesquiterpenes, flavonoids, lactones, tannins, organic acids, saponins and so on. 82 components and 11 metabolites were found in intestinal solution. 28 chemical constituents and 32 metabolites were found in serum. 15 chemical constituents were found in brain microdialysate. Vanillic acid, abiflorin, paeoniflorin, 4-hydroxybenzoic acid, Lactiflorin, Z-butylidenephthalide, saikosaponin c, saikosaponin a, atractylenolide III, saikosaponin g, saikosaponin b1, sesquiterpenes, butylphthalide, saikosaponin d and glycyrrhetinic acid directly passed through the blood-brain barrier, which might be speculated that Chaigui granule plays an antidepressant role mainly through regulating brain central mechanism and endocrine mechanism, and so on. It is a systematically applicable approach for rapid identification and relative quantitation of Chaigui granules in vivo by UHPLC-Q-orbitrap-MS/MS, provides an important basis for the safety evaluation and rational clinical application of Chaigui granules.
Characterization of phytochemicals in the roots of wild herbaceous peonies from China and screening for medicinal resources.[Pubmed:32146385]
Phytochemistry. 2020 Jun;174:112331.
Paeonia Radix Rubra (PRR) is a very common traditional Chinese medicine (TCM). The roots of Paeonia lactiflora and Paeonia anomala subsp. veitchii are used for the production of PRR. However, other species of section Paeonia in China are also used to produce PRR. The roots of section Paeonia from 20 populations of seven species and two subspecies in China were analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (HPLC-Q-TOF- MS). A total of 21 metabolites were identified, including nine monoterpene glycosides, seven tannins, three phenols, one paeonol and one flavonoid. There were significant differences in the composition and content of metabolites among different populations. The relative contents of monoterpene glycosides and tannins were generally higher in most samples. Cluster analysis showed that 20 populations could be divided into four groups. Among them, the populations of P. lactiflora and Paeonia mairei were clustered together in one group. The content of paeoniflorin in P. lactiflora was high (>22.20 mg g(-1), dry weight, the same below), and the content of Lactiflorin in P. mairei (>17.50 mg g(-1)) was significantly higher than in other species (<2.30 mg g(-1)). The monoterpene glycoside content in P. mairei (>51.60 mg g(-1)) was significantly higher than in other species (<43.40 mg g(-1)), suggesting that it could be useful medicinal germplasm for the development of monoterpene glycosides. In addition, some populations of Paeonia emodi, Paeonia sterniana and P. mairei may also be used as potential germplasm resources for use in PRR. Genetic and environmental factors resulted in differences in the composition and content of metabolites in different populations of the same species. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully consider the origin of Paeonia germplasm when selecting medicinal materials to be used as resources for the production of PRR.
Intramolecular [2+2] photocycloaddition reactions as an entry to the 2-oxatricyclo[4.2.1.0(4,9)]nonan-3-one skeleton of lactiflorin.[Pubmed:22653868]
Chem Asian J. 2012 Aug;7(8):1947-58.
Two [2+2] photocycloaddition routes were evaluated as possible ways to access the tricyclic core structure found in the terpene monoglycoside Lactiflorin. While the first route via gamma-substituted cyclopentenones was quickly discarded, the reactions of racemic (5R*)-3-benzyloxy-5-but-3'-enyl-4-methoxycarbonylfuran-2(5H)-ones proceeded in high yields and with perfect diastereoselectivity. However, it turned out that the regioselectivity was strongly dependent on the substitution pattern within the but-3'-enyl chain, which connects the terminal olefinic double bond to the photoexcited butenolide chromophor. If the chain was unsubstituted or if a tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy group was placed at the 2' position in a syn-relationship to the existing stereogenic center (5R*,2'S*), the crossed product prevailed with regioselectivities of 89:11 to 69:31. If the tert-butyldimethylsilyloxy group was positioned at 2' in an anti-relationship to the existing stereogenic center (5R*,2'R*), the desired straight products were obtained in regioselectivities of 74:24 to 55:45 (61-83% yield). Following this route, the aglycon part of Lactiflorin was obtained by an intramolecular [2+2] photocycloaddition and a subsequent hydrogenolysis in 53% yield. Its further conversion into the natural product after glycosylation included a methyl addition to the lactone carbonyl group, which was optimized to give the desired key intermediate in a yield of 70%. The further conversion to Lactiflorin was achieved in four steps and with an overall yield of 49%.
Monoterpene glycosides from Paeonia hybrida.[Pubmed:18400238]
Phytochemistry. 2008 May;69(8):1767-72.
Monoterpene glycosides (1-5, and 7), together with 14 known compounds, were isolated from the methanol extract of the roots of Paeonia hybrida. These compounds included a paeoniflorin-related glycoside with a hybrid structure of paeoniflorin and paeonovicinoside (1), a monoterpene glucoside biogenetically related to Lactiflorin (2), a paeoniflorin-related monoterpene (3), arbiflorin-related monoterpenes (4 and 5), and a tymol-related monoterpene glycoside (7). Their structures were elucidated by extensive spectroscopic examinations.
[Studies on chemical constituents in root of Paeonia sinjiangensis].[Pubmed:15506284]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2004 Aug;29(8):748-51.
OBJECTIVE: To study the chemical constituents of the root of Paeonia sinjiangensis. METHOD: The constituents were isolated by silica column chromatography, and their structures were identified on the basis of spectral analysis and their physical-chemical constants. RESULT: Five compounds, paeoniflorin( I ), albiflorin (II), Lactiflorin(III), daucosterol(IV), sucrose (V), were obtained. CONCLUSION: All of the compounds were obtained from this plant for the first time.


