AucuparinCAS# 3687-28-3 |
Quality Control & MSDS
3D structure
Package In Stock
Number of papers citing our products

| Cas No. | 3687-28-3 | SDF | Download SDF |
| PubChem ID | 442508 | Appearance | Powder |
| Formula | C14H14O3 | M.Wt | 230.26 |
| Type of Compound | Phenols | Storage | Desiccate at -20°C |
| Solubility | Soluble in Chloroform,Dichloromethane,Ethyl Acetate,DMSO,Acetone,etc. | ||
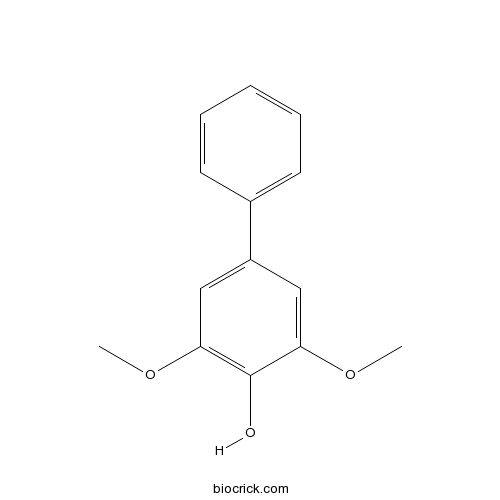
| Chemical Name | 2,6-dimethoxy-4-phenylphenol | ||
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1O)OC)C2=CC=CC=C2 | ||
| Standard InChIKey | KCKBEANTNJGRCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | ||
| Standard InChI | InChI=1S/C14H14O3/c1-16-12-8-11(9-13(17-2)14(12)15)10-6-4-3-5-7-10/h3-9,15H,1-2H3 | ||
| General tips | For obtaining a higher solubility , please warm the tube at 37 ℃ and shake it in the ultrasonic bath for a while.Stock solution can be stored below -20℃ for several months. We recommend that you prepare and use the solution on the same day. However, if the test schedule requires, the stock solutions can be prepared in advance, and the stock solution must be sealed and stored below -20℃. In general, the stock solution can be kept for several months. Before use, we recommend that you leave the vial at room temperature for at least an hour before opening it. |
||
| About Packaging | 1. The packaging of the product may be reversed during transportation, cause the high purity compounds to adhere to the neck or cap of the vial.Take the vail out of its packaging and shake gently until the compounds fall to the bottom of the vial. 2. For liquid products, please centrifuge at 500xg to gather the liquid to the bottom of the vial. 3. Try to avoid loss or contamination during the experiment. |
||
| Shipping Condition | Packaging according to customer requirements(5mg, 10mg, 20mg and more). Ship via FedEx, DHL, UPS, EMS or other couriers with RT, or blue ice upon request. | ||
| Description | 1. Aucuparin is a phytoalexin. 2. Aucuparin exhibits potent inhibitory activity against fMLP-induced superoxide (O(*-)(2)) production by human neutrophils with the IC(50) value of 17.0+/-6.8 microM. 3. Aucuparin shows significant scavenging activity by the ABTS and FRAP assays. |
| Targets | NADPH-oxidase |

Aucuparin Dilution Calculator

Aucuparin Molarity Calculator
| 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | 20 mg | 25 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3429 mL | 21.7146 mL | 43.4292 mL | 86.8583 mL | 108.5729 mL |
| 5 mM | 0.8686 mL | 4.3429 mL | 8.6858 mL | 17.3717 mL | 21.7146 mL |
| 10 mM | 0.4343 mL | 2.1715 mL | 4.3429 mL | 8.6858 mL | 10.8573 mL |
| 50 mM | 0.0869 mL | 0.4343 mL | 0.8686 mL | 1.7372 mL | 2.1715 mL |
| 100 mM | 0.0434 mL | 0.2171 mL | 0.4343 mL | 0.8686 mL | 1.0857 mL |
| * Note: If you are in the process of experiment, it's necessary to make the dilution ratios of the samples. The dilution data above is only for reference. Normally, it's can get a better solubility within lower of Concentrations. | |||||

