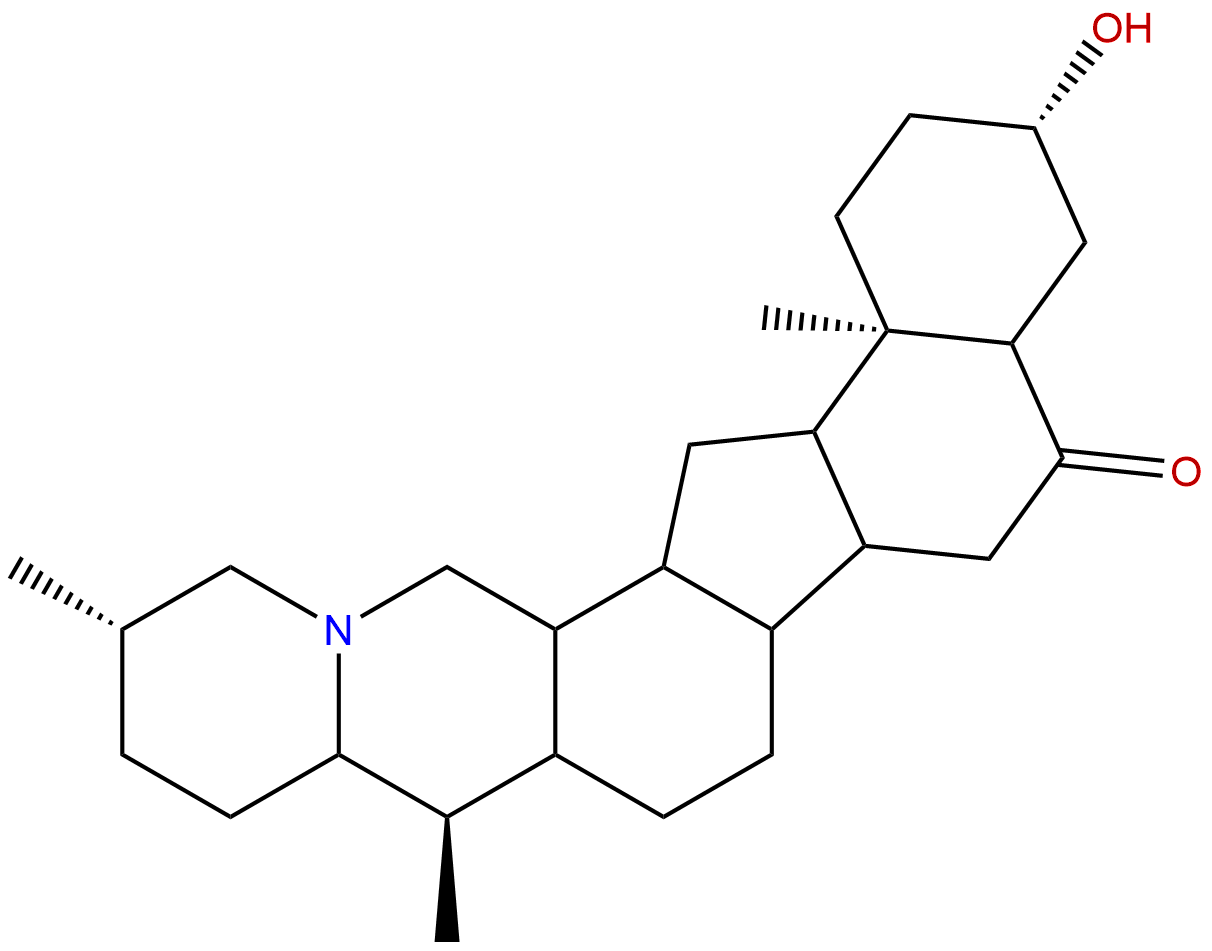
EbeiedinoneCAS# 25650-68-4 |
Quality Control & MSDS
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 25650-68-4 | SDF | File under preparation. |
| PubChem ID | N/A | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C27H43NO2 | M.Wt | 413.65 |
| Type of Compound | Alkaloids | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||

Ebeiedinone Dilution Calculator

Ebeiedinone Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.4175 mL | 12.0875 mL | 24.175 mL | 48.3501 mL | 60.4376 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.4835 mL | 2.4175 mL | 4.835 mL | 9.67 mL | 12.0875 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.2418 mL | 1.2088 mL | 2.4175 mL | 4.835 mL | 6.0438 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0484 mL | 0.2418 mL | 0.4835 mL | 0.967 mL | 1.2088 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0242 mL | 0.1209 mL | 0.2418 mL | 0.4835 mL | 0.6044 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Sibiricaxanthone A
Catalog No.:BCX1551
CAS No.:241125-76-8
- Dihydrolapachenole
Catalog No.:BCX1550
CAS No.:20213-26-7
- Lactiflorin
Catalog No.:BCX1549
CAS No.:1361049-59-3
- Rotundifuran
Catalog No.:BCX1548
CAS No.:50656-65-0
- Ursonic acid methyl ester
Catalog No.:BCX1547
CAS No.:989-72-0
- 8-Methyl Chrysophanol
Catalog No.:BCX1546
CAS No.:3300-25-2
- 7α-Hydroxycholesterol
Catalog No.:BCX1545
CAS No.:566-26-7
- Oleanolic acid -3-O-glucosyl(1-2)xylyl(1-3)glucosiduronic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1544
CAS No.:1447508-78-2
- Momordin IIc
Catalog No.:BCX1543
CAS No.:96990-19-1
- Anemarrhenasaponin Ia
Catalog No.:BCX1542
CAS No.:221317-02-8
- N-Desmethyl Galanthamine
Catalog No.:BCX1541
CAS No.:41303-74-6
- Epigalantamine
Catalog No.:BCX1540
CAS No.:1668-85-5
- Yubeinine
Catalog No.:BCX1553
CAS No.:157478-01-8
- Delavinone
Catalog No.:BCX1554
CAS No.:96997-98-7
- Docosahexaenoic acid
Catalog No.:BCX1555
CAS No.:6217-54-5
- cis-Myrislignan
Catalog No.:BCX1556
CAS No.:52190-21-3
- Pantolactone
Catalog No.:BCX1557
CAS No.:599-04-2
- 5-Methyl-5H-furan-2-one
Catalog No.:BCX1558
CAS No.:591-11-7
- Lutein laurate-myristate
Catalog No.:BCX1559
CAS No.:117116-36-6
- Lutein monostearate
Catalog No.:BCX1560
CAS No.:115156-87-1
- Lutein monopalmitate
Catalog No.:BCX1561
CAS No.:115182-29-1
- Lutein palmitate stearate
Catalog No.:BCX1562
CAS No.:79313-82-9
- Lutein monomyristate
Catalog No.:BCX1563
CAS No.:56842-49-0
- Lutein dimyristate
Catalog No.:BCX1564
CAS No.:86853-02-3
Total alkaloids of bulbus of Fritillaria cirrhosa alleviate bleomycin-induced inflammation and pulmonary fibrosis in rats by inhibiting TGF-beta and NF-kappaB signaling pathway.[Pubmed:38187805]
Food Nutr Res. 2023 Dec 29;67.
BACKGROUND: Bulbus of Fritillaria cirrhosa is a medicinal and edible plant that has the functions of clearing away heat and moisturizing the lungs, resolving phlegm, and relieving coughs. Its ethanol extract has been proven to have a therapeutic effect on lung diseases. Pulmonary fibrosis is a respiratory disease that forms scars in lung tissue, leading to severe respiratory problems. However, the therapeutic effect of total alkaloids of bulbus of Fritillaria cirrhosa (BFC-TA) on pulmonary fibrosis has not been confirmed. OBJECTIVE: This study aimed to investigate the therapeutic effect of total alkaloids of Fritillaria cirrhosa on pulmonary fibrosis rat model and explore its potential mechanism. DESIGN: The total alkaloids in the bulbus of Fritillaria cirrhosa were purified using cation exchange resin. The alkaloids contained in the BFC-TA were identified, and the concentration of alkaloids was determined by High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Diode Array Detector-Evaporative Light Scattering Detector (HPLC-DAD-ELSD). Bleomycin (BLM) (5.0 mg/kg) was instilled into the trachea of 60 rats to establish a pulmonary fibrosis model. After 7 days, BFC-TA (34.2, 68.4, and 136.8 mg/kg) was administered continuously for 21 days. During this period, the body weight changes of the rats were measured, the levels of hydroxyproline (HYP) and inflammatory factors were measured in the collected serum, and the histological analysis of the lung tissue was performed by staining technology. Western blotting and quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) were used to assess the protein and gene composition of inflammation and transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling pathways. RESULTS: Nine main components (Peimisine, Imperialine-3-beta-D-glucoside, Yibeinoside A, Imperialine, Peiminine, Isopeimine, Hupehenine, Delavinone, Ebeiedinone) were determined by HPLC-DAD-ELSD, and the contents of Peimisine, Imperialine-3-beta-D-glucoside and Imperialine were determined. BFC-TA (34.2, 68.4, and 136.8 mg/kg) reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory factors, increased the levels of anti-inflammatory factors, dose-dependently improved the morphology of lung tissue. And during epithelial-mesenchymal transition process, BFC-TA dose-dependently reduced the expression of E-cadherin, dose-dependently increased the expression of Fibronectin. In addition, Western blot analysis and qPCR results showed that inhibiting NF-kappaB and TGF-beta-related signaling pathways