Calcutta University

University of Minnesota

University of Maryland School of Medicine

University of Illinois at Chicago

The Ohio State University

University of Zurich

Harvard University

Colorado State University

Auburn University

Yale University

Worcester Polytechnic Institute

Washington State University

Stanford University

University of Leipzig

Universidade da Beira Interior

The Institute of Cancer Research

Heidelberg University

University of Amsterdam

University of Auckland

TsingHua University

The University of Michigan

Miami University

DRURY University

Jilin University

Fudan University

Wuhan University

Sun Yat-sen University

Universite de Paris

Deemed University

Auckland University

The University of Tokyo

Korea University
- Tramiprosate
Catalog No.:BCC7727
CAS No.:3687-18-1
- Meclofenoxate hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC4170
CAS No.:3685-84-5
- 1,5-Pentanediol diacrylate
Catalog No.:BCC8426
CAS No.:36840-85-4
- Naringenin triacetate
Catalog No.:BCN5425
CAS No.:3682-04-0
- Isohemiphloin
Catalog No.:BCN5424
CAS No.:3682-02-8
- Puerarin
Catalog No.:BCN5958
CAS No.:3681-99-0
- Vitexin
Catalog No.:BCN5423
CAS No.:3681-93-4
- Ribavirin
Catalog No.:BCC4935
CAS No.:36791-04-5
- MRS 2279
Catalog No.:BCC5880
CAS No.:367909-40-8
- 4-Aminophthalimide
Catalog No.:BCC8689
CAS No.:3676-85-5
- 10-Shogaol
Catalog No.:BCN3267
CAS No.:36752-54-2
- AR-M 1896
Catalog No.:BCC5931
CAS No.:367518-31-8
- TC 14012
Catalog No.:BCC7910
CAS No.:368874-34-4
- p-Coumaryl alcohol
Catalog No.:BCN3922
CAS No.:3690-05-9
- Zebularine
Catalog No.:BCC1136
CAS No.:3690-10-6
- 6-epi-Augustifolin
Catalog No.:BCN3233
CAS No.:369390-94-3
- Hydramicromelin B
Catalog No.:BCN7560
CAS No.:369391-55-9
- Icilin
Catalog No.:BCC4074
CAS No.:36945-98-9
- Oroxylin A 7-O-beta-D-glucuronide
Catalog No.:BCN2337
CAS No.:36948-76-2
- TMPyP4 tosylate
Catalog No.:BCC7899
CAS No.:36951-72-1
- FCCP
Catalog No.:BCC5659
CAS No.:370-86-5
- Zinterol hydrochloride
Catalog No.:BCC6911
CAS No.:37000-20-7
- (-)-Variabilin
Catalog No.:BCN4815
CAS No.:370102-93-5
- Carbetocin
Catalog No.:BCC6304
CAS No.:37025-55-1
[Antioxidant xanthones from Securidaca inappendiculata].[Pubmed:19086633]
Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2008 Aug;33(16):1982-5.
OBJECTIVE: To study the antioxidant constituents from the roots of Securidaca inappendiculata. METHOD: The bioassay-guided isolation of antioxidant constituents was carried out by the column chromatographic techniques. The combination of IR, MS, NMR and 2D-NMR spectroscopics methods was used to identify their structures. RESULT: Two new xanthones, 1, 2, 5-trihydroxy-6, 8-dimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(1), 1, 5-dihydroxy-2, 6, 8-trimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one (2), along with seven known ones, 3, 8-dihydroxy-1, 4-dimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(3), 4, 6-dihydroxy-1, 5, 7-trimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(4), 7-hydroxy-1, 2, 3, 8-tetramethoxy-9H-xanthen- 9-one(5), 1, 7-dihydroxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(6), 4-hydroxy-3, 7-dimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(7), 1,7-dimethoxy-9H-xanthen-9-one(8) and Aucuparin(9), were isolated from the roots of S. inappendiculata. CONCLUSION: Compounds 1 and 2 were new xanthones, and compound 3 was isolated as a natural product for the first time, and compounds 4 and 6 were isolated for the first time from this genus. The antioxidant activities of all compounds were evaluated by ABTS, FRAP and DPPH assays respectively. Compound 9 showed significant activity by the ABTS and FRAP assays. Compound 1 showed significant activity with IC50 value of 0.31 mg x L(-1) in DPPH assay. Scavenging capacity of all compounds determined by all assays were well correlated between ABTS and FRAP assay (r = 0.9555).
Endogenous hydrogen peroxide is a key factor in the yeast extract-induced activation of biphenyl biosynthesis in cell cultures of Sorbus aucuparia.[Pubmed:22086110]
Planta. 2012 Jan;235(1):217-23.
Biphenyls are unique phytoalexins produced by plants belonging to Pyrinae, a subtribe of the economically important Rosaceae family. The formation of Aucuparin, a well-known biphenyl, is induced by yeast extract (YE) in cell cultures of Sorbus aucuparia. However, the molecular mechanism underlying YE-induced activation of biphenyl biosynthesis remains unknown. Here we demonstrate that the addition of YE to the cell cultures results in a burst of reactive oxygen species (ROS; H(2)O(2) and O(2) (-)), followed by transcriptional activation of the biphenyl synthase 1 gene (BIS1) encoding the key enzyme of the biphenyl biosynthetic pathway and Aucuparin accumulation. Pretreatment of the cell cultures with ROS scavenger dihydrolipoic acid and NADPH oxidase-specific inhibitor diphenylene iodonium abolished all of the above YE-induced biological events. However, when the cell cultures was pretreated with superoxide dismutase specific inhibitor N,N-diethyldithiocarbamic acid, although O(2) (-) continued to be generated, the H(2)O(2) accumulation, BIS1 expression and Aucuparin production were blocked. Interestingly, exogenous supply of H(2)O(2) in the range of 0.05-10 mM failed to induce Aucuparin accumulation. These results indicate that endogenous generation of H(2)O(2) rather than that of O(2) (-) is a key factor in YE-induced accumulation of biphenyl phytoalexins in cell cultures of S. aucuparia.
A new dibenzofuran and further constituents from the stems of Pourthiaea lucida with inhibitory activity on superoxide generation by neutrophils.[Pubmed:19479843]
Chem Biodivers. 2009 May;6(5):774-8.
A new dibenzofuran, lucidafuran (1), was isolated from the stems of Pourthiaea lucida, together with eight known compounds. The structure of this new compound was determined through NMR and mass-spectrometric analyses. Among the isolated compounds, lucidafuran (1) and Aucuparin (3) exhibited potent inhibitory activity against fMLP-induced superoxide (O(*-)(2)) production by human neutrophils with IC(50) values of 18.7+/-4.4 and 17.0+/-6.8 microM, resp.