effectively slowed down the occurrence of BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis in rats. And the therapeutic effect of BFC-TA (136.8 mg/kg) is better than that of pirfenidon (PFD) (150 mg/kg). CONCLUSION: BFC-TA effectively alleviates the progression of the BLM-induced pulmonary fibrosis rat model by regulating the inflammatory response in the lungs and the expression of the TGF-beta signaling pathway.
Discovery of potential quality markers of Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus in pneumonia by combining UPLC-QTOF-MS, network pharmacology, and molecular docking.[Pubmed:36843054]
Mol Divers. 2023 Feb 26:1-18.
Fritillariae thunbergii bulbus (FTB) is a popular Chinese herbal medicine with various applications in respiratory diseases. The quality evaluation of FTB has been insufficient to date, as the active ingredients and mechanisms of action of FTB remain unclear. This study proposes a novel strategy for exploring the quality markers (Q-markers) of FTB based on UPLC-QTOF-MS analysis, network pharmacology, molecular docking, and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation. A total of 26 compounds in FTB were identified by UPLC-QTOF-MS. Ten of these compounds were screened as Q-markers based on network pharmacology for their anti-pneumonia effects, including imperialine, peimisine, peiminine, Ebeiedinone, zhebeirine, puqiedine, 9-hydroxy-10,12-octadecadienoic acid, (9Z,12Z,15Z)-13-hydroxy-9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid, 9,12,15-octadecatrienoic acid, and (2E,4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)-2,4,7,10,13,16,19-docosaheptaenoic acid methyl ester (DAME). These Q-markers were predicted to act on multiple targets and pathways associated with pneumonia. Molecular docking results revealed that most of the Q-markers showed high affinity with at least one of the main targets of pneumonia, and the top ten complexes were confirmed with MD simulation. Network pharmacology indicated that FTB may act on the TNF signaling pathway, HIF-1 signaling pathway, JAK-STAT signaling pathway, etc. The results demonstrated that imperialine (P8), peimisine (P9), peiminine (P11), ebeiedine (P15), zhebeirine (P16), and puqiedine (P18) may be potential Q-markers of FTB, and AKT1, IL-6, VEGFA, TP53, EGFR, STAT3, PPARG, MMP9, and CASP3 may be promising therapeutic targets for pneumonia treatment that are worthy of further research.
Revealing active components and action mechanism of Fritillariae Bulbus against non-small cell lung cancer through spectrum-effect relationship and proteomics.[Pubmed:36587416]
Phytomedicine. 2023 Feb;110:154635.
BACKGROUND: Fritillariae Bulbus (FB) is widely used as a traditional medicine for the treatment of lung meridian diseases. It has been proved that FB has good anti-non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) activity. However, the active components and potential mechanism are still not clear. PURPOSE: To reveal the bioactive components of FB against NSCLC and potential mechanism through spectrum-effect relationship and proteomics. METHOD: First, the FB extract was chemically profiled by UHPLC-QTOF-MS and the inhibitory effect of FB extract on A549 cell viability was evaluated by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. Second, orthogonal-partial least squares-regression analysis was applied to screen potential active compounds through correlating the chemical profile with corresponding inhibitory effect. Third, the anti-NSCLC activities of potential active components were further investigated in terms of cell proliferation, cell cycle and cell apoptosis in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. Finally, proteomics was utilized to reveal the underlying anti-NSCLC mechanism. RESULTS: Six potential active components including verticine, verticinone, zhebeirine, Ebeiedinone, yibeissine and peimisine were screened out by spectrum-effect relationship. Among them, zhebeirine showed higher inhibitory effect on A549 cell viability with IC(50) value of 36.93 muM and dosage-dependent inhibition of A549 xenograft tumor growth in nude mice. Proteomics and western blotting assays indicated that zhebeirine could arrest cell cycle by down-regulating the expressions of CDK1, CDK2, Cyclin A2, Cyclin B2 and inhibiting the phosphorylation of p53. Moreover, the proteins participating in p53 signaling pathway including PCNA, 14-3-3sigma, CHEK1 were significantly decreased, which suggested that zhebeirine affected cell cycle progression through p53 signaling pathway. CONCLUSION: This study not only provides scientific evidence to support the clinical application of FB against NSCLC, but also demonstrates that zhebeirine is a promising anti-NSCLC lead compound deserving further studies.
In silico Exploration of Bioactive Phytochemicals Against Neurodegenerative Diseases Via Inhibition of Cholinesterases.[Pubmed:32178608]
Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(33):4151-4162.
Neurodegenerative disorders are estimated to become the second leading cause of death worldwide by 2040. Despite the widespread use of diverse allopathic drugs, these brain-associated disorders can only be partially addressed and long term treatment is often linked with dependency and other unwanted side effects. Nature, believed to be an arsenal of remedies for any illness, presents an interesting avenue for the development of novel neuroprotective agents. Interestingly, inhibition of cholinesterases, involved in the breakdown of acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft, has been proposed to be neuroprotective. This review therefore aims to provide additional insight via docking studies of previously studied compounds that have shown potent activity against acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) in vitro. Indeed, the determination of potent plant-based ligands for this purpose through in silico methods enables the elimination of lengthy and costly traditional methods of drug discovery. Herein, a literature search was conducted to identify active phytochemicals which are cholinesterase inhibitors. Following which in silico docking methods were applied to obtain docking scores. Compound structures were extracted from online ZINC database and optimized using AM1 implemented in gaussian09 software. Noteworthy ligands against AChE highlighted in this study include: 19,20-dihydroervahanine A and 19, 20-dihydrotabernamine. Regarding BChE inhibition, the best ligands were found to be 8-Clavandurylkaempferol, Na-methylepipachysamine D; Ebeiedinone; and dictyophlebine. Thus, ligand optimization between such phytochemicals and cholinesterases coupled with in vitro, in vivo studies and randomized clinical trials can lead to the development of novel drugs against neurodegenerative disorders.
Investigation of association of chemical profiles with the tracheobronchial relaxant activity of Chinese medicinal herb Beimu derived from various Fritillaria species.[Pubmed:28842340]
J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:39-46.
ETHNOPHARMACOLOGICAL RELEVANCE: Fritillariae Bulbus (Beimu in Chinese) is derived from the bulbus of many Fritillaria species (family Liliaceae), which has been used as an antitussive herb in traditional Chinese medicine for more than 2000 years. Due to the complexity of plant origins and significant variations in chemical profiles, the characterization of the profile of the major bioactive constituents and its association with pharmacological activity are important for the quality control of Beimu herbs from different origins. AIM OF THE STUDY: This study aims to investigate the distribution of major bioactive isosteroidal alkaloids in Beimu herbs of different origins and its correlation with the tracheobronchial relaxant activity. METHODS: Quantification of 7 main bioactive 5alpha-cevanine isosteroidal alkaloids, including ebeiedine, Ebeiedinone, hupehenine, isoverticine, verticine, verticinone and imperialine, in 23 Fritillaria species was performed using gas chromatography. The relaxant effect of different extracts of 4 commonly used Beimu herbs, namely Zhe-Beimu (F. thunbergii Miq.), Chuan-Beimu (F. cirrhosa D. Don), Hubei-Beimu (F. hupehensis Hsiao et K. C. Hsia) and Yi-Beimu (F. pallidiflora Schrenk), was evaluated using rat isolated tracheal and bronchial preparations pre-contracted with carbachol, the well established in vitro antitussive model. RESULTS: Amongst 23 Fritillaria species detected, significant variations of the types and quantities of 7 major isosteroidal alkaloids were determined, which served as an important indicator for the classification of different Beimu herbs with distinct geographic distributions. Based on the type and quantity of these alkaloids, different origins of Beimu could be clearly clustered into several subgroups by principal component analysis. Furthermore, both crude alkaloid and water extracts of all 4 Beimu herbs showed a dose-dependent tracheobronchial relaxation with different potencies. The total content of alkaloids (weight adjusted based on the activity of individual alkaloids) in Beimu extracts significantly correlated with their tracheobronchial relaxation effects (r(2) > 0.9, p < 0.001). CONCLUSIONS: The results demonstrated that the differences in chemical profile of major bioactive isosteroidal alkaloids and pharmacological activity of Beimu could be incorporated into a simple and unified method for quality control and potential prediction of activity of Beimu herbs from different origins.
[Identification of alkaloids and flavonoids in all parts of Fritillaria thunbergii using LC-LTQ-Orbitrap MSn].[Pubmed:28901111]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2016 Jun;41(11):2124-2130.
Alkaloids and flavonoids in flowers, flower buds, stems, leaves, and bulbs of Fritillaria thunbergii were identified by LC-LTQ-Orbitrap MSn.Alkaloids were identified by ACQUITY UPLC BEH C(1)(8)(2.1 mmx50 mm, 1.7 mum ) chromatographic column with a mobile phase of 10 mmol*L(-)(1) ammonium formate-acetonitrile and gradient elution in positive MS scan mode.Meanwhile, flavonoids were analyzed by Agilent-Zorbax SB C(1)(8) (4.6 mmx250 mm, 5 mum) chromatographic column with a mobile phase of 0.2% acetic acid-acetonitrile and gradient elution in negative MS scan mode.Combined with literature reports, chemical constituents were identified and determined by accurate molecular weights and fragment ion peaks in the ESI-MS/MS spectra based on high resolution mass spectrometer.In all parts of F.thunbergii, 37 alkaloids including 7 alkaloids (zhebeininoside, peimisine, peimine, peiminine, Ebeiedinone/puqiedinone, ebeiedine/ puqiedine, peimisine-N-oxide) were simultaneously analyzed.Moreover, 16 flavonoids including quercetin, kaempferol and their glycosides were identified.The results indicated that the aerial parts had the similar alkaloids as the bulbs on the whole.Meanwhile, it had a series of flavonoids undetected in the bulbs.Our results provided the scientific basis for the development and utilization of aerial parts of F.thunbergii.
A new alkaloid from Fritillaria ussuriensis Maxim.[Pubmed:22037568]
Fitoterapia. 2012 Jan;83(1):137-41.
Pingbeimunone A (1), a new compound, together with the known ussuriedine (2), benzo[7,8]fluoreno[2,1-b]quinolizine cevane-3,6,16,20-tetrol (3), Ebeiedinone (4), pingbeimine C (5) and verticine (6) were isolated from Fritillaria ussuriensis. The structure was elucidated on the basis of spectral analysis (IR, NMR and MS spectroscopy). In addition, their AChE inhibitory activities were also tested.
Inhibitors of acetylcholine esterase in vitro--screening of steroidal alkaloids from Fritillaria species.[Pubmed:16881015]
Planta Med. 2006 Jul;72(9):814-8.
18 alkaloids were successfully isolated from five Fritillaria species and 5 derivatives were synthesized. Their effects on the bioactivity of human whole blood cholinesterase (ChE) were assessed. The results showed that N-demethylpuqietinone, hupeheninoside, Ebeiedinone, yibeinoside A and chuanbeinone inhibited the bioactivity of human whole blood ChE at the concentration of 1.0 x 10 ( - 4) M, with the inhibitory effects of 55.5 +/- 2.7 %, 66.8 +/- 2.0 %, 69.0 +/- 1.7 %, 71.2 +/- 1.8 % and 70.7 +/- 3.3 %, respectively. The effects of the five alkaloids on human red blood cell (RBC) acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and human plasma butyrylcholinesterase (BChE) were further studied, and their IC (50) values for human RBC AChE were 6.4 +/- 0.003 microM, 16.9 +/- 0.018 microM, 5.7 +/- 0.004 microM, 6.5 +/- 0.013 microM and 7.7 +/- 0.001 microM, respectively, and the IC50 values for human plasma BChE were 12.5 +/- 0.026 microM, 2.1 +/- 0.005 microM, 5.2 +/- 0.002 microM, 7.3 +/- 0.005 microM and 0.7 +/- 0.001 microM, respectively. These data suggest, therefore, that N-demethylpuqietinone, hupeheninoside, Ebeiedinone, yibeinoside A and chuanbeinone have both anti-RBC AChE and anti-plasma BChE activities, N-demethylpuqietinone is a selective inhibitor of AChE, whereas hupeheninoside and chuanbeinone are the selective inhibitors of BChE.
Simultaneous determination of seven major isosteroidal alkaloids in bulbs of Fritillaria by gas chromatography.[Pubmed:10757299]
J Chromatogr A. 2000 Mar 24;873(2):221-8.
The present paper describes the development of a most simple, sensitive, and specific gas chromatographic method to date, for the direct determination of seven major bioactive isosteroidal alkaloids, namely ebeiedine, Ebeiedinone, ebeienine, hupehenine, isoverticine, verticine, verticinone and imperialine, in Fritillaria species, a commonly used antitussive traditional Chinese medicinal (TCM) herb. In the present study, a commercially available Supelco SAC-5 capillary column (30 m x 0.25 mm, 0.25 microm) specifically designed for the analysis of steroids was utilized for the direct determination of Fritillaria alkaloids. Calibration curves were obtained by spiking authentic compounds and the internal standard (solanidine) into herbal samples prior to extraction. Extraction was conducted simply by shaking the pre-alkalized diethyl ether solution (5.0 ml) containing dried herb (0.1 g) for 2 h. All calibration curves showed good linear regressions (r2>0.995) within test ranges. The assay was reproducible and accurate with the overall intra- and inter-day variation and accuracy of less than 10% and more than 90%, respectively. The developed GC method was successfully utilized to analyze seven major bioactive alkaloids in seven Fritillaria species, and the results demonstrate that this direct GC analytical method is suitable for the quality control of this commonly used antitussive TCM herb.
Pre-column derivatization and gas chromatographic determination of alkaloids in bulbs of Fritillaria.[Pubmed:10574211]
J Chromatogr A. 1999 Oct 29;859(2):183-92.
A method of precolumn derivatization GC with FID detection was developed for a simultaneous analysis of five major steroidal alkaloids of Fritillaria species, namely ebeiedine, Ebeiedinone, verticine, verticinone and imperialine. Derivatization was carried out by trimethylsilylation of the hydroxyl-containing Fritillaria alkaloids to the corresponding trimethylsilylates with trimethylsilylimidazole. Reaction conditions were optimised and the alkaloids derivatives were characterised by on-line GC-MS. The validated GC method demonstrated a good linearity at the sampling ranges used. This analytical method is simple, convenient and reproducible. The developed assay was successfully applied to the determination of the major pharmacologically active alkaloids in three commonly used antitussive Fritillaria species: F. cirrhosa, F. thunbergii and F. pallidiflora.
Prederivatization and high-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of alkaloids of bulbs of Fritillaria.[Pubmed:8923321]
J Pharm Sci. 1996 Nov;85(11):1174-9.
A method of prederivatization and HPLC with UV detection was developed for the simultaneous analysis of five major steroidal alkaloids of the Fritillaria species: verticine, verticinone, isoverticine, ebeiedine, and Ebeiedinone. Derivatization was carried out by esterification of the hydroxyl-containing Fritillaria alkaloids to the corresponding naphthoates with 1-naphthoyl chloride. Reaction conditions were optimized and the yields of the derivatization were between 94 and 100% for all test alkaloids. Derivatized alkaloids were characterized by mass spectrometry and HPLC-MS. The validated HPLC-UV method demonstrated linear UV response at the sampling ranges used, and a test limit of 1 microgram/mL was determined for all analytes. This analytical method is simple, convenient, and readily reproducible. The developed method was applied to the analysis of the major pharmacologically active alkaloids in three medicinally used Fritillaria species: F. cirrhosa, F. thunbergii, and F. hupehensis. Five major Fritillaria alkaloids were simultaneously analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively from crude extracts of each of these herbs.